在Android的触摸消息中,已经实现了三种监测,它们分别是
1)pre-pressed:对应的语义是用户轻触(tap)了屏幕
2)pressed:对应的语义是用户点击(press)了屏幕
3)long pressed:对应的语义是用户长按(long press)了屏幕
下图是触摸消息随时间变化的时间轴示意图:
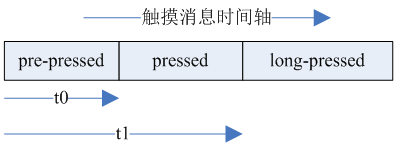
其中,t0和t1定义在ViewConfiguration类中,标识了tap和longpress的超时时间,定义如下:
- /**
- * Defines the duration in milliseconds we will wait to see if a touch event
- * is a tap or a scroll. If the user does not move within this interval, it is
- * considered to be a tap.
- */
- private static final int TAP_TIMEOUT = 115; // t0
- /**
- * Defines the duration in milliseconds before a press turns into
- * a long press
- */
- private static final int LONG_PRESS_TIMEOUT = 500; // t1
- case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
- if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
- mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
- }
- mPrivateFlags |= PREPRESSED;
- mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
- postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
- break;
- case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
- boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PREPRESSED) != 0; //获取prepressed状态
- if ((mPrivateFlags & PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) { //如果是pressed状态或者是prepressed状态,才进行处理
- // 如果当前view不具有焦点,则需要先获取焦点,因为我们当前处理触摸模式
- boolean focusTaken = false;
- if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
- focusTaken = requestFocus(); // 请求获得焦点
- }
- if (!mHasPerformedLongPress) { // 是否处理过长按操作了,如果是,则直接返回
- // 进入该代码段,说明这是一个tap操作,首先移除长按回调操作
- removeLongPressCallback();
- // Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
- if (!focusTaken) {
- // Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
- // performClick directly. This lets other visual state
- // of the view update before click actions start.
- if (mPerformClick == null) {
- mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
- }
- if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
- performClick(); // 执行点击的处理函数
- }
- }
- }
- if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
- mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
- }
- if (prepressed) {
- mPrivateFlags |= PRESSED;
- refreshDrawableState();
- // 发送重置触摸状态的异步延迟消息
- postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
- ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
- } else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
- // If the post failed, unpress right now
- mUnsetPressedState.run();
- }
- removeTapCallback(); // 移除tap的回调操作
- }
- break;
1)PostDelayed函数
该函数的主要工作是获取UI线程的Handler对象,然后调用Handler类的postDelayed函数将指定的Runnable对象放到消息队列中。
- public boolean postDelayed(Runnable action, long delayMillis) {
- Handler handler;
- if (mAttachInfo != null) {
- handler = mAttachInfo.mHandler;
- } else {
- // Assume that post will succeed later
- ViewRoot.getRunQueue().postDelayed(action, delayMillis);
- return true;
- }
- return handler.postDelayed(action, delayMillis);
- }
2)CheckForTap类
该类实现了Runnable接口,在run函数中设置触摸标识,并刷新Drawable的状态,同时用于发送一个检测长按事件的异步延迟消息,代码如下:
- private final class CheckForTap implements Runnable {
- public void run() {
- // 进入该函数,说明已经过了ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout()时间,
- // 即pre-pressed状态结束,宣告触摸进入pressed状态
- mPrivateFlags &= ~PREPRESSED;
- mPrivateFlags |= PRESSED;
- refreshDrawableState(); // 刷新控件的背景Drawable
- // 如果长按检测没有被去使能,则发送一个检测长按事件的异步延迟消息
- if ((mViewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) {
- postCheckForLongClick(ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
- }
- }
- }
- private void postCheckForLongClick(int delayOffset) {
- mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
- // 实例化CheckForLongPress对象
- if (mPendingCheckForLongPress == null) {
- mPendingCheckForLongPress = new CheckForLongPress();
- }
- mPendingCheckForLongPress.rememberWindowAttachCount();
- // 调用PostDelayed函数发送长按事件的异步延迟消息
- postDelayed(mPendingCheckForLongPress,
- ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout() - delayOffset);
- }
3)CheckForLongPress类
该类定义了长按操作发生时的响应处理,同样实现了Runnable接口
- class CheckForLongPress implements Runnable {
- private int mOriginalWindowAttachCount;
- public void run() {
- // 进入该函数,说明检测到了长按操作
- if (isPressed() && (mParent != null)
- && mOriginalWindowAttachCount == mWindowAttachCount) {
- if (performLongClick()) {
- mHasPerformedLongPress = true;
- }
- }
- }
- public void rememberWindowAttachCount() {
- mOriginalWindowAttachCount = mWindowAttachCount;
- }
- }
- public boolean performLongClick() {
- sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_LONG_CLICKED);
- boolean handled = false;
- if (mOnLongClickListener != null) {
- // 回调用户实现的长按操作监听函数(OnLongClickListener)
- handled = mOnLongClickListener.onLongClick(View.this);
- }
- if (!handled) {
- // 如果OnLongClickListener的onLongClick返回false
- // 则需要继续处理该长按事件,这里是显示上下文菜单
- handled = showContextMenu();
- }
- if (handled) {
- // 长按操作事件被处理了,此时应该给用户触觉上的反馈
- performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS);
- }
- return handled;
- }