Java环境下shiro的测试
1.导入依赖的核心jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
2.认证程序
2.1 构建users配置文件 xxx.ini doGetAuthenticationInfo方法从该配置文件中获取数据与token中比对
[users]
test=123456
lisi=123456
测试程序
public class TestShiro {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取安全管理器工厂
IniSecurityManagerFactory iniSecurityManagerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//获取安全管理器
SecurityManager securityManager = iniSecurityManagerFactory.getInstance();
//set认证器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//subject发起认证,获取subject
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
AuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("test","123456");
//认证失败会抛出异常 密码:CredentialsException 账户:UnknownAccountException
try {
subject.login(authenticationToken);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//当前subject是否认证通过
boolean authenticated = subject.isAuthenticated();
System.out.println(authenticated);
}
}
认证流程:
token携带身份和凭证信息--->subject发起认证--->SimpleAccountRealm(doGetAuthenticationInfo)获取配置文件中的用户信息---->CredentialsMatcher接口的实现类SimpleCredentialsMatcher:doCredentialsMatch方法对配置文件中的信息与token携带的信息进行比对--->认证成功或者失败。
3.Shiro框架中的关键对象:
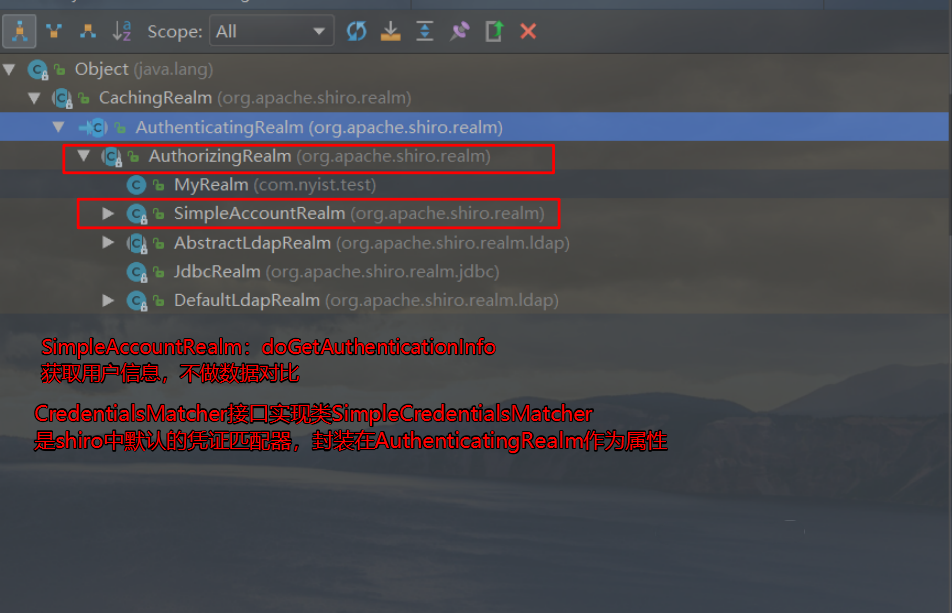
AuthenticatingRealm //抽象类
//3.关键属性 该属性为凭证匹配器
CredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher;
//1.该方法为抽象方法 其作用使用来获取数据
protected abstract AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken var1) throws AuthenticationException;
SimpleAccountRealm
//2.实现了AuthenticatingRealm抽象方法,用来获取配置文件中的用户信息,该类不做数据比对
SimpleCredentialsMatcher
//4.shiro中默认的凭证匹配器
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
Object tokenCredentials = this.getCredentials(token);
Object accountCredentials = this.getCredentials(info);
return this.equals(tokenCredentials, accountCredentials);
}
必须要知道的类与接口,不然很难理解自定义Realm时属性为什么设置,使用哪种实现类方法等等:
以下代码或者截图贴出最重要的地方.
类继承关系

AuthenticatingRealm类
abstract class AuthenticatingRealm{
//凭证匹配器 接口,其实现类做数据比对
private CredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher;
//获取配置文件中的用户信息
protected abstract AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken var1) throws AuthenticationException;
}
该抽象方法返回类型AuthenticationInfo接口:

AuthorizingRealm类 抽象方法后面测试授权时使用
abstract class AuthorizingRealm{
//
//该抽象方法 获取数据 获取授权的数据
protected abstract AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection var1);
}
该抽象方法返回类型AuthorizationInfo接口:

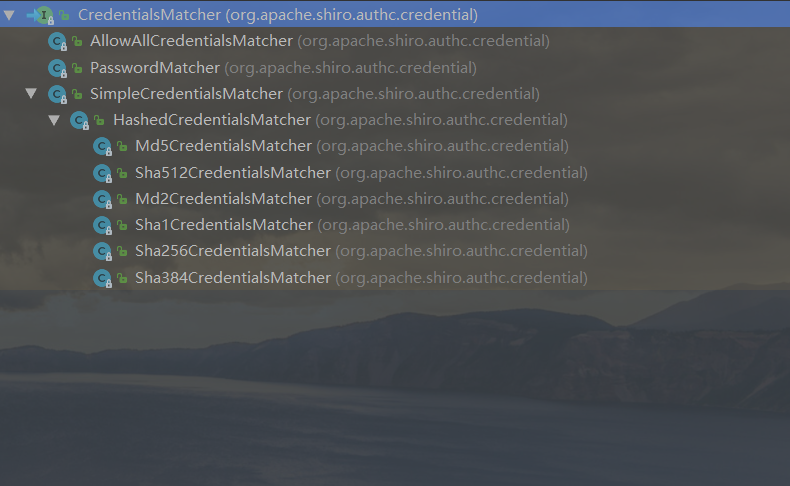
CredentialsMatcher凭证匹配器接口:
其中:SimpleCredentialsMatcher是shiro中默认的凭证匹配器,其子类Hashxxx等都是做加密认证时使用

4.开发自定义Realm
public class MyRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm {
//实现抽象方法doGetAuthenticationInfo
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException {
String principal =(String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
//查库取回User对象
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MySqlSession.getSqlSession();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.queryUserByUserName(principal);
AuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,user.getPassword(),this.getName());
return authenticationInfo;
}
}
4.1通知shiro使用自定义realm
[main]
#自定义 realm
customRealm=com.nyist.test.MyRealm
#将realm设置到securityManager
securityManager.realms=$customRealm
注意:需要导入一个jar
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
5.shiro的加密认证方式
5.1.使用shiro提供的Md5Hash类为一个字符串加密进行测试
public class TestMD5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Md5Hash hash = new Md5Hash("123456","salt",1024);
String s = hash.toHex();
System.out.println(s);
//a18d2133f593d7b0e3ed488560404083
}
}
5.2.修改配置文件,加入凭证匹配器的相关配置
[main]
#自定义凭证匹配器
hashedCredentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher
#凭证匹配器通知AuthenticatingRealm,由于自定义realm继承了AuthenticatingRealm,直接设置已有的MyRealm属性即可
#自定义 realm
customRealm=com.nyist.test.MyRealm
customRealm.credentialsMatcher=$hashedCredentialsMatcher
hashedCredentialsMatcher.hashAlgorithmName=MD5
hashedCredentialsMatcher.hashIterations=1024
#将realm设置到securityManager .realms使用set方式赋值
securityManager.realms=$customRealm
坑:Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Required 'hashAlgorithmName' property has not been set. This is required to execute the hashing algorithm.
HashedCredentialsMatcher类中set方法非常规,set方法为:setHashAlgorithmName
为什么这么设置凭证匹配器?
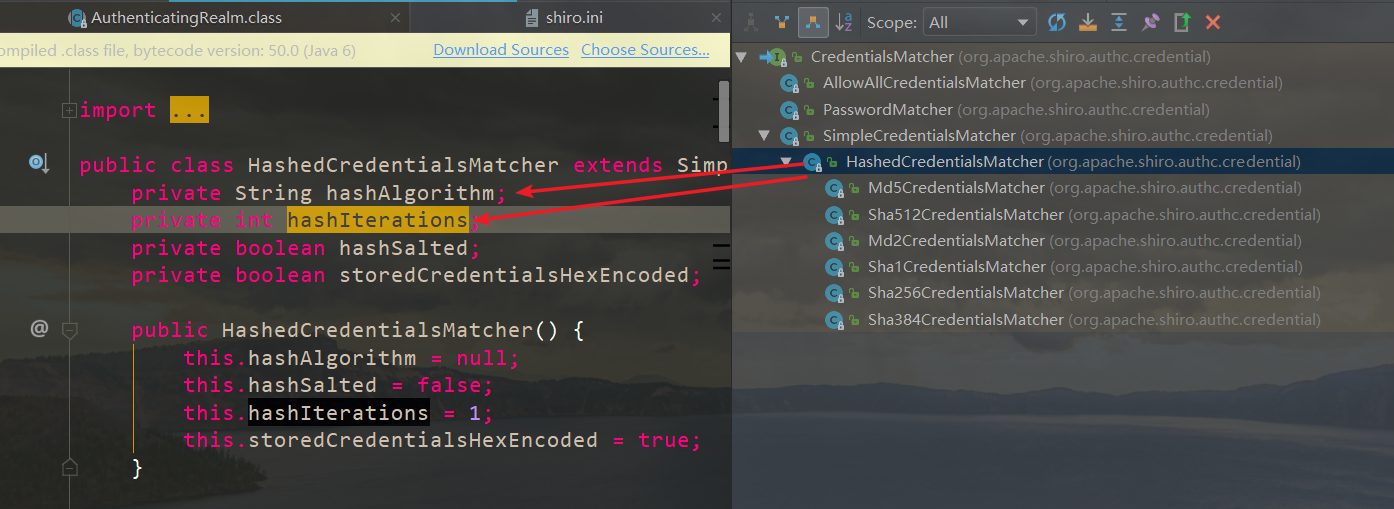

自定义MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm,实现两个抽象方法
AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo()来自于AuthenticatingRealm类,获取认证数据
AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo()来自于AuthorizingRealm类,获取授权数据
public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException {
String principal =(String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
//userDao.queryUserByUserName
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MySqlSession.getSqlSession();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.queryUserByUserName(principal);
/*
* ByteSource.Util.bytes("salt") 盐字段来自数据库,凭证匹配器不能写死盐值
* 安全管理器可以获取到AuthenticationInfo中的盐值 对用户界面的凭证加密
* */
AuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,user.getPassword(),ByteSource.Util.bytes("salt"),this.getName());
return authenticationInfo;
}
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//获取身份信息 Principal用户名、手机号、邮箱地址等 一个主体可以有多个身份,但是必须有一个主身份(Primary Principal)
String primaryPrincipal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
/*
* 用户----角色----权限
* 中间表 中间表
* */
//由primaryPrincipal查库--->获得角色info ---->获取权限info
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MySqlSession.getSqlSession();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.queryUserByUserName(primaryPrincipal);
//测试基于角色的授权
/*if (primaryPrincipal.equals(user.getUsername())){
// class SimpleAuthorizationInfo implements AuthorizationInfo
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
authorizationInfo.addRole("super");
return authorizationInfo;
}*/
//测试基于资源的授权
if(primaryPrincipal.equals(user.getUsername())){
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:delete");
authorizationInfo.addStringPermissions(Arrays.asList("admin:delete","admin:add"));
return authorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}
一张图看懂认证授权关系:

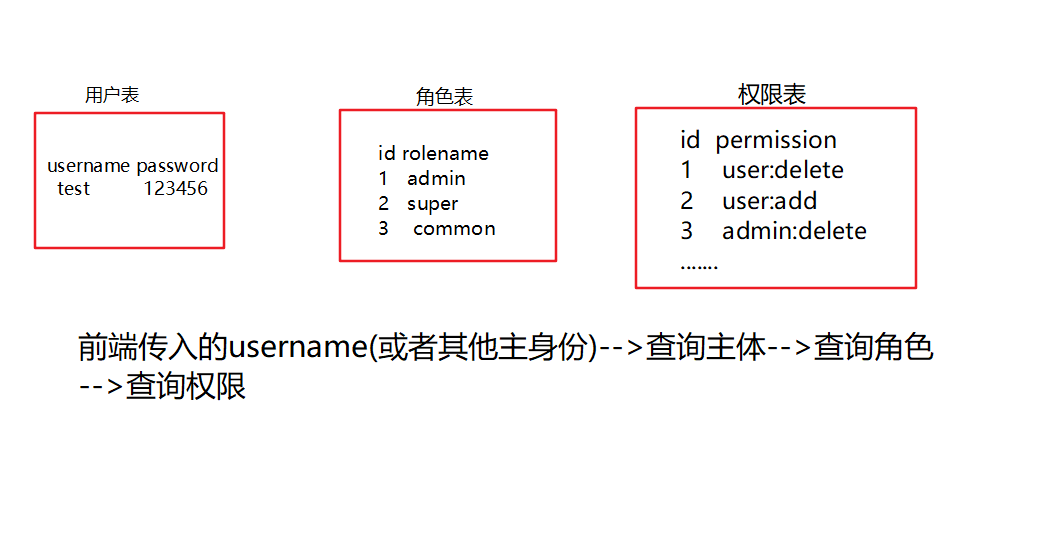

授权的api
-
基于角色
//判断当前主体是否包含此角色 boolean b = subject.hasRole("super"); List<String> list = Arrays.asList("super", "admin"); //判断当前主体是否包含某个角色 boolean[] booleans = subject.hasRoles(list); //判断当前主体是否包含全部的角色 boolean b = subject.hasAllRoles(list); -
基于资源
boolean b = subject.isPermitted("admin:delete"); String[] strs={"admin:delete", "admin:add"}; boolean[] permitted = subject.isPermitted(strs); boolean permittedAll = subject.isPermittedAll(strs);
资源权限的标识符
权限字符串的规则是:“资源标识符:操作:资源实例标识符”,意思是对哪个资源的哪个实例具有什么操作,“:”是资源/操作/实例的分割符,权限字符串也可以使用*通配符。
例子:
- 用户创建权限:user:create,或user:create:*
- 用户修改实例001的权限:user:update:001
- 用户实例001的所有权限:user:*:001