1. 什么是注解?
Java注解又被称为标注,是JDK 1.5 引入的一种注释机制。
Java源码的类、方法、参数、变量等前的一种特殊“注释”。
Java语言中类、方法、变量、参数和包等可以被标注。
注解就是用作标注的“元数据”。
和Javadoc不同,Java标注分为运行时和编译时两个实现。
运行时:Java标注在运行时可以通过反射获取标注内容。
编译时:Java标注在编译生成类文件时,标注可以被嵌入到字节码中,Java虚拟机可以保留标注内容,在运行时可以获取到标注内容。
PS:注解不会影响代码正常逻辑执行。
2. 注解本质
java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口中是这样描述注解:所有的注解类型都继承于Annotation接口。
3. 注解的好处
- 保存于class文件中,降低维护成本。
- 无需工具支持,无需解析。
- 编译期即可验证正确性,查错变得容易。
- 提升开发效率。
4. 注解实现
1. 什么是元注解?
元注解:用于修饰注解的注解,通常用在注解的定义上。
- @target:作用于注解的目标,标记这个应用作用于哪些Java成员,包括:类、方法、参数、变量、包等。
- Retention:注解的生命周期,标记这个注解什么时保存,1. 保存于代码中;2. 保存于编译生成class文件中;3. 保存于运行时通过反射访问。
- Documented:注解是否被包含在Javadoc文档中。
- @Inherited:是否允许子类继承该注解。
Java中@Override注解实现:
/** * Indicates that a method declaration is intended to override a * method declaration in a supertype. If a method is annotated with * this annotation type compilers are required to generate an error * message unless at least one of the following conditions hold: * * <ul><li> * The method does override or implement a method declared in a * supertype. * </li><li> * The method has a signature that is override-equivalent to that of * any public method declared in {@linkplain Object}. * </li></ul> * * @author Peter von der Ahé * @author Joshua Bloch * @jls 9.6.1.4 @Override * @since 1.5 */ @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface Override { }
编译后:
public interface Override extends Annotation{ }
注解本质就是一个继承了Annotation的接口。
注解其实就是一个特殊的注释,如果不解析它的代码,注解就没有任何作用。
2. 元注解的实现
@Target:
源码:
/** * Indicates the contexts in which an annotation type is applicable. The * declaration contexts and type contexts in which an annotation type may be * applicable are specified in JLS 9.6.4.1, and denoted in source code by enum * constants of {@link ElementType java.lang.annotation.ElementType}. * * <p>If an {@code @Target} meta-annotation is not present on an annotation type * {@code T} , then an annotation of type {@code T} may be written as a * modifier for any declaration except a type parameter declaration. * * <p>If an {@code @Target} meta-annotation is present, the compiler will enforce * the usage restrictions indicated by {@code ElementType} * enum constants, in line with JLS 9.7.4. * * <p>For example, this {@code @Target} meta-annotation indicates that the * declared type is itself a meta-annotation type. It can only be used on * annotation type declarations: * <pre> * @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) * public @interface MetaAnnotationType { * ... * } * </pre> * * <p>This {@code @Target} meta-annotation indicates that the declared type is * intended solely for use as a member type in complex annotation type * declarations. It cannot be used to annotate anything directly: * <pre> * @Target({}) * public @interface MemberType { * ... * } * </pre> * * <p>It is a compile-time error for a single {@code ElementType} constant to * appear more than once in an {@code @Target} annotation. For example, the * following {@code @Target} meta-annotation is illegal: * <pre> * @Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD}) * public @interface Bogus { * ... * } * </pre> * * @since 1.5 * @jls 9.6.4.1 @Target * @jls 9.7.4 Where Annotations May Appear */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Target { /** * Returns an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type * can be applied to. * @return an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type * can be applied to */ ElementType[] value(); }
元注解Target作用就是注解作用于谁,指明注解修改的是类、方法、变量或者参数等等。
Target的元素类型:
/** * The constants of this enumerated type provide a simple classification of the * syntactic locations where annotations may appear in a Java program. These * constants are used in {@link Target java.lang.annotation.Target} * meta-annotations to specify where it is legal to write annotations of a * given type. * * <p>The syntactic locations where annotations may appear are split into * <em>declaration contexts</em> , where annotations apply to declarations, and * <em>type contexts</em> , where annotations apply to types used in * declarations and expressions. * * <p>The constants {@link #ANNOTATION_TYPE} , {@link #CONSTRUCTOR} , {@link * #FIELD} , {@link #LOCAL_VARIABLE} , {@link #METHOD} , {@link #PACKAGE} , * {@link #PARAMETER} , {@link #TYPE} , and {@link #TYPE_PARAMETER} correspond * to the declaration contexts in JLS 9.6.4.1. * * <p>For example, an annotation whose type is meta-annotated with * {@code @Target(ElementType.FIELD)} may only be written as a modifier for a * field declaration. * * <p>The constant {@link #TYPE_USE} corresponds to the 15 type contexts in JLS * 4.11, as well as to two declaration contexts: type declarations (including * annotation type declarations) and type parameter declarations. * * <p>For example, an annotation whose type is meta-annotated with * {@code @Target(ElementType.TYPE_USE)} may be written on the type of a field * (or within the type of the field, if it is a nested, parameterized, or array * type), and may also appear as a modifier for, say, a class declaration. * * <p>The {@code TYPE_USE} constant includes type declarations and type * parameter declarations as a convenience for designers of type checkers which * give semantics to annotation types. For example, if the annotation type * {@code NonNull} is meta-annotated with * {@code @Target(ElementType.TYPE_USE)}, then {@code @NonNull} * {@code class C {...}} could be treated by a type checker as indicating that * all variables of class {@code C} are non-null, while still allowing * variables of other classes to be non-null or not non-null based on whether * {@code @NonNull} appears at the variable's declaration. * * @author Joshua Bloch * @since 1.5 * @jls 9.6.4.1 @Target * @jls 4.1 The Kinds of Types and Values */ public enum ElementType { /** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */ TYPE, /** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */ FIELD, /** Method declaration */ METHOD, /** Formal parameter declaration */ PARAMETER, /** Constructor declaration */ CONSTRUCTOR, /** Local variable declaration */ LOCAL_VARIABLE, /** Annotation type declaration */ ANNOTATION_TYPE, /** Package declaration */ PACKAGE, /** * Type parameter declaration * * @since 1.8 */ TYPE_PARAMETER, /** * Use of a type * * @since 1.8 */ TYPE_USE }
-
- ElementType.Type:允许被修饰的注解作用于类、接口、枚举上。
- ElementType.FIELD:允许作用于属性上。
- ElementType.METHOD:允许作用于方法上。
- ElementType.PARAMETER:允许作用于参数上。
- ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR:允许作用于构造函数上。
- ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE:允许作用于本地局部变量上。
- ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE:允许作用于注解上。
- ElementType.PACKAGE:允许作用于包上。
示例:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention:作用指明注解的生命周期。
/** * Annotation retention policy. The constants of this enumerated type * describe the various policies for retaining annotations. They are used * in conjunction with the {@link Retention} meta-annotation type to specify * how long annotations are to be retained. * * @author Joshua Bloch * @since 1.5 */ public enum RetentionPolicy { /** * Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler. */ SOURCE, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler * but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default * behavior. */ CLASS, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and * retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively. * * @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement */ RUNTIME }
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:当前注解编译期可见,但不会写入class文件。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS:类加载阶段丢弃,会写入class文件。
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:永久保存,运行时可以通过反射获取。
示例:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
5. Java 内置三大注解
- @Override
- @Deprecated
- @SuppressWarnings
6. 注解处理机制及原理
1. 运行时通过反射获取注解内容元数据
@URIParse
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(value = {ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE}) public @interface URIParse { String value() default ""; }
通过反射获取注解内容:
import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class AnnotationParse { public static void annotation(Object target) { try { Class<?> forName = Class.forName(target.getClass().getName()); for (Field field : forName.getDeclaredFields()) { if (field.isAnnotationPresent(URIParse.class)) { field.setAccessible(true); field.set(target, field.getAnnotation(URIParse.class).value()); } } } catch (ClassNotFoundException | IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2. 编译时注解处理器(Annotation Processor:注解处理器)
什么是注解处理器?
注解处理器是javac的一个工具,用于在编译时扫描和处理注解(Annotation)。
编译时注解处理器处理流程:
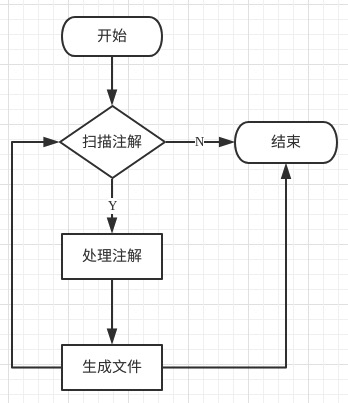
@RDateFormat
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.CLASS) @Target(value = {ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE}) public @interface RDateFormat { String value() default ""; String format() default ""; }
注解处理器:
import javax.annotation.processing.*; import javax.lang.model.SourceVersion; import javax.lang.model.element.Element; import javax.lang.model.element.TypeElement; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.Set; public class RDateFormatProcessor extends AbstractProcessor { /** * If the processor class is annotated with {@link * SupportedOptions}, return an unmodifiable set with the same set * of strings as the annotation. If the class is not so * annotated, an empty set is returned. * * 自定义参数给注解处理器。 * * @return the options recognized by this processor, or an empty * set if none */ @Override public Set<String> getSupportedOptions() { return super.getSupportedOptions(); } /** * Initializes the processor with the processing environment by * setting the {@code processingEnv} field to the value of the * {@code processingEnv} argument. An {@code * IllegalStateException} will be thrown if this method is called * more than once on the same object. * * @param processingEnv environment to access facilities the tool framework * provides to the processor * @throws IllegalStateException if this method is called more than once. */ @Override public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv) { super.init(processingEnv); } /** * 这相当于每个处理器的主函数main(),你在这里写你的扫描、评估和处理注解的代码,以及生成Java文件。 * 输入参数RoundEnviroment,可以让你查询出包含特定注解的被注解元素 * * @param annotations 请求处理的注解类型 * @param roundEnv 有关当前和以前的信息环境 * @return 如果返回 true,则这些注解已声明并且不要求后续 Processor 处理它们; * 如果返回 false,则这些注解未声明并且可能要求后续 Processor 处理它们 */ @Override public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) { for (Element element : roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(RDateFormat.class)) { System.out.println(element.getEnclosingElement().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(element.getEnclosingElement().getEnclosingElement().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(element.getEnclosingElement().getEnclosingElement().getEnclosingElement().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(element.getEnclosingElement().getEnclosingElement().getEnclosingElement().getEnclosingElement()); } return false; } /** * If the processor class is annotated with {@link * SupportedAnnotationTypes}, return an unmodifiable set with the * same set of strings as the annotation. If the class is not so * annotated, an empty set is returned. * * 这个方法必须覆写,用于指定注解是属于哪个注解处理器的,用于注解注册,返回一个注册的注解集合。 * * @return the names of the annotation types supported by this * processor, or an empty set if none */ @Override public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes() { Set<String> annotations = new LinkedHashSet<>(); annotations.add(RDateFormat.class.getCanonicalName()); return annotations; } /** * If the processor class is annotated with {@link * SupportedSourceVersion}, return the source version in the * annotation. If the class is not so annotated, {@link * SourceVersion#RELEASE_6} is returned. * * 返回JDK版本 * * @return the latest source version supported by this processor */ @Override public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() { return SourceVersion.latestSupported(); } }
示例使用的是Java自带注解处理器,Google提供的注解处理器:com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc3