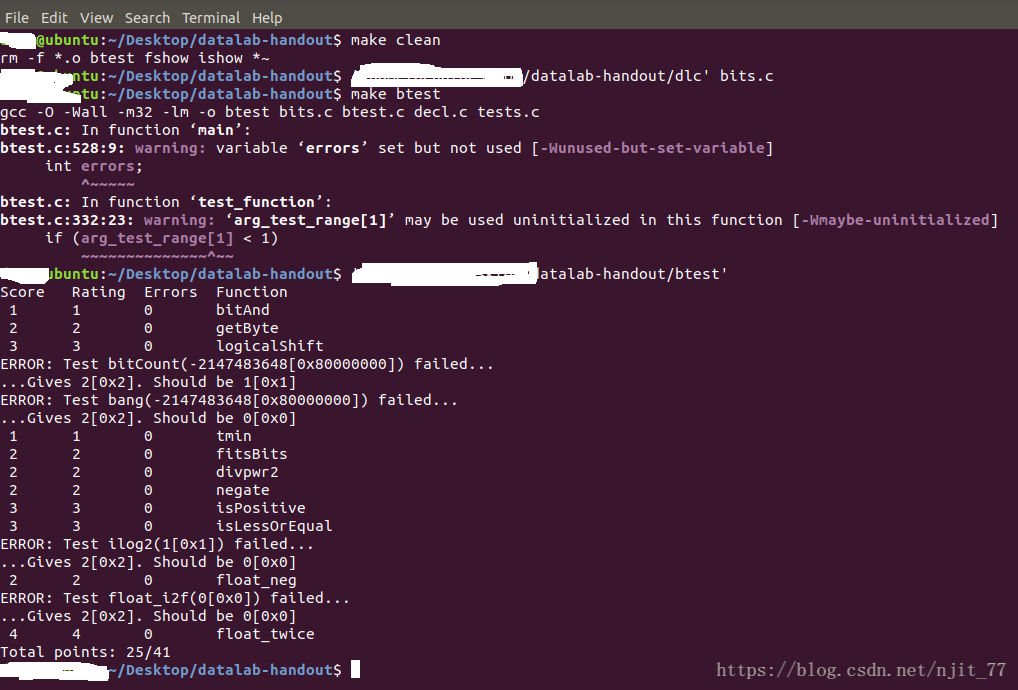
首先声明datalab本人未完成,有4道题目没有做出来。本文博客记录下自己的解析,以便以后回忆。如果能帮助到你就更好了,如果觉得本文没啥技术含量,也望多多包涵。
/*
* bitAnd - x&y using only ~ and |
* Example: bitAnd(6, 5) = 4
* Legal ops: ~ |
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 1
*/
int bitAnd(int x, int y) {
return ~(~x | ~y);
}
/*
* getByte - Extract byte n from word x
* Bytes numbered from 0 (LSB) to 3 (MSB)
* Examples: getByte(0x12345678,1) = 0x56
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 2
*/
int getByte(int x, int n) {
int offsetValue = 0xff;
int offsetIndex = n << 3;
int value = (x & (offsetValue << offsetIndex)) >> offsetIndex;
return value & offsetValue;
}
/*
* logicalShift - shift x to the right by n, using a logical shift
* Can assume that 0 <= n <= 31
* Examples: logicalShift(0x87654321,4) = 0x08765432
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 20
* Rating: 3
*/
int logicalShift(int x, int n) {
int offset = 0x1 << 31;
int offsetValue = ~(offset >> n << 1);
return (x >> n) & offsetValue;
}
/*
* bitCount - returns count of number of 1's in word
* Examples: bitCount(5) = 2, bitCount(7) = 3
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 40
* Rating: 4
*/
int bitCount(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* bang - Compute !x without using !
* Examples: bang(3) = 0, bang(0) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
int bang(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* tmin - return minimum two's complement integer
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 4
* Rating: 1
*/
int tmin(void) {
return (0x1 << 31);
}
/*
* fitsBits - return 1 if x can be represented as an
* n-bit, two's complement integer.
* 1 <= n <= 32
* Examples: fitsBits(5,3) = 0, fitsBits(-4,3) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
int fitsBits(int x, int n) {
int offsetValue = 0x1 << n;
int addValue = (offsetValue >> 1) & (~offsetValue);//2^(n-1)
int value1 = x + addValue;//x - {-[2^(n-1)]}
int value2 = addValue + (~x);//[2^(n-1)-1] - x
int maxValue = 0x1 << 31;
return (n >> 5) | ((!(value1 & maxValue)) & (!(value2 & maxValue)));
}
/*
* divpwr2 - Compute x/(2^n), for 0 <= n <= 30
* Round toward zero
* Examples: divpwr2(15,1) = 7, divpwr2(-33,4) = -2
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
int divpwr2(int x, int n) {
int maxValue = 0x1 << 31;
int offsetValue = ~(0x1 << 31 >> (32 + ~n));
int andValue = offsetValue & x;
return (x >> n) + ((!!(x & maxValue)) & (!!(andValue)));
}
/*
* negate - return -x
* Example: negate(1) = -1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 5
* Rating: 2
*/
int negate(int x) {
return ~x + 1;
}
/*
* isPositive - return 1 if x > 0, return 0 otherwise
* Example: isPositive(-1) = 0.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 3
*/
int isPositive(int x) {
return (!(x >> 31)) ^ (!x);
}
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
int offsetValue = 0x1;
int offsetIndex = 31;
int offsetSign = offsetValue << offsetIndex;
int signX = !(x & offsetSign);
int signY = !(y & offsetSign);
int value1 = ((!signX) & signY )^ 0x0;
int value2 = (signX & (!signY)) ^ 0x1;
int value3 = (!((y + ~x + 1) & offsetSign)) ^ 0x0;
return value1 | (value2 & value3);
}
/*
* ilog2 - return floor(log base 2 of x), where x > 0
* Example: ilog2(16) = 4
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 90
* Rating: 4
*/
int ilog2(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* float_neg - Return bit-level equivalent of expression -f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representations of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 10
* Rating: 2
*/
unsigned float_neg(unsigned uf) {
int offsetValue = 0x1;
int offsetIndex = 0;
int andValue = 0;
int signValue;
while (offsetIndex < 31)
{
signValue = (uf & offsetValue) >> offsetIndex;
if (offsetIndex < 23)
{
andValue = andValue | signValue;
}
else
{
andValue = andValue & signValue;
}
offsetIndex += 1;
offsetValue <<= 1;
}
if (andValue)
{
return uf;//NaN
}
return uf ^ offsetValue;
}
/*
* float_i2f - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (float) x
* Result is returned as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point values.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned float_i2f(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* float_twice - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned float_twice(unsigned uf) {
int signIndex = 31;
int expIndex = 23;
int offsetValue = 0x1;
int offsetSign = offsetValue << signIndex;
int andValue = 1;
int orValue = 0;
int signValue;
int offsetIndex = expIndex;
while (offsetIndex < signIndex)
{
signValue = (uf & (offsetValue << offsetIndex)) >> offsetIndex;
andValue = andValue & signValue;
orValue = orValue | signValue;
offsetIndex += 1;
}
if (andValue == 1)//exp==255
{
return uf;
}
else if (orValue == 0)//非规格化
{
signValue = !!(uf & offsetSign);
uf <<= 1;
if (signValue == 0)
{
return uf & (~offsetSign);
}
return uf | offsetSign;
}
else
{
signValue = ((uf >> expIndex) + 1) << expIndex;
offsetIndex = expIndex;
while (offsetIndex < signIndex)
{
uf &= ~(offsetValue << offsetIndex);
offsetIndex += 1;
}
return uf | signValue;
}
}