字符串,我现在正在写的就是一个字符串。我们的源代码就是一个字符串,计算机科学里面,一大部分问题都是字符串处理的问题。比如,编译器,就是一个字符串处理程序。还有,搜索引擎,也在处理一个字符串问题。数据库,最难处理的还是字符串部分。索引,一般是一种预处理的中间程序。在我们写代码的时候,往往需要对一个对象进行预处理。这个预处理时间可能比较长,但是,处理完了以后,就能很快的多次的在上面进行查询。比如,你要在一组数里面进行查找,可能先要进行排序,这样速度就会快一些, 排序可以看做是建立索引的一个过程。
字符串的全文索引,怎么样才能非常的省空间,查找速度也还可以,我这里介绍一种数据结构,叫做后缀数组。
概念不多说,我就在例子中说明什么东西是后缀数组吧。
step 1. 所有的后缀:
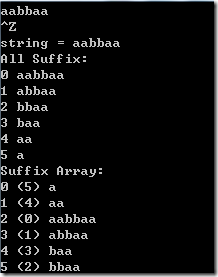
string a = ‘aabbaa’;
找到所有的后缀:
0 aabbaa
1 abbaa
2 bbaa
3 baa
4 aa
5 a
step 2. 对所有的后缀进行排序:
0 (5)a
1 (4)aa
2 (0)aabbaa
3 (1)abbaa
4 (3)baa
5 (2)bbaa
小括号里面的就是原来的索引值。
排序后的这个数组就叫做后缀数组。
下面这个程序,我想让大家更加感性的认识一下后缀数组是什么东西:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>//5M#define MAX_LEN 1024 * 1024 * 5char str[MAX_LEN + 1], *suffix_array[MAX_LEN + 32];int readstr();int cmpnum, charcmpnum;int pstrcmp(const void *a, const void *b);int main(){int n, i;n = readstr();printf("string = %s\n", str);printf("All Suffix:\n");for (i = 0; i < n; i++){suffix_array[i] = str + i;printf("%d %s\n", i, suffix_array[i]);}qsort(suffix_array, n , sizeof(char *), pstrcmp);printf("Suffix Array:\n");for (i = 0; i < n; i++){printf("%d (%d) %s\n", i, suffix_array[i] - str, suffix_array[i]);}return 0;}int readstr(){int ch;int n = 0;while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF){str[n++] = (char)ch;if (n >= MAX_LEN) {break;}}while (str[n-1] == '\r' || str[n-1] == '\n'){n--;}str[n] = 0;return n;}int pstrcmp(const void *a, const void *b){unsigned char *p = *((unsigned char **)a), *q = *((unsigned char **)b);unsigned char c1 , c2;cmpnum++;do {c1 = (unsigned char)*p++;c2 = (unsigned char)*q++;charcmpnum++;if (c1 == '\0') {return c1 - c2;}} while (c1 == c2);return c1 - c2;}运行这个程序的方法是输入一个字符串,然后输入EOF 字符串
比如输入 aabbaa[回车][ctrl+z][回车] 的结果是
后缀数组就是将所有的字符串后缀进行排序,注意,代码空间复杂度,每一个后缀只是保存了一个指针,并没有复制整个字符串。
啰嗦了半天,到底这个东西怎么做全文索引呢?你看非常简单的代码,核心的代码就几行,你肯定觉得这个东西没有用。编程珠玑的 第15章 字符串 有关于这个话题的讨论,大家可以去看看。介绍算法不是我写这篇博客的目的,我想写一些超越算法了一些东西,这篇只是开一个头。
这个后缀数组的所有前缀就是所有的substring(子串)。用过数据库的人可能知道数据库里面的 like 查询 查前缀(like prefix% )要比查后缀(like %suffix )或者任意的查询(like %query%)快很多.原因就是数据库里面是按照字母顺序存储的,这样前缀查询可以二分查找,速度就快了。后缀数组的原理也是这样。一个查询问题转换为一个前缀查询的问题,但是转换的方法却是通过后缀, 很有老庄哲学的韵味。
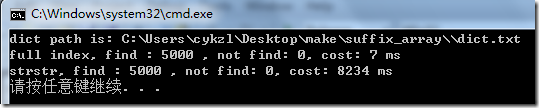
下面的程序是读入一个很长的字符串,我测试的是一本23万个英语单词的字典。先随机从这本英文字典里面抽取了5000个单词,然后,把正本字典看做一个字符串,在这本字典里面进行查询,分别用系统自带的 strstr (kMP算法) 和 我们的全文索引(后缀数组进行查询) 看看性能会差多少:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>#include <windows.h>//5M#define MAX_LEN 1024 * 1024 * 5//一个单词的最大长度#define MAX_WORD 255#define MAX_DICT 500000//路径的最大长度#ifndef MAX_PATH#define MAX_PATH 256#endif#define TEST_NUM 5000//函数列表static int read_str();static int read_dict(const char * filepath);static int pstrcmp(const void *a, const void *b);static char * dirname(const char *path, int count);static int range_rand(int min, int max);static int prefixcmp(const void *a, const void *b);static void test_full_index();static void test_strstr();//全局变量char