当我们使用@DiscoveryClient注解的时候,会不会有如下疑问:它为什么会进行注册服务的操作,它不是应该用作服务发现的吗?下面我们就来深入的探究一下其源码。
一、Springframework的LifeCycle接口
要搞明白这个问题我们需要了解一下这个重要的接口:

/* * Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.context; /** * A common interface defining methods for start/stop lifecycle control. * The typical use case for this is to control asynchronous processing. * <b>NOTE: This interface does not imply specific auto-startup semantics. * Consider implementing {@link SmartLifecycle} for that purpose.</b> * * <p>Can be implemented by both components (typically a Spring bean defined in a * Spring context) and containers (typically a Spring {@link ApplicationContext} * itself). Containers will propagate start/stop signals to all components that * apply within each container, e.g. for a stop/restart scenario at runtime. * * <p>Can be used for direct invocations or for management operations via JMX. * In the latter case, the {@link org.springframework.jmx.export.MBeanExporter} * will typically be defined with an * {@link org.springframework.jmx.export.assembler.InterfaceBasedMBeanInfoAssembler}, * restricting the visibility of activity-controlled components to the Lifecycle * interface. * * <p>Note that the Lifecycle interface is only supported on <b>top-level singleton * beans</b>. On any other component, the Lifecycle interface will remain undetected * and hence ignored. Also, note that the extended {@link SmartLifecycle} interface * provides integration with the application context's startup and shutdown phases. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.0 * @see SmartLifecycle * @see ConfigurableApplicationContext * @see org.springframework.jms.listener.AbstractMessageListenerContainer * @see org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.SchedulerFactoryBean */ public interface Lifecycle { /** * Start this component. * <p>Should not throw an exception if the component is already running. * <p>In the case of a container, this will propagate the start signal to all * components that apply. * @see SmartLifecycle#isAutoStartup() */ void start(); /** * Stop this component, typically