一、什么是系统服务及哪些是系统服务
系统服务包括:AMS、WMS、PMS、PKMS等。
二、Binder应用服务
三、系统服务与Binder应用服务启动
1. 系统服务启动是通过SystemServer中的run函数中启动的。
// Start services. try { t.traceBegin("StartServices"); startBootstrapServices(t); startCoreServices(t); startOtherServices(t); } catch (Throwable ex) { Slog.e("System", "******************************************"); Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex); throw ex; } finally { t.traceEnd(); // StartServices }
2. Bind应用服务启动
通过ActivityThread中函数handleCreateService启动:
@UnsupportedAppUsage private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) { // If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well // we are back active so skip it. unscheduleGcIdler(); LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck( data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo); Service service = null; try { if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name); ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo); Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation); java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); service = packageInfo.getAppFactory() .instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent); // Service resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the application // context. context.getResources().addLoaders( app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0])); context.setOuterContext(service); service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManager.getService()); service.onCreate(); mServices.put(data.token, service); try { ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting( data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to create service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } }
二、注册服务
1. 注册系统服务
系统服务注册到ServiceManager中,通过SystemServiceRegistry.java类注册。
比如注册AMS服务:
registerService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, ActivityManager.class, new CachedServiceFetcher<ActivityManager>() { @Override public ActivityManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) { return new ActivityManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), ctx.mMainThread.getHandler()); }});
2. 注册应用服务
应用服务是应用通过AMS与Service进行通信
Intent(this, MyService::class.java).also { intent -> bindService(intent, object : ServiceConnection { override fun onServiceConnected(name: ComponentName?, service: IBinder?) { val binder = service as MyService.LocalBinder _service = binder.getService() } override fun onServiceDisconnected(name: ComponentName?) { } }, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) }
在onServiceConnected回调中,通过binder代理对象获取Service的本地方法接口。这样,就可以通过_service对象调用Service服务的方法了。
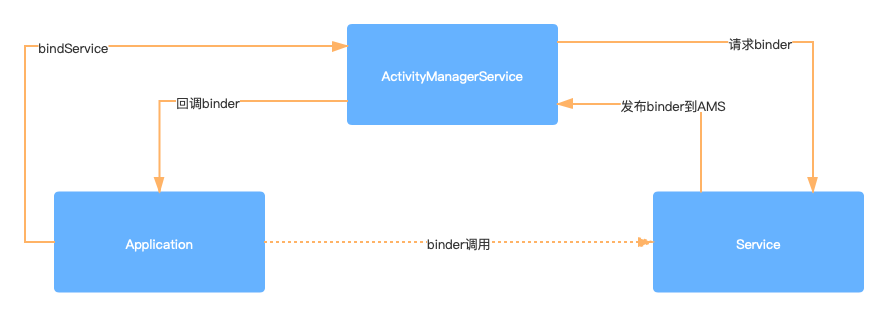
应用服务是应用通过AMS与Service绑定并获取binder对象:
- 应用服务调用binderService通过AMS与Service绑定,如果,应用服务未注册,首先将应用服务Service的binder对象发布到AMS中。
- 通过AMS将Service的binder代理对象返回给应用。
- 应用通过Service的binder代理对象proxy调用Service方法。
系统服务与应用服务的注册是不同:
-
- 系统服务是系统启动时通过SystemServer注册并启动的,是主动注册。
- 应用服务是应用在获取Service的binder时,在AMS中没有对应Service的binder对象,由应用服务本身发布binder到AMS中,再由AMS将Service的binder代理对象回调给应用。应用服务是被动注册的。
三、系统服务与应用服务的使用
1. 获取系统服务
系统服务通过Context的getSystemService函数获取服务的对象。
val service = getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE) as ActivityManager
2. 获取应用服务binder
通过ServiceConnection回调返回binder代理对象。
public interface ServiceConnection { /** * Called when a connection to the Service has been established, with * the {@link android.os.IBinder} of the communication channel to the * Service. * * <p class="note"><b>Note:</b> If the system has started to bind your * client app to a service, it's possible that your app will never receive * this callback. Your app won't receive a callback if there's an issue with * the service, such as the service crashing while being created. * * @param name The concrete component name of the service that has * been connected. * * @param service The IBinder of the Service's communication channel, * which you can now make calls on. */ void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service); /** * Called when a connection to the Service has been lost. This typically * happens when the process hosting the service has crashed or been killed. * This does <em>not</em> remove the ServiceConnection itself -- this * binding to the service will remain active, and you will receive a call * to {@link #onServiceConnected} when the Service is next running. * * @param name The concrete component name of the service whose * connection has been lost. */ void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name); /** * Called when the binding to this connection is dead. This means the * interface will never receive another connection. The application will * need to unbind and rebind the connection to activate it again. This may * happen, for example, if the application hosting the service it is bound to * has been updated. * * @param name The concrete component name of the service whose * connection is dead. */ default void onBindingDied(ComponentName name) { } /** * Called when the service being bound has returned {@code null} from its * {@link android.app.Service#onBind(Intent) onBind()} method. This indicates * that the attempting service binding represented by this ServiceConnection * will never become usable. * * <p class="note">The app which requested the binding must still call * {@link Context#unbindService(ServiceConnection)} to release the tracking * resources associated with this ServiceConnection even if this callback was * invoked following {@link Context#bindService Context.bindService() bindService()}. * * @param name The concrete component name of the service whose binding * has been rejected by the Service implementation. */ default void onNullBinding(ComponentName name) { } }