str[MAX_LEN + 1]; //原始字符串char *suffix_array[MAX_LEN + 32]; //后缀数组char *dict[MAX_DICT]; //测试字典int cmpnum, charcmpnum; //以后可能用来测试性能的计数char *query[TEST_NUM]; //查询表达式int dictn, strn;int main(int argc, char *argv[]){int i;if (argc < 2) {printf("usage: %s dict_path", argv[0]);exit(0);}//读取字典,构建测试查询printf("dict path is: %s\n", argv[1]);dictn = read_dict(argv[1]);for (i = 0; i < TEST_NUM; i++){query[i] = dict[range_rand(0, dictn)];}//最好free掉dict的内存,对于这样简单的程序,没有多少必要,程序结束以后,自动释放。//创建后缀数组, 从stdin读取strn = read_str();for (i = 0; i < strn; i++){suffix_array[i] = str + i;}qsort(suffix_array, strn, sizeof(char *), pstrcmp);//测试通过后缀数组建立的索引进行全文查找test_full_index();//测试通过普通子串查询, 这些算法一般用KMP算法。test_strstr();return 0;}static void test_full_index(){int i , t, nofind = 0, find = 0;t = clock();for (i = 0; i < TEST_NUM; i++){char **index;index = (char **)bsearch(query[i], suffix_array, strn, sizeof(char *), prefixcmp);if (index == NULL) {nofind++;} else {find++;}}printf("full index, find : %d , not find: %d, cost: %d ms\n", find, nofind, clock() - t);}static void test_strstr(){int i , t, nofind = 0, find = 0;t = clock();for (i = 0; i < TEST_NUM; i++){char *index;index = strstr(str, query[i]);if (index == NULL) {nofind++;} else {find++;}}printf("strstr, find : %d , not find: %d, cost: %d ms\n", find, nofind, clock() - t);}static int read_str(){int ch;int n = 0;while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF){str[n++] = (char)ch;if (n >= MAX_LEN) {break;}}while (str[n-1] == '\r' || str[n-1] == '\n'){n--;}str[n] = 0;return n;}static int read_dict(const char * filepath){char buffer[MAX_WORD];FILE *fp = fopen(filepath, "r");int n = 0;if (fp == NULL) return 0;while (fscanf(fp, "%s", buffer) != EOF){int word_len = strlen(buffer) + 1;if (n >= MAX_DICT) {break;}dict[n++] = (char *)malloc(word_len);memcpy(dict[n-1], buffer, word_len);}return n;}static int pstrcmp(const void *a, const void *b){unsigned char *p = *((unsigned char **)a), *q = *((unsigned char **)b);unsigned char c1 , c2;cmpnum++;do {c1 = (unsigned char)*p++;c2 = (unsigned char)*q++;charcmpnum++;if (c1 == '\0') {return c1 - c2;}} while (c1 == c2);return c1 - c2;}static int prefixcmp(const void *a, const void *b){unsigned char *p = (unsigned char *)a, *q = *(unsigned char **)b;unsigned char c1 , c2;do {c1 = (unsigned char)*p++;c2 = (unsigned char)*q++;if (c1 == '\0') {return 0; //match}} while (c1 == c2);return c1 - c2;}static int range_rand(int min, int max){double r = 0;int i;double mul = 1;for (i = 0; i < 3; i++){mul *= 0.0001;r += (rand() % 10000) * mul;}//0 - 1 中的一个随机数return (int)(r * (max - min)) + min;}后面的一些小函数大概比较多,其实主要看main函数就可以了。
命令行运行:suffix_array dict.txt < dict.txt , 用了一个文件重定向到stdin,附件中有这本测试字典。
测试结果是:
可以发现,性能差的挺多了,有1000倍。如果字符串更加的长,差别会更加的大。
这篇博客还只是个引子,实际上,理论上来说,我们采用qsort的方法来排序后缀数组性能比较低。但是,实际用起来这几乎是最好的方法。这是一个典型的一行顶一万行的例子。后缀数组的应用也不仅仅是做全文索引这样一种功能,欲知详情,请关注下一篇博客:字符串之后缀数组倍增算法。