一. NLTK的几个常用函数
1. Concordance
实例如下:
>>> text1.concordance("monstrous") Displaying 11 of 11 matches: ong the former , one was of a most monstrous size . ... This came towards us , ON OF THE PSALMS . " Touching that monstrous bulk of the whale or ork we have r ll over with a heathenish array of monstrous clubs and spears . Some were thick d as you gazed , and wondered what monstrous cannibal and savage could ever hav that has survived the flood ; most monstrous and most mountainous ! That Himmal they might scout at Moby Dick as a monstrous fable , or still worse and more de th of Radney .'" CHAPTER 55 Of the Monstrous Pictures of Whales . I shall ere l ing Scenes . In connexion with the monstrous pictures of whales , I am strongly ere to enter upon those still more monstrous stories of them which are to be fo ght have been rummaged out of this monstrous cabinet there is no telling . But of Whale - Bones ; for Whales of a monstrous size are oftentimes cast up dead u >>>
这个函数就是用来搜索单词word在text 中出现多的情况,包括出现的那一行,重点强调上下文。从输出来看 concordance 将要查询的单词,基本显示在一列,这样容易观察其上下文.
2. Similar
实例:
>>> text1.similar("monstrous") modifies horrible singular mouldy contemptible determined tyrannical candid wise lamentable pitiable fearless loving maddens domineering careful true mystifying part passing >>>
这个函数的作用则是根据word 的上下文的单词的情况,来查找具有相似的上下文的单词. 比如monstrous 在上面可以看到,有这样的用法:
most monstrous size
the monstrous pictures
this monstrous cabinet
等等, similar() 函数会在文本中 搜索具有类似结构的其他单词, 不过貌似这个函数只会考虑一些简单的指标,来作为相似度,比如上下文的词性,更多的完整匹配, 不会涉及到语义.
3. Common_contexts
实例:
>>> text1.common_contexts(["monstrous", "very"]) No common contexts were found >>> text2.common_contexts(["monstrous", "very"]) a_pretty a_lucky am_glad be_glad is_pretty >>>
这个函数跟simailar() 有点类似,也是在根据上下文搜索的.
不同的是,这个函数是用来搜索 共用 参数中的列表中的所有单词,的上下文.即: word1,word2 相同的上下文.
4. Dispersion_plot
实例:
>>> text4.dispersion_plot(["citizens", "democracy", "freedom", "duties", "Americ a"])
这个函数是用离散图 表示 语料中word 出现的位置序列表示. 效果如下:
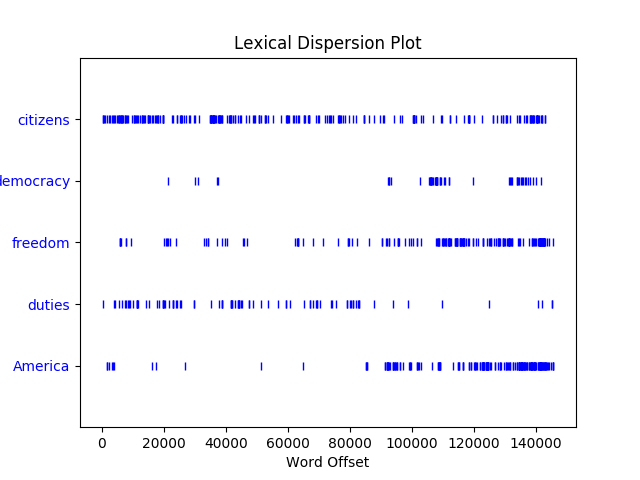
其中横坐标表示文本的单词位置.纵坐标表示查询的单词, 坐标里面的就是,单词出现的位置.就是 单词的分布情况。
5. generate
实例:
>>> text3.generate() Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: generate() missing 1 required positional argument: 'words' >>>
产生一些与text3风格类似的随机文本。但在本机上却出错,原因是我使用的是nltk3.2.4和Python3.4.4,该版本下generate函数被注释了,所以无法使用。而《python自然语言处理时》书中用的是NLTK2.0版本。
6. _future_模块
_future_模块使得在Python2.x的版本下能够兼容更多的Python3.x的特性。把下一个新版本的特性导入到当前版本,于是我们就可以在当前版本中测试一些新版本的特性。所以Python3.x以后的版本中都不含有该模块。