注解
@Conditional({condition}):按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器注册 bean
一、给容器中注册组件
创建一个配置类,并在容器中创建两个Bean 组件:
@Configuration
public class MainConfig3 {
@Bean(value = "bill")
public Person person01() {
return new Person("Bill Gates", 62);
}
@Bean(value = "linus")
public Person person02() {
return new Person("Linus", 48);
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void test03() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class);
Environment env = ioc.getEnvironment();
System.out.println(env.getProperty("os.name"));
System.out.println("IOC容器创建完成");
String[] names = ioc.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
Map<String, Person> persons = ioc.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println("persons = " + persons);
}
运行结果:

此时可以看到在容器中的两个组件。
二、@Condition 按条件注册 bean
现在有这样一种情况:
如果系统是windows,给容器中注册 ("bill")
如果系统是Linux,给容器中注册 ("linus")
@Conditional({condition}):按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器注册 bean
@Condition 是一个接口,里面有一个 matches() 方法,根据方法的返回值来注册bean,返回 true,注册bean,返回 false,不会注册bean。
@Conditional注解:
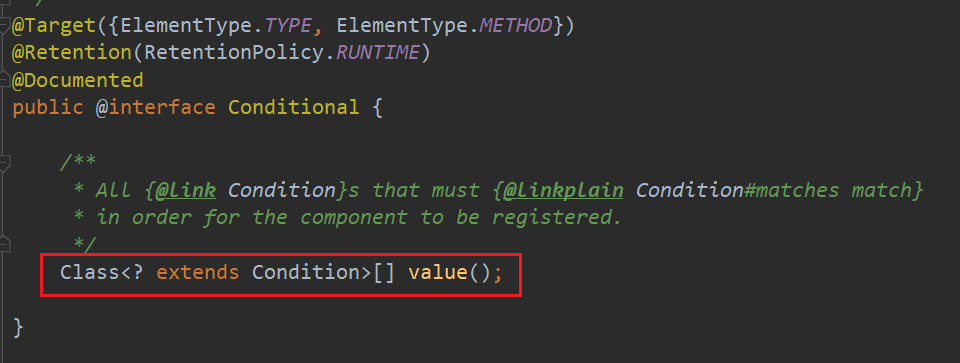
Condition 接口:

@Conditional 该注解可以作用在类与方法上面。
@Conditional 里面有一个 Conditin 数组,用来放置判断条件的类。
@Condition 接口中有一个 matches() 方法,当此方法返回为 true,就添加该组件;否则不添加。
为了实现上面的需求,自定义两个两个 Condition 条件类:
LinuxCondition:
//判断是否 linux 系统
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
/**
* ConditionContext context:判断条件能使用的上下文(环境)
* AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata :注解信息
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//1. 能获取到 IOC 使用的 beanFactory 工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//2. 获取类的加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
//3. 获取环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
//4. 获取到 bean 定义的注册类的信息
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
//扩展:可以判断容器中的bean注册情况,也可以给容器中注册bean
boolean definition = registry.containsBeanDefinition("person");
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("linux")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
WindowsCondition:
//判断是否 window 系统
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("Windows")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
应用一:加在方法上面
把 @Conditional 加到方法上时,只有返回值为 true,才会注册对应的bean。
@Conditional(value = {WindowsCondition.class})
@Bean(value = "bill")
public Person person01() {
return new Person("Bill Gates", 62);
}
@Conditional(value = {LinuxCondition.class})
@Bean(value = "linus")
public Person person02() {
return new Person("Linus", 48);
}
上面的案例:如果系统是 Windows,容器中注册 bill 组件,如果是Linux系统,容器中注册 linus 组件;


应用二:加在类上面
@Conditional 还可以加到类上
//加类上的时候,只有满足当前条件,这个类中配置的所有的bean注册才能生效
@Conditional(value = {WindowsCondition.class})
@Configuration
public class MainConfig3 {
@Conditional(value = {WindowsCondition.class})
@Bean(value = "bill")
public Person person01() {
return new Person("Bill Gates", 62);
}
@Conditional(value = {LinuxCondition.class})
@Bean(value = "linus")
public Person person02() {
return new Person("Linus", 48);
}
}
当加到类上时,是对类中组件统一的设置。
即只有满足当前条件,这个类中配置的所有的bean注册才能生效。