in a synchronous fashion, such that the component is * fully stopped upon return of this method. Consider implementing {@link SmartLifecycle} * and its {@code stop(Runnable)} variant when asynchronous stop behavior is necessary. * <p>Note that this stop notification is not guaranteed to come before destruction: On * regular shutdown, {@code Lifecycle} beans will first receive a stop notification before * the general destruction callbacks are being propagated; however, on hot refresh during a * context's lifetime or on aborted refresh attempts, only destroy methods will be called. * <p>Should not throw an exception if the component isn't started yet. * <p>In the case of a container, this will propagate the stop signal to all components * that apply. * @see SmartLifecycle#stop(Runnable) * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean#destroy() */ void stop(); /** * Check whether this component is currently running. * <p>In the case of a container, this will return {@code true} only if <i>all</i> * components that apply are currently running. * @return whether the component is currently running */ boolean isRunning(); }
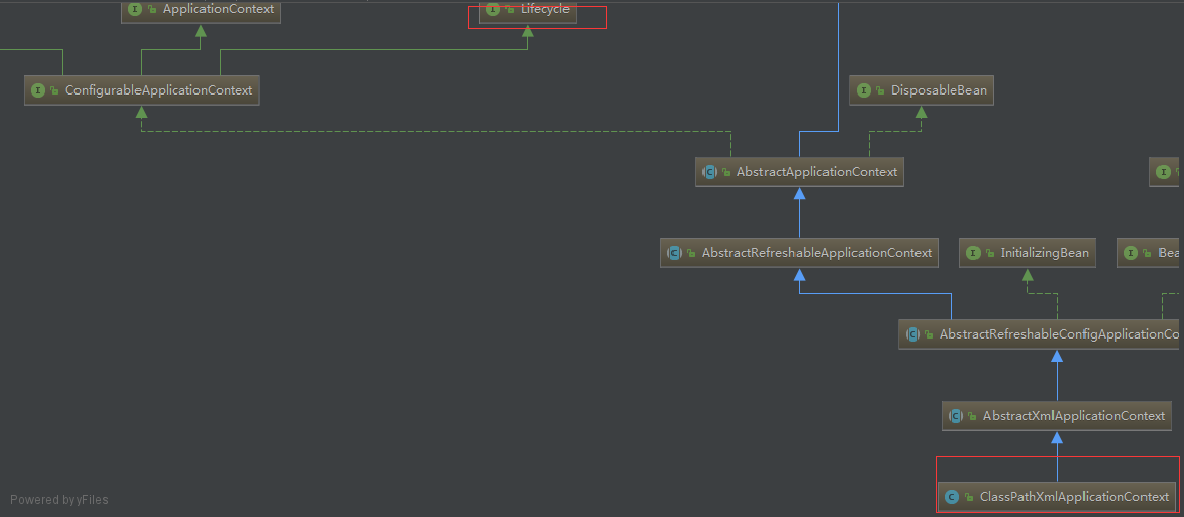
该接口定义启动/停止生命周期控制方法,当spring ioc容器启动或停止时将发送一个启动或者停止的信号通知到各个组件,因此我们可以在对应的方法里做我们想要的事情。我们可以通过类图发现我们常用的ClasspathXmlApplicationContext类就实现了该接口
下面我们来简单演示一下案例,创建类MyLifeCycle:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.context; import org.springframework.context.SmartLifecycle; public class MyLifeCycle implements SmartLifecycle { @Override public void start() { System.out.println("MyLifeCycle start ...."); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("MyLifeCycle stop ....."); } @Override public boolean isRunning() { return false; } @Override public boolean isAutoStartup() { return true; } @Override public void stop(Runnable callback) { } @Override public int getPhase() { System.out.println("phase"); return 10; } }
在这里我们继承SmartLifeCycle该接口继承了LifeCycle, isRunning方法用于检测当前的组件是否处在运行状态,注意只有当isRunning返回值为false才可以运行
我们把MyLifeCycle配置到spring配置文件里,通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext运行 会得到如下结果:

另外在这里的getPhase方法,这个是定义阶段值(可以理解为优先级,值越小对应的LifeCycle越先执行)
二、服务自动注册原理
在spring-cloud-commons的jar包里的META-INF/spring.factories里有如下配置:
# AutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration= org.springframework.cloud.client.CommonsClientAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.noop.NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.hypermedia.CloudHypermediaAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.commons.util.UtilAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.composite.CompositeDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.simple.SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.commons.httpclient.HttpClientConfiguration, org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration
在这里其中有一项是AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration的自动化配置,我们来看一下其源码:
package org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; /** * @author Spencer Gibb */ @Configuration @Import(AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public class AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration { @Autowired(required = false) private AutoServiceRegistration autoServiceRegistration; @Autowired private AutoServiceRegistrationProperties properties; @PostConstruct protected void init() { if (autoServiceRegistration == null && this.properties.isFailFast()) { throw new IllegalStateException("Auto Service Registration has been requested, but there is no AutoServiceRegistration bean"); } } }
通过源码我们可以发现在这里会自动注入一个AutoServiceRegistration的接口类型
其中该接口有一个实现类:org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AbstractAutoServiceRegistration,我们来看一下结构图:
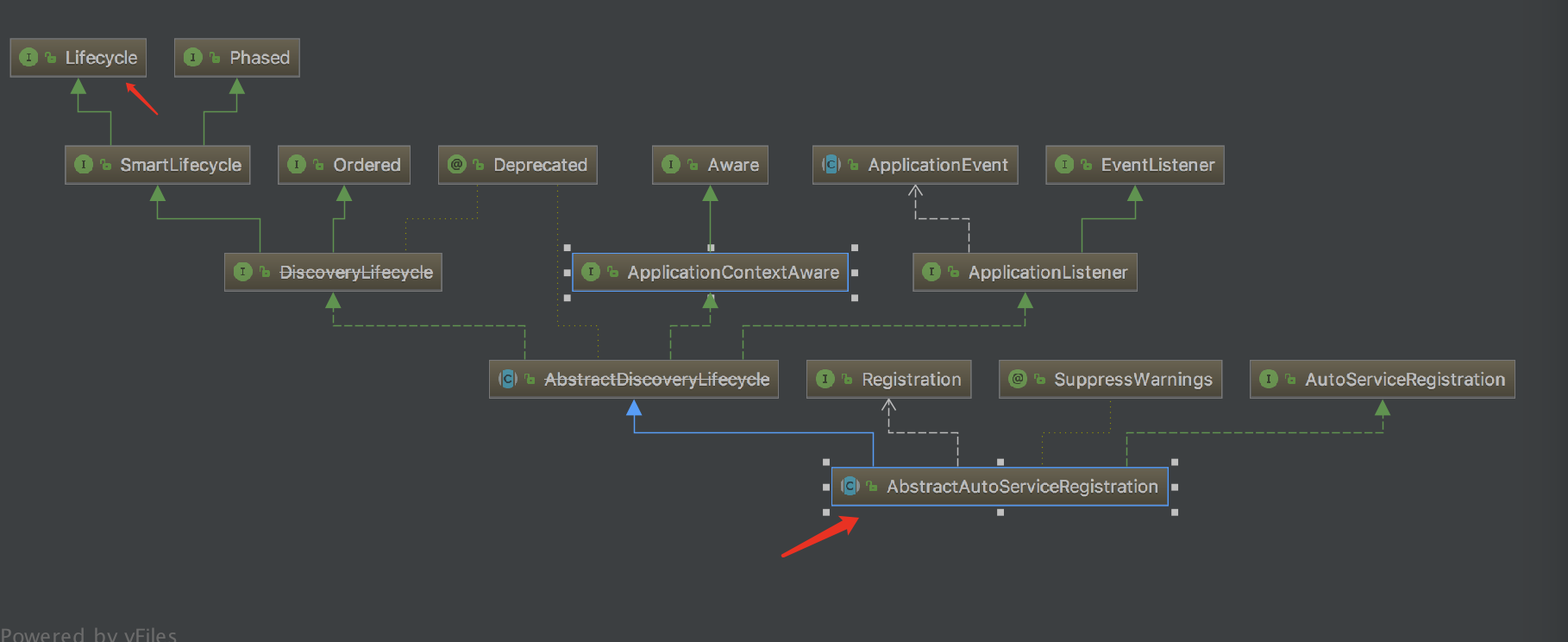
我们可以得知这个类实现了Lifecycle接口,并实现了AutoServiceRegistration接口。那么我们看一看start方法,此方法在它的父类AbstractDiscoveryLifecycle里:

/* * Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.event.InstanceRegisteredEvent; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.ServiceRegistry; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; /** * Lifecycle methods that may be useful and common to various DiscoveryClient implementations. * * @deprecated use {@link org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AbstractAutoServiceRegistration} instead. This class will be removed in the next release train. * * @author Spencer Gibb */ @Deprecated public abstract class AbstractDiscoveryLifecycle implements DiscoveryLifecycle, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent> { private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(AbstractDiscoveryLifecycle.class); private boolean autoStartup = true; private AtomicBoolean running = new AtomicBoolean(false); private int order = 0; private ApplicationContext context; private Environment environment; private AtomicInteger port = new AtomicInteger(0); protected ApplicationContext getContext() { return context; } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.context = applicationContext; this.environment = this.context.getEnvironment(); } @Deprecated protected Environment getEnvironment() { return environment; } @Deprecated protected AtomicInteger getPort() { return port; } @Override public boolean isAutoStartup() { return this.autoStartup; } @Override public void stop(Runnable callback) { try { stop(); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("A problem occurred attempting to stop discovery lifecycle", e); } callback.run(); } @Override public void start() { if (!isEnabled()) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Discovery Lifecycle disabled. Not starting"); } return; } // only set the port if the nonSecurePort is 0 and this.port != 0 if (this.port.get() != 0 && getConfiguredPort() == 0) { setConfiguredPort(this.port.get()); } // only initialize if nonSecurePort is greater than 0 and it isn't already running // because of containerPortInitializer below if (!this.running.get() && getConfiguredPort() > 0) { register(); if (shouldRegisterManagement()) { registerManagement(); } this.context.publishEvent(new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, getConfiguration())); this.running.compareAndSet(false, true); } } @Deprecated protected abstract int getConfiguredPort(); @Deprecated protected abstract void setConfiguredPort(int port); /** * @return if the management service should be registered with the {@link ServiceRegistry} */ protected boolean shouldRegisterManagement() { return getManagementPort() != null && ManagementServerPortUtils.isDifferent(this.context); } /** * @return the object used to configure the registration */ @Deprecated protected abstract Object getConfiguration(); /** * Register the local service with the DiscoveryClient */ protected abstract void register(); /** * Register the local management service with the DiscoveryClient */ protected void registerManagement() { } /** * De-register the local service with the DiscoveryClient */ protected abstract void deregister(); /** * De-register the local management service with the DiscoveryClient */ protected void deregisterManagement() { } /** * @return true, if the {@link DiscoveryLifecycle} is enabled */ protected abstract boolean isEnabled(); /** * @return the serviceId of the Management Service */ @Deprecated protected String getManagementServiceId() { // TODO: configurable management suffix return this.context.getId() + ":management"; } /** * @return the service name of the Management Service */ @Deprecated protected String getManagementServiceName() { // TODO: configurable management suffix return getAppName() + ":management"; } /** * @return the management server port */ @Deprecated protected Integer getManagementPort() { return ManagementServerPortUtils.getPort(this.context); } /** * @return the app name, currently the spring.application.name property */ @Deprecated protected String getAppName() { return this.environment.getProperty("spring.application.name", "application"); } @Override public void stop() { if (this.running.compareAndSet(true, false) && isEnabled()) { deregister(); if (shouldRegisterManagement()) { deregisterManagement(); } } } @PreDestroy public void destroy() { stop(); } @Override public boolean isRunning() { return this.running.get(); } protected AtomicBoolean getRunning() { return running; } @Override public int getOrder() { return this.order; } @Override public int getPhase() { return 0; } @Override @Deprecated public void onApplicationEvent(EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent event) { // TODO: take SSL into account // Don't register the management port as THE port if (!"management".equals(event.getApplicationContext().getNamespace())) { this.port.compareAndSet(0, event.getEmbeddedServletContainer().getPort()); this.start(); } } }
注意在start方法里有一段这个代码:
if (!this.running.get() && getConfiguredPort() > 0) { register(); if (shouldRegisterManagement()) { registerManagement(); } this.context.publishEvent(new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, getConfiguration())); this.running.compareAndSet(false, true); }
请注意register() 这个方法是本类里的抽象方法。那么我们回过头看一下AbstractAutoServiceRegistration类里的代码,我这里只贴出关键部分:

//..... protected AbstractAutoServiceRegistration(ServiceRegistry<R> serviceRegistry, AutoServiceRegistrationProperties properties) { this.serviceRegistry = serviceRegistry; this.properties = properties; } //...... /** * Register the local service with the {@link ServiceRegistry} */ @Override protected void register() { this.serviceRegistry.register(getRegistration()); }
我们可以发现在构造函数里传了一个ServiceRegistry类型,这个接口是SpringCloud给我们提供用于服务注册的接口。在这里EurekaServiceRegistry就是实现了此接口:

/* * Copyright 2013-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. * */ package org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.serviceregistry; import java.util.HashMap; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.ServiceRegistry; import com.netflix.appinfo.InstanceInfo; /** * @author Spencer Gibb */ public class EurekaServiceRegistry implements ServiceRegistry<EurekaRegistration> { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(EurekaServiceRegistry.class); @Override public void register(EurekaRegistration reg) { maybeInitializeClient(reg); if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Registering application " + reg.getInstanceConfig().getAppname() + " with eureka with status " + reg.getInstanceConfig().getInitialStatus()); } reg.getApplicationInfoManager() .setInstanceStatus(reg.getInstanceConfig().getInitialStatus()); if (reg.getHealthCheckHandler() != null) { reg.getEurekaClient().registerHealthCheck(reg.getHealthCheckHandler()); } } private void maybeInitializeClient(EurekaRegistration reg) { // force initialization of possibly scoped proxies reg.getApplicationInfoManager().getInfo(); reg.getEurekaClient().getApplications(); } @Override public void deregister(EurekaRegistration reg) { if (reg.getApplicationInfoManager().getInfo() != null) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Unregistering application " + reg.getInstanceConfig().getAppname() + " with eureka with status DOWN"); } reg.getApplicationInfoManager().setInstanceStatus(InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.DOWN); //shutdown of eureka client should happen with EurekaRegistration.close() //auto registration will create a bean which will be properly disposed //manual registrations will need to call close() } } @Override public void setStatus(EurekaRegistration registration, String status) { InstanceInfo info = registration.getApplicationInfoManager().getInfo(); //TODO: howto deal with delete properly? if ("CANCEL_OVERRIDE".equalsIgnoreCase(status)) { registration.getEurekaClient().cancelOverrideStatus(info); return; } //TODO: howto deal with status types across discovery systems? InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus newStatus = InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.toEnum(status); registration.getEurekaClient().setStatus(newStatus, info); } @Override public Object getStatus(EurekaRegistration registration) { HashMap<String, Object> status = new HashMap<>(); InstanceInfo info = registration.getApplicationInfoManager().getInfo(); status.put("status", info.getStatus().toString()); status.put("overriddenStatus", info.getOverriddenStatus().toString()); return status; } public void close() { } }
那么至此我们可以知道自动注册服务是利用了LifeCycle机制,在容器启动时会执行ServiceRegistry的register()方法。
三、服务自动注册实战之redis注册中心
下面我们实现一个基于redis为注册中心的需求,来理解一下Discoveryclient。顺便理解一下Springcloud重要的接口:ServiceRegistry,ServiceInstance,再此之前我们先添加对redis的支持:
compile group: 'org.springframework.boot', name: 'spring-boot-starter-data-redis'
1、实现Registration接口

package com.hzgj.lyrk.member; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.Registration; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.NetworkInterface; import java.net.URI; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.Map; @Component public class RedisRegistration implements Registration { @Value("${server.port}") private Integer port; @Value("${spring.application.name}") private String applicationName; private String host; public void setHost(String host) { this.host = host; } public void setPort(Integer port) { this.port = port; } public void setApplicationName(String applicationName) { this.applicationName = applicationName; } @Override public String getServiceId() { return applicationName + ":" + getHost() + ":" + getPort(); } @Override public String getHost() { try { if (host == null) return getLocalHostLANAddress().getHostAddress(); else return host; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } @Override public int getPort() { return port; } @Override public boolean isSecure() { return false; } @Override public URI getUri() { return null; } @Override public Map<String, String> getMetadata() { return null; } public String getServiceName() { return this.applicationName; } public InetAddress getLocalHostLANAddress() throws Exception { try { InetAddress candidateAddress = null; // 遍历所有的网络接口 for (Enumeration ifaces = NetworkInterface.getNetworkInterfaces(); ifaces.hasMoreElements(); ) { NetworkInterface iface = (NetworkInterface) ifaces.nextElement(); // 在所有的接口下再遍历IP for (Enumeration inetAddrs = iface.getInetAddresses(); inetAddrs.hasMoreElements(); ) { InetAddress inetAddr = (InetAddress) inetAddrs.nextElement(); if (!inetAddr.isLoopbackAddress()) {// 排除loopback类型地址 if (inetAddr.isSiteLocalAddress()) { // 如果是site-local地址,就是它了 return inetAddr; } else if (candidateAddress == null) { // site-local类型的地址未被发现,先记录候选地址 candidateAddress = inetAddr; } } } } if (candidateAddress != null) { return candidateAddress; } // 如果没有发现 non-loopback地址.只能用最次选的方案 InetAddress jdkSuppliedAddress = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); return jdkSuppliedAddress; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
该接口继承了ServiceIntance,那么此接口最主要作用就是定义了一个服务实例的规范,比如说它的serviceId是什么,端口号是什么等
2、实现ServiceRegistry的接口

package com.hzgj.lyrk.member; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.ServiceRegistry; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate; public class RedisServiceRegistry implements ServiceRegistry<RedisRegistration> { @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public void register(RedisRegistration registration) { String serviceId = registration.getServiceId(); redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(serviceId, registration.getHost() + ":" + registration.getPort()); } @Override public void deregister(RedisRegistration registration) { redisTemplate.opsForList().remove(registration.getServiceId(), 1, registration.getHost() + ":" + registration.getPort()); } @Override public void close() { //redisTemplate.d System.out.println("closed ..."); } @Override public void setStatus(RedisRegistration registration, String status) { } @Override public <T> T getStatus(RedisRegistration registration) { return null; } }
该接口主要作用是定义如何进行服务注册 ,服务注销,设置与获取服务状态等操作
3、继承 AbstractAutoServiceRegistration抽象类

package com.hzgj.lyrk.member; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AbstractAutoServiceRegistration; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationProperties; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.ServiceRegistry; public class RedisAutoServiceRegistration extends AbstractAutoServiceRegistration<RedisRegistration> { @Autowired private RedisRegistration redisRegistration; protected RedisAutoServiceRegistration(ServiceRegistry<RedisRegistration> serviceRegistry, AutoServiceRegistrationProperties properties) { super(serviceRegistry, properties); // serviceRegistry.register(getRegistration()); } @Override protected int getConfiguredPort() { return redisRegistration.getPort(); } @Override protected void setConfiguredPort(int port) { } @Override protected Object getConfiguration() { return null; } @Override protected boolean isEnabled() { return true; } @Override protected RedisRegistration getRegistration() { return redisRegistration; } @Override protected RedisRegistration getManagementRegistration() { return null; } }
4、定义DiscoveryClient的实现类RedisDiscoveryClient

package com.hzgj.lyrk.member; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.function.Function; import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class RedisDiscoveryClient implements DiscoveryClient { @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public String description() { return "redis注册中心的服务发现"; } @Override public ServiceInstance getLocalServiceInstance() { return null; } @Override public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) { return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(serviceId, 0, -1). parallelStream().map((Function<String, ServiceInstance>) s -> { RedisRegistration redisRegistration = new RedisRegistration(); redisRegistration.setApplicationName(serviceId); String hostName = StringUtils.split(s, ":")[0]; String port = StringUtils.split(s, ":")[1]; redisRegistration.setHost(hostName); redisRegistration.setPort(Integer.parseInt(port)); //redisRegistration return redisRegistration; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); } @Override public List<String> getServices() { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.addAll(redisTemplate.keys("*")); return list; } }
该类主要是针对于redis注册中心的服务发现
5、定义自动装配的类用以创建对应的bean

package com.hzgj.lyrk.member; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; @Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisConfig.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.redis.registry.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public class RedisRegistryAutoConfiguration { @Bean RedisServiceRegistry redisServiceRegistry(RedisConfig redisConfig) { System.out.println(redisConfig.getHost()); return new RedisServiceRegistry(); } @Bean RedisAutoServiceRegistration redisAutoServiceRegistration(RedisServiceRegistry redisServiceRegistry) { return new RedisAutoServiceRegistration(redisServiceRegistry, new AutoServiceRegistrationProperties()); } @Bean @Primary RedisDiscoveryClient redisDiscoveryClient() { return new RedisDiscoveryClient(); } }
6、定义启动类

package com.hzgj.lyrk.member; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.composite.CompositeDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.simple.SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class, CompositeDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class}) public class MemberApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(MemberApplication.class, args); DiscoveryClient discoveryClient = applicationContext.getBean(DiscoveryClient.class); discoveryClient.getServices().forEach(action -> { System.out.println(action); }); } }
这里在SpringbootApplication注解里排除DiscoveryClient的默认装配。
当我们启动成功后可以发现,控制台已经输出对应的服务名称与地址:
![]()
我们再次通过gradle打包生成jar文件并运行:
java -jar member-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8800
我们可以看到redis里已经缓存的有服务注册的值了:

