现在第三方登录的例子数见不鲜。其实在这种示例当中,oauth2.0是使用比较多的一种授权登录的标准。oauth2.0也是从oauth1.0升级过来的。那么关于oauth2.0相关的概念及其原理,大家可以参考这篇文章,这篇文章中会有更详细的解释,下来我们直接进入正题。
1.1、gradle依赖
compile('org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-oauth2')
compile('org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-security')
在这里我直接引入的是spring-cloud的依赖项,这种依赖的jar包更全面一些,这里面的核心基础还是spring-security。这里SpringBoot的版本为2.0.6.REALEASE
1.2、@EnableAuthorizationServer
在这里我着重强调一下这个注解:@EnableAuthorizationServer,这个注解源代码如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import({AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration.class, AuthorizationServerSecurityConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableAuthorizationServer {
}
这个注解主要是导入两个配置类,分别是:
AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration,这个配置类主要配置授权端点,获取token的端点。大家就把对应的端点想象成controller即可,在这个controller下开放了若干个@RequestMapping,比如常见的有:/oauth/authorize(授权路径),/oauth/token(获取token)等AuthorizationServerSecurityConfiguration,主要是做spring-security的安全配置,我们可以看一下相关代码:
public class AuthorizationServerSecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private List<AuthorizationServerConfigurer> configurers = Collections.emptyList();
@Autowired
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
@Autowired
private AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration endpoints;
@Autowired
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clientDetails) throws Exception {
for (AuthorizationServerConfigurer configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configure(clientDetails);
}
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// Over-riding to make sure this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr = false
// This will ensure that when this configurer builds the AuthenticationManager it will not attempt
// to find another 'Global' AuthenticationManager in the ApplicationContext (if available),
// and set that as the parent of this 'Local' AuthenticationManager.
// This AuthenticationManager should only be wired up with an AuthenticationProvider
// composed of the ClientDetailsService (wired in this configuration) for authenticating 'clients' only.
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//....省略部分代码
String tokenEndpointPath = handlerMapping.getServletPath("/oauth/token");
String tokenKeyPath = handlerMapping.getServletPath("/oauth/token_key");
String checkTokenPath = handlerMapping.getServletPath("/oauth/check_token");
if (!endpoints.getEndpointsConfigurer().isUserDetailsServiceOverride()) {
UserDetailsService userDetailsService = http.getSharedObject(UserDetailsService.class);
endpoints.getEndpointsConfigurer().userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
// @formatter:off
//上述节点的请求需要授权验证
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(tokenEndpointPath).fullyAuthenticated()
.antMatchers(tokenKeyPath).access(configurer.getTokenKeyAccess())
.antMatchers(checkTokenPath).access(configurer.getCheckTokenAccess())
.and()
.requestMatchers()
.antMatchers(tokenEndpointPath, tokenKeyPath, checkTokenPath)
.and()
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.NEVER);
// @formatter:on
http.setSharedObject(ClientDetailsService.class, clientDetailsService);
}
protected void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer oauthServer) throws Exception {
for (AuthorizationServerConfigurer configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configure(oauthServer);
}
}
}
1.2.1、AuthorizationServerConfigurer
这个接口是认证授权配置的核心接口,不过既然是SpringBoot我们就先来看看它怎么帮我们装配的,我们可以在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.authserver这个包下面找到对应配置的Bean:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(EnableAuthorizationServer.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AuthorizationServerConfigurer.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AuthorizationServerProperties.class)
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration
extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
//....
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
//默认基于内存创建ClientDetails
ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<InMemoryClientDetailsServiceBuilder>.ClientBuilder builder = clients
.inMemory().withClient(this.details.getClientId());
builder.secret(this.details.getClientSecret())
.resourceIds(this.details.getResourceIds().toArray(new String[0]))
.authorizedGrantTypes(
this.details.getAuthorizedGrantTypes().toArray(new String[0]))
.authorities(
AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(this.details.getAuthorities())
.toArray(new String[0]))
.scopes(this.details.getScope().toArray(new String[0]));
if (this.details.getAutoApproveScopes() != null) {
builder.autoApprove(
this.details.getAutoApproveScopes().toArray(new String[0]));
}
if (this.details.getAccessTokenValiditySeconds() != null) {
builder.accessTokenValiditySeconds(
this.details.getAccessTokenValiditySeconds());
}
if (this.details.getRefreshTokenValiditySeconds() != null) {
builder.refreshTokenValiditySeconds(
this.details.getRefreshTokenValiditySeconds());
}
if (this.details.getRegisteredRedirectUri() != null) {
builder.redirectUris(
this.details.getRegisteredRedirectUri().toArray(new String[0]));
}
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints)
throws Exception {
if (this.tokenConverter != null) {
endpoints.accessTokenConverter(this.tokenConverter);
}
if (this.tokenStore != null) {
endpoints.tokenStore(this.tokenStore);
}
if (this.details.getAuthorizedGrantTypes().contains("password")) {
endpoints.authenticationManager(this.authenticationManager);
}
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security)
throws Exception {
security.passwordEncoder(NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
if (this.properties.getCheckTokenAccess() != null) {
security.checkTokenAccess(this.properties.getCheckTokenAccess());
}
if (this.properties.getTokenKeyAccess() != null) {
security.tokenKeyAccess(this.properties.getTokenKeyAccess());
}
if (this.properties.getRealm() != null) {
security.realm(this.properties.getRealm());
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(BaseClientDetails.class)
protected static class BaseClientDetailsConfiguration {
private final OAuth2ClientProperties client;
protected BaseClientDetailsConfiguration(OAuth2ClientProperties client) {
this.client = client;
}
/**
由此可知它会寻找security.oauth2.client的配置
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "security.oauth2.client")
public BaseClientDetails oauth2ClientDetails() {
BaseClientDetails details = new BaseClientDetails();
if (this.client.getClientId() == null) {
this.client.setClientId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
details.setClientId(this.client.getClientId());
details.setClientSecret(this.client.getClientSecret());
details.setAuthorizedGrantTypes(Arrays.asList("authorization_code",
"password", "client_credentials", "implicit", "refresh_token"));
details.setAuthorities(
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_USER"));
details.setRegisteredRedirectUri(Collections.<String>emptySet());
return details;
}
}
}
如果没有用spring-boot的用户,可以也可以参考上述的配置方法,自行配置
1.3、application.yml的配置
根据上述代码我们可以知道,springboot通过外部化配置的security.oauth2.client的前缀来配置客户端。那么因此我们不妨在外部化配置文件里做如下配置:
server:
port: 8080
security:
oauth2:
client:
client-id: root
client-secret: root
scope:
- email
- username
- face
spring:
security:
user:
name: root
password: root
roles: ADMIN
这里先做最基本的配置,配置client-id,client-secret,scope。特别注意oauth2.0一定要先经过springsecurity的auth认证,因此需要在这里配置一个内存用户名与密码为root与root
1.4、配置资源服务器
通过资源服务器来保护我们指定的资源,必须在获取授权认证的时候才能访问。在SpringBoot当中,我们可以通过@EnableResourceServer注解来开启此功能。该注解定义如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(ResourceServerConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableResourceServer {
}
我们可以看到这个注解导入了默认的资源配置信息:ResourceServerConfiguration,它的源代码如下:
@Configuration
public class ResourceServerConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter implements Ordered {
//....
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources = new ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer();
ResourceServerTokenServices services = resolveTokenServices();
if (services != null) {
resources.tokenServices(services);
}
else {
if (tokenStore != null) {
resources.tokenStore(tokenStore);
}
else if (endpoints != null) {
resources.tokenStore(endpoints.getEndpointsConfigurer().getTokenStore());
}
}
if (eventPublisher != null) {
resources.eventPublisher(eventPublisher);
}
//配置资源
for (ResourceServerConfigurer configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configure(resources);
}
// @formatter:off
http.authenticationProvider(new AnonymousAuthenticationProvider("default"))
// N.B. exceptionHandling is duplicated in resources.configure() so that
// it works
.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedHandler(resources.getAccessDeniedHandler()).and()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
.csrf().disable();
// @formatter:on
http.apply(resources);
if (endpoints != null) {
// Assume we are in an Authorization Server
http.requestMatcher(new NotOAuthRequestMatcher(endpoints.oauth2EndpointHandlerMapping()));
}
for (ResourceServerConfigurer configurer : configurers) {
// Delegates can add authorizeRequests() here
configurer.configure(http);
}
//如果没有任何配置资源,则所有请求保护
if (configurers.isEmpty()) {
// Add anyRequest() last as a fall back. Spring Security would
// replace an existing anyRequest() matcher with this one, so to
// avoid that we only add it if the user hasn't configured anything.
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
//....
}
在这里主要是配置资源服务器的配置,我们可以得到如下几点信息:
- 资源配置的核心
ResourceServerConfigurer,在这里如果没有任何配置,则所有请求都要进行token认证 TokenStore主要定义了对token的增删改查操作,用于持久化tokenResourceServerTokenServices资源服务的service(服务层),这里主要还是根据token来拿到OAuth2Authentication与OAuth2AccessToken
1.5、完整示例
1.5.1、资源认证配置
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceConfigure extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable().sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.IF_REQUIRED)
.and().authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/free/**").permitAll().and()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin().permitAll();//必须认证过后才可以访问
}
}
在这里如果以/free/**请求路径的,都允许直接访问。否则,都必须携带access_token才能访问。
1.5.2 、授权认证配置
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable().requestMatchers().anyRequest().and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/oauth/*").authenticated().and().formLogin().permitAll();
}
}
根据上文所述,AuthorizationServerEndpoint与TokenEndpoint会开放/oauth/authorize与/oauth/token端点,因此我们必须保证访问端点进行授权认证前,通过springsecurity的用户认证,因此在这里配置了/oauth/*
1.5.3、启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAuthorizationServer
@Controller
public class AuthorizationServer {
@GetMapping("/order")
public ResponseEntity<String> order() {
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity("order", HttpStatus.OK);
return responseEntity;
}
@GetMapping("/free/test")
public ResponseEntity<String> test() {
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity("free", HttpStatus.OK);
return responseEntity;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AuthorizationServer.class, args);
}
}
1.5.4、访问请求
首先我们通过postman 访问http://localhost:8080/order会得到如下界面:
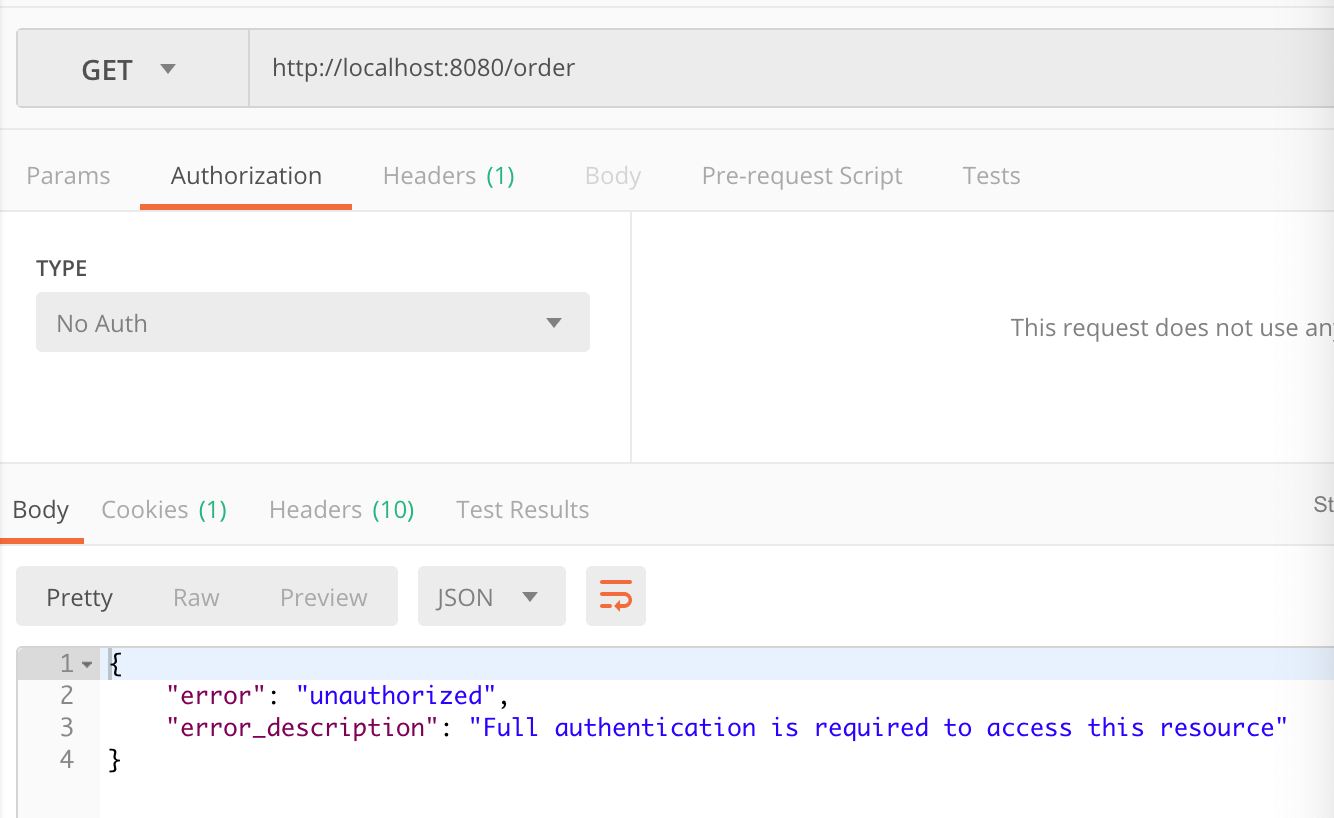
此时我们明显可以看到对应的资源需要携带有效的token才可以访问,那么我们此时要在postman的Authorization进行oauth2.0配置认证。截图如下:
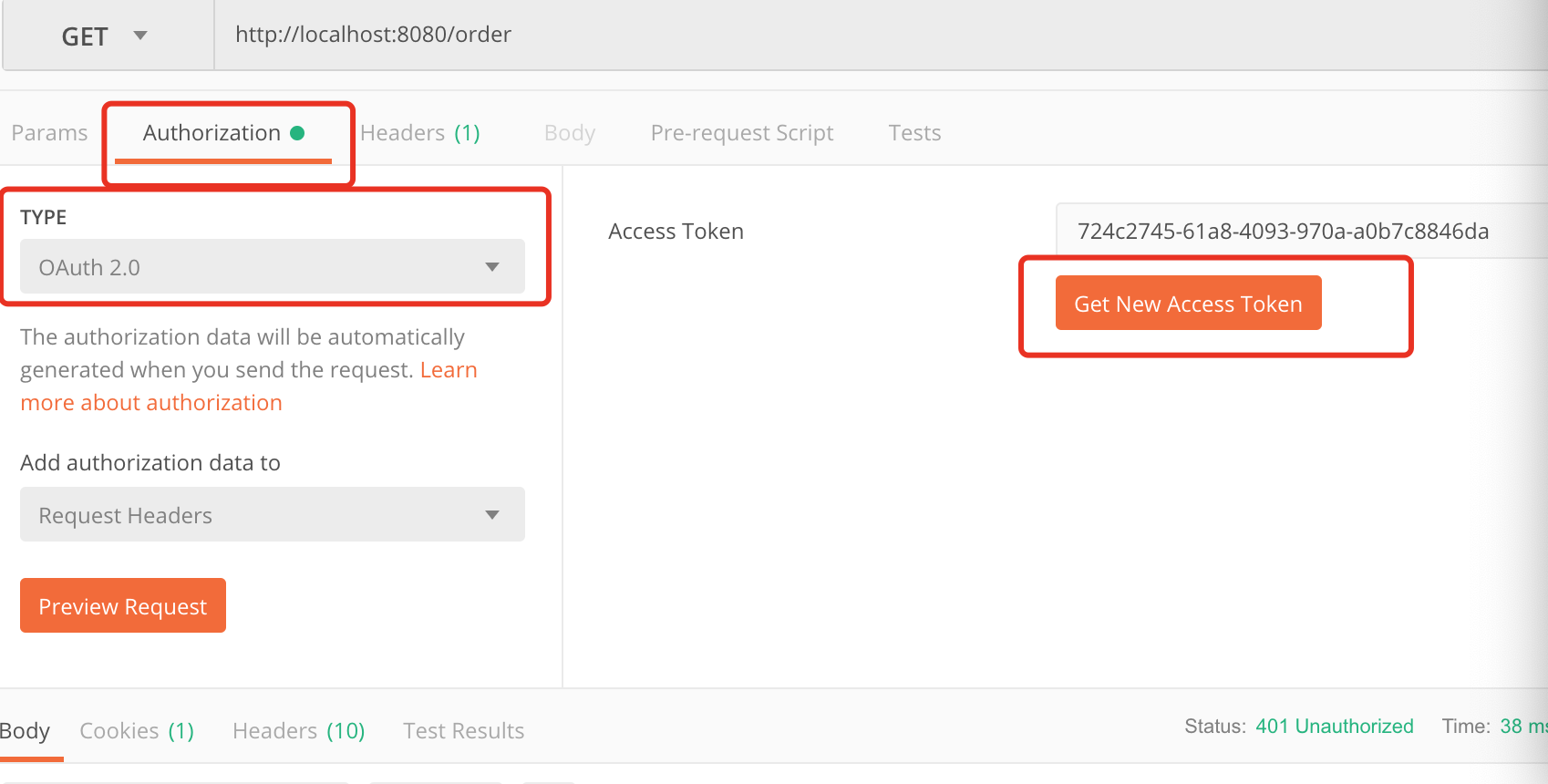
在这里点击Get New Access Token 来从认证服务器获取token,点击后配置如下:
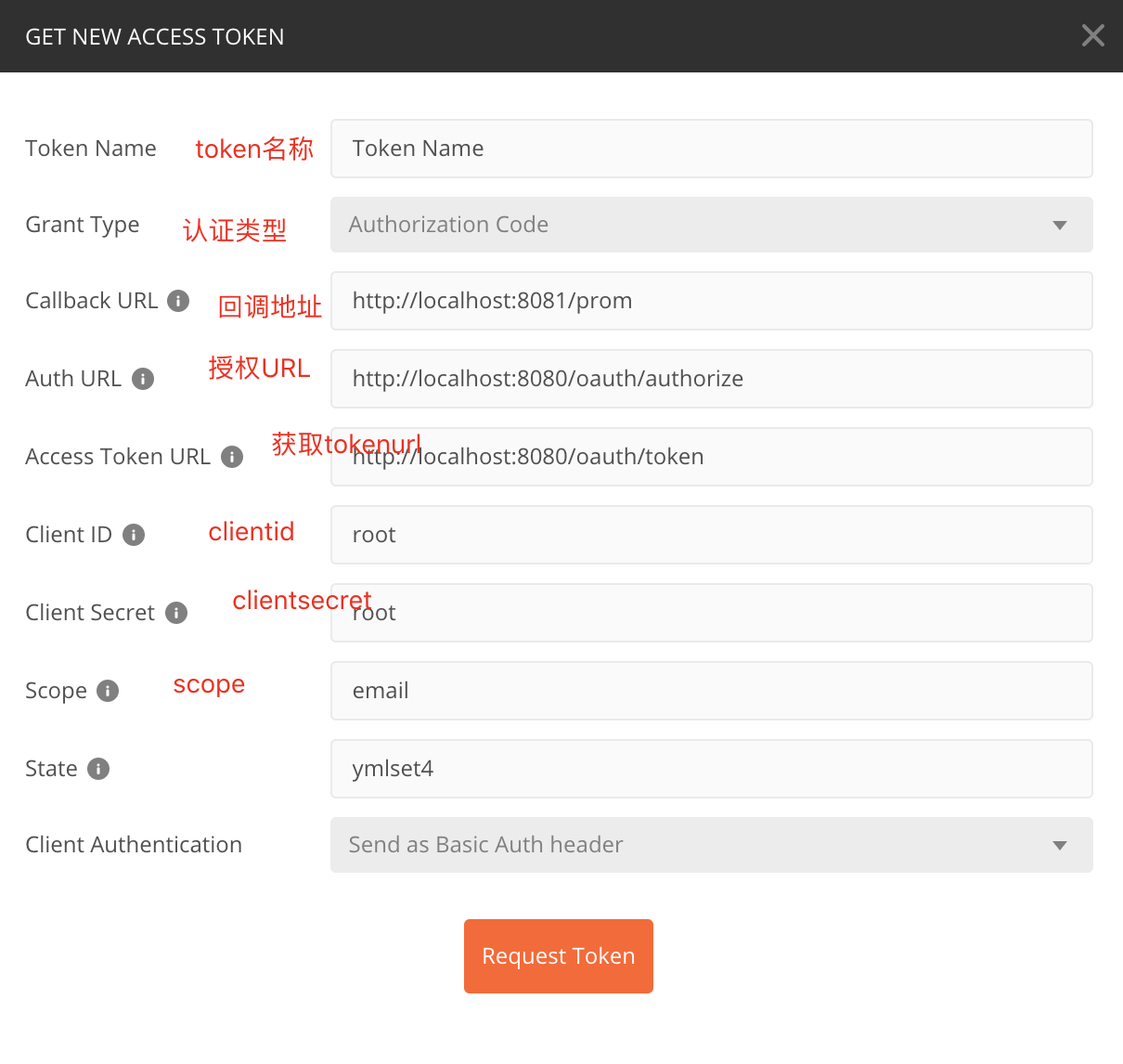
scope配置对应application.yml中的配置信息,这里面可以放置用户的属性信息,比如说昵称 头像 电话等等State代表状态码,设置一个State标志- 回调地址这里必须配置,通过这个地址当同意授权后会返回一个认证的code给我们,我们根据这个code请求token
- 认证地址与获取token的地址请填写,相关Endpoint生成的地址
当经过一连串认证后,我们即可拿到token:
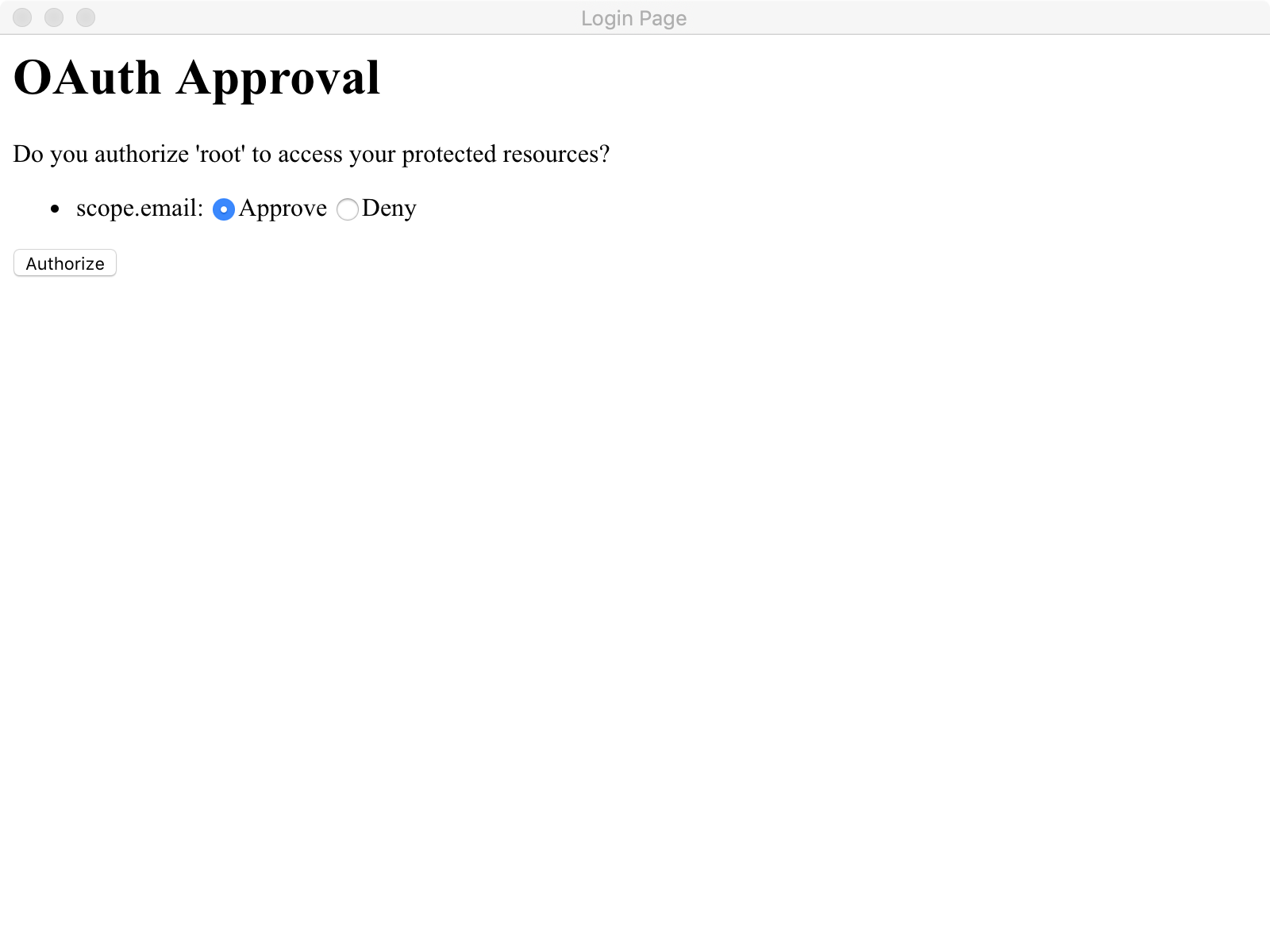
当我们获取到最新的token以后,我们即可访问到对应的请求资源:
