一、context的理解
很多优秀的React组件都通过Context来完成自己的功能,比如react-redux的<Provider />,就是通过Context提供一个全局态的store,拖拽组件react-dnd,通过Context在组件中分发DOM的Drag和Drop事件,路由组件react-router通过Context管理路由状态等等。在React组件开发中,如果用好Context,可以让你的组件变得强大,而且灵活
当你不想在组件树中通过逐层传递props或者state的方式来传递数据时,可以使用Context来实现跨层级的组件数据传递
使用context可以实现跨组件传递
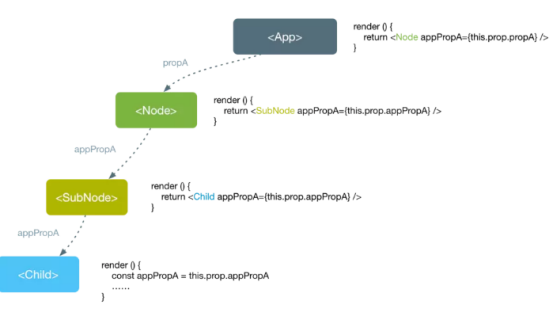
二、如何使用context
如果要Context发挥作用,需要用到两种组件,一个是Context生产者(Provider),通常是一个父节点,另外是一个Context的消费者(Consumer),通常是一个或者多个子节点。所以Context的使用基于生产者消费者模式。
对于父组件,也就是Context生产者,需要通过一个静态属性childContextTypes声明提供给子组件的Context对象的属性,并实现一个实例getChildContext方法,返回一个代表Context的对象
1、getChildContext 根组件中声明,一个函数,返回一个对象,就是context
2、childContextTypes 根组件中声明,指定context的结构类型,如不指定,会产生错误
3、contextTypes 子孙组件中声明,指定要接收的context的结构类型,可以只是context的一部分结构。contextTypes 没有定义,context将是一个空对象。
4、this.context 在子孙组件中通过此来获取上下文
三、代码演示
目录结构
src/app.js
src/index.js
src/components/one.js
src/components/two.js
src/components/three.js
1、app.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import One from "./components/one";
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
class App extends Component {
//根组件中声明,指定context的结构类型,如不指定,会产生错误
static childContextTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string,
age:PropTypes.number,
}
//根组件中声明,一个函数,返回一个对象,就是context
getChildContext(){
return {
name:"zhangsan",
age:18,
}
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<One/>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
2、one.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Two from "./two";
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
export default class One extends Component {
/*
contextTypes 子孙组件中声明,指定要接收的context的结构类型,
contextTypes 没有定义,context将是一个空对象。
*/
static contextTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string,
age:PropTypes.number
}
render() {
console.log(this)
return (
<div>
<Two/>
</div>
)
}
}
3、two.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Three from "./three";
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
export default class Two extends Component {
static contextTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string,
age:PropTypes.number
}
render() {
console.log(this)
return (
<div>
<Three/>
</div>
)
}
}
4、three.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
export default class Three extends Component {
static contextTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string,
age:PropTypes.number
}
render() {
console.log(this)
return (
<div>
</div>
)
}
}
5、结果

四、总结
1、context在如下的生命周期钩子中可以使用
constructor(props, context)
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, nextContext)
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext)
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext)
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, prevContext)
2、context的局限性
1. 在组件树中,如果中间某一个组件 ShouldComponentUpdate return false 了,会阻 碍 context 的正常传值,导致子组件无法获取更新。
2. 组件本身 extends React.PureComponent 也会阻碍 context 的更新。