Spring Boot 和 ASP.NET Core 都是企业中流行的 Web 框架, 对于喜欢 C# 的人会使用 ASP.NET Core, 而对于 Java 或 Kotlin 等基于 JVM 的语言,Spring Boot 是最受欢迎的。
这本文中,会对比这两个框架在以下方面有何不同:
- 控制器
- 模型绑定和验证
- 异常处理
- 数据访问
- 依赖注入
- 认证与授权
- 性能
基础项目
这是一个有关订单的基础项目, 非常简单的后端 api, 客户可以创建一个订单来购买一个或多个产品, 我使用了 MySQL 作为数据库,下面是实体关系图。
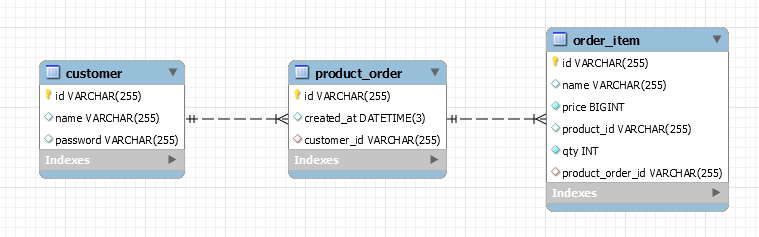
这里使用的框架版本分别是, Spring Boot (v2.5.5) 和 .NET 6, 让我们开始对比吧!
1.控制器
控制器是负责处理传入请求的层, 为了在 Spring Boot 中定义一个控制器,我创建了一个类 ProductOrderController, 然后使用了 @RestController 和 @RequestMapping 注解, 然后在控制器的每个方法上, 可以使用下面的注解来定义支持的 HTTP 方法和路径(可选)。
- @GetMapping
- @PostMapping
- @PutMapping
- @DeleteMapping
- @PatchMapping
如果要绑定到路径变量, 我们可以将参数添加到用@PathVariable 注释的控制器方法中,并指定与参数同名的路由路径模板,下面的 getOrderById() 方法,我们将id绑定为路径变量。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v1/orders")
class ProductOrderController(
private val productOrderService: IProductOrderService
) {
@GetMapping
fun getOrders(query: ProductOrderQuery): List<ProductOrderDto> = when {
query.productId?.isNotEmpty() == true -> productOrderService.getByProductId(query.productId!!)
query.customerId?.isNotEmpty() == true -> productOrderService.getByCustomerId(query.customerId!!)
else -> productOrderService.getAllOrders()
}
@GetMapping("{id}")
fun getOrderById(@PathVariable id: String): ProductOrderDto = productOrderService.getById(id)
}
在 .NET Core 中, 控制器和上面是相似的, 首先创建一个 ProductOrderController类, 并继承 ControllerBase ,标记 [ApiController] 特性, 然后通过 [Route] 特性指定基本路径, 然后在控制器的每个方法上, 可以使用下面的特性来定义支持的 HTTP 方法和路径(可选)。
[ApiController]
[Route("v1/orders")]
public class ProductOrderController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IProductOrderService _productOrderService;
public ProductOrderController(IProductOrderService productOrderService)
{
_productOrderService = productOrderService;
}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<List<ProductOrderDto>> GetOrders([FromQuery] ProductOrderQuery query)
{
List<ProductOrderDto> orders;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(query.ProductId))
{
orders = await _productOrderService.GetAllByProductId(query.ProductId);
}
else if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(query.CustomerId))
{
orders = await _productOrderService.GetAllByCustomerId(query.CustomerId);
}
else
{
orders = await _productOrderService.GetAll();
}
return orders;
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ProductOrderDto> GetOrderById(string id) => await _productOrderService.GetById(id);
}
模型绑定和验证
在 Spring Boot 中, 我们只需要给控制器的方法的参数加上下面的注解
- @RequestParam → 从查询字符串绑定
- @RequestBody → 从请求体绑定
- @RequestHeader → 从请求头绑定
对比表单的请求,不需要给参数加注解就可以绑定。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v1/customer")
class CustomerController(
private val customerService: CustomerService
) {
@PostMapping("/register")
fun register(@Valid @RequestBody form: RegisterForm) = customerService.register(form)
@PostMapping("/login")
fun login(@Valid @RequestBody form: LoginForm) = customerService.login(form)
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v1/orders")
class ProductOrderController(
private val productOrderService: IProductOrderService
) {
@GetMapping
fun getOrders(query: ProductOrderQuery): List<ProductOrderDto> {
...
}
}
如果要对参数进行验证, 需要添加 spring-boot-starter-validation 依赖项, 然后给 DTO 的属性加上 @NotEmpty、@Length 等注解, 最后给DTO加上 @Valid 即可。
.NET Core 和上面类似, 同样你可以使用下面的特性标记控制器的方法
- [FromQuery] → 从查询字符串绑定
- [FromRoute] → 从路由数据绑定
- [FromForm] → 从表单数据绑定
- [FromBody] → 从请求体绑定
- [FromHeader] → 从请求头绑定
[Route("v1/customer")]
[ApiController]
public class CustomerController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpPost("register")]
public async Task<AuthResultDto> Register([FromBody] RegisterForm form) => await _customerService.Register(form);
[HttpPost("login")]
public async Task<AuthResultDto> Login([FromBody] LoginForm form) => await _customerService.Login(form);
}
[Route("v1/orders")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductOrderController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public async Task<List<ProductOrderDto>> GetOrders([FromQuery] ProductOrderQuery query)
{
.....
}
}
模型验证也是类似的, 给 DTO 的属性上加上 [Required]、[MinLength]、[MaxLength] 等特性就可以了。
public class RegisterForm
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please enter user id")]
public string UserId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please enter name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please enter password")]
[MinLength(6, ErrorMessage = "Password must have minimum of 6 characters")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
异常处理
Spring Boot 的异常处理,主要用 @RestControllerAdvice 和 ExceptionHandler
注解,如下
abstract class AppException(message: String) : RuntimeException(message) {
abstract fun getResponse(): ResponseEntity<BaseResponseDto>
}
@RestControllerAdvice
class ControllerExceptionHandler : ResponseEntityExceptionHandler() {
@ExceptionHandler(AppException::class)
fun handleAppException(ex: AppException, handlerMethod: HandlerMethod): ResponseEntity<BaseResponseDto> {
return ex.getResponse()
}
}
在 ASP.NET Core 中,异常处理程序被注册为过滤器/中间件,我们可以创建一个异常处理类,并继承 IExceptionFilter 接口。
public class ControllerExceptionFilter : IExceptionFilter
{
public void OnException(ExceptionContext context)
{
if (context.Exception is AppException exception)
{
context.Result = exception.GetResponse();
}
}
}
然后注册这个异常过滤器
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers(options =>
{
options.Filters.Add<ControllerExceptionFilter>();
});
数据访问
在 Spring Boot 中, 你可以使用 Hibernate ORM, 创建一个Repository 接口, 并继承 JpaRepository , 这样就有了开箱即用的基本查询方法,比如 findAll() 和 findById()。
您还可以在定义自定义查询方法。只要遵循严格的方法命名约定,Spring 就会构建这个存储库的实现,包括运行时的所有查询,魔法?是的!
interface IProductOrderRepository : JpaRepository<ProductOrder, String> {
@EntityGraph(type = EntityGraph.EntityGraphType.FETCH, value = "product-order-graph")
override fun findById(id: String): Optional<ProductOrder>
@EntityGraph(type = EntityGraph.EntityGraphType.FETCH, value = "product-order-graph")
fun findAllByCustomer(customer: Customer): List<ProductOrder>
@EntityGraph(type = EntityGraph.EntityGraphType.FETCH, value = "product-order-graph")
@Query("SELECT ord FROM ProductOrder ord JOIN OrderItem item ON item.productOrder = ord WHERE item.productId = :productId")
fun findAllByProductId(productId: String): List<ProductOrder>
}
而在 .NET Core 中,我们可以使用官方的 Entity Framework ORM, 首先,我们需要创建一个 DB Context 类, 这是 ORM 框架用来连接数据库和运行查询的桥梁。
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Customer> Customer { get; set; }
public DbSet<Product> Product { get; set; }
public DbSet<ProductOrder> ProductOrder { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrderItem> OrderItem { get; set; }
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options) : base(options)
{
Customer = Set<Customer>();
Product = Set<Product>();
ProductOrder = Set<ProductOrder>();
OrderItem = Set<OrderItem>();
}
}
接下来,还需要注册上面的 DB Context,并配置数据库连接字符串
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(options =>
{
// Using Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql library
options.UseMySql(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("EaterMysql"), ServerVersion.Parse("8.0.21-mysql"));
});
在我们的 Repository 中,我们访问 DB 上下文中的 DbSet 字段来执行查询, 在这里,我们使用 LINQ,这是一组直接融入 C# 语言的 API,用于从各种数据源进行查询。这是我非常喜欢的一项功能,因为它提供了 Fluent API,例如 Where()、Include() 或 OrderBy(),这非常方便!
public class ProductOrderRepository : BaseRepository<ProductOrder>, IProductOrderRepository
{
public ProductOrderRepository(AppDbContext context) : base(context)
{
}
public Task<ProductOrder?> GetById(string id) => _context.ProductOrder
.Include(o => o.Customer)
.Include(o => o.Items)
.Where(o => o.Id == id)
.FirstOrDefaultAsync();
public Task<List<ProductOrder>> GetAllByCustomer(Customer customer) => _context.ProductOrder
.Include(o => o.Items)
.Where(o => o.Customer == customer)
.ToListAsync();
public Task<List<ProductOrder>> GetAllByProductId(string productId) => _context.ProductOrder
.Include(o => o.Customer)
.Include(o => o.Items)
.Where(o => o.Items.Any(item => item.ProductId == productId))
.ToListAsync();
}
依赖注入
Spring Boot 中的依赖注入真的非常简单, 只需根据类的角色使用 @Component、@Service 或@Repository 等注解即可,在启动时,它会进行扫描,然后注册。
@Service
class ProductOrderService(
private val customerRepository: ICustomerRepository,
private val productOrderRepository: IProductOrderRepository,
private val mapper: IMapper
) : IProductOrderService {
// ...
// ...
// ...
}
在 .NET Core 中, 服务根据生命周期分成3中类型,单例的,范围的, 瞬时的,并且在启动时手动注册到 DI 容器中
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
// Services
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IPasswordEncoder, PasswordEncoder>();
builder.Services.AddSingleton<ITokenService, TokenService>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<IProductOrderService, ProductOrderService>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<ICustomerService, CustomerService>();
// Repositories
builder.Services.AddScoped<IProductOrderRepository, ProductOrderRepository>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<ICustomerRepository, CustomerRepository>();
身份验证和授权
在 Spring Boot 中, 首先需要添加依赖 spring-boot-starter-security, 然后,在 build.gradle 文件(或 pom.xml,如果您使用 Maven)中为 JWT 库添加以下依赖项:
implementation("io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-api:${jjwtVersion}")
implementation("io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-impl:${jjwtVersion}")
implementation("io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-jackson:${jjwtVersion}")
接下来, 需要创建一个负责 JWT 令牌解析和验证的过滤器/中间件, 然后重写 doFilterInternal 方法, 编写解析和验证逻辑。
class JwtAuthenticationFilter(
private val tokenService: ITokenService
) : OncePerRequestFilter() {
override fun doFilterInternal(
request: HttpServletRequest,
response: HttpServletResponse,
filterChain: FilterChain
) {
val authorization = request.getHeader("Authorization")
if (authorization == null || !authorization.startsWith("Bearer")) {
return filterChain.doFilter(request, response)
}
val token = authorization.replaceFirst("Bearer ", "")
val claims = try {
tokenService.parse(token).body
} catch (ex: JwtException) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext()
return
}
// Set authentication to tell Spring that the user is valid and authenticated.
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().authentication = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(claims.id, null, arrayListOf())
filterChain.doFilter(request, response)
}
}
要配置和强制执行身份验证,需要先创建一个继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的配置类,并使用 @Configuration 注解, 在这里注册我们上面创建的 JWT 过滤器,并在configure方法中配置哪些端点应该进行身份验证。比如,我允许匿名访问客户登录和注册端点。其他所有内容都应进行身份验证
class ApiAccessDeniedHandler : AccessDeniedHandler {
override fun handle(
request: HttpServletRequest,
response: HttpServletResponse,
accessDeniedException: AccessDeniedException
) {
response.status = HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value()
}
}
class AuthEntryPoint : AuthenticationEntryPoint {
override fun commence(
request: HttpServletRequest,
response: HttpServletResponse,
authException: AuthenticationException
) {
response.status = HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value()
}
}
@Configuration
class SecurityConfig(
tokenService: ITokenService
) : WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter() {
private val jwtAuthenticationFilter = JwtAuthenticationFilter(tokenService)
@Bean
fun passwordEncoder(): PasswordEncoder = BCryptPasswordEncoder()
override fun configure(http: HttpSecurity) {
http.csrf().disable().cors().disable()
.addFilterAfter(jwtAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter::class.java)
.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedHandler(ApiAccessDeniedHandler())
.authenticationEntryPoint(AuthEntryPoint())
.and()
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/v1/customer/register", "/v1/customer/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
}
}
在 ASP.NET Core 中实现 JWT 身份验证和授权非常简单, 首先安装Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer` NuGet 包, 然后,在 Program.cs 文件中配置一些设置,例如密钥、颁发者和到期时间。
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Configure JWT Authentication
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.SaveToken = true;
options.RequireHttpsMetadata = true;
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters()
{
ValidateAudience = false,
ValidIssuer = builder.Configuration["JWT:ValidIssuer"],
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(builder.Configuration["JWT:Secret"])),
ClockSkew = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30)
};
});
var app = builder.Build();
// Enable Authentication & Authorization
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
如果需要认证,就在控制或者方法上,加上 [Authorize] 特性, 同样,可以加上 [AllowAnonymous] 代表允许匿名访问。
[Route("v1/customer")]
[ApiController]
[Authorize]
public class CustomerController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpPost("login")]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<AuthResultDto> Login([FromBody] LoginForm form) => await _customerService.Login(form);
[HttpGet]
public async Task<CustomerDto> GetProfile() => await _customerService.GetProfile();
}
性能
最后是关键的部分,性能, 这两个框架在 QPS 和 内存使用率方面的表现如何?
在这里,我做了一个负载测试,调用一个 API,通过 id 获取一个产品订单。
测试环境
CPU:Intel Core i7–8750H( 4.10 GHz),6 核 12 线程
RAM:32 GB
操作系统:Windows 11
测试设置
我使用的压力测试工具是 K6, 进行了2次测试, 因为我想看看程序预热后性能提高了多少。在每次测试中,前 30 秒将从 0 增加到 1000 个虚拟用户,然后在那里停留 1 分钟。然后再过 30 秒,测试将从 1000 用户减少到 0 用户。
我还将 Golang(使用 Gin 框架和 Gorm)添加到基准测试, 这里只是为了对比 我们都知道 Golang 非常快。

测试结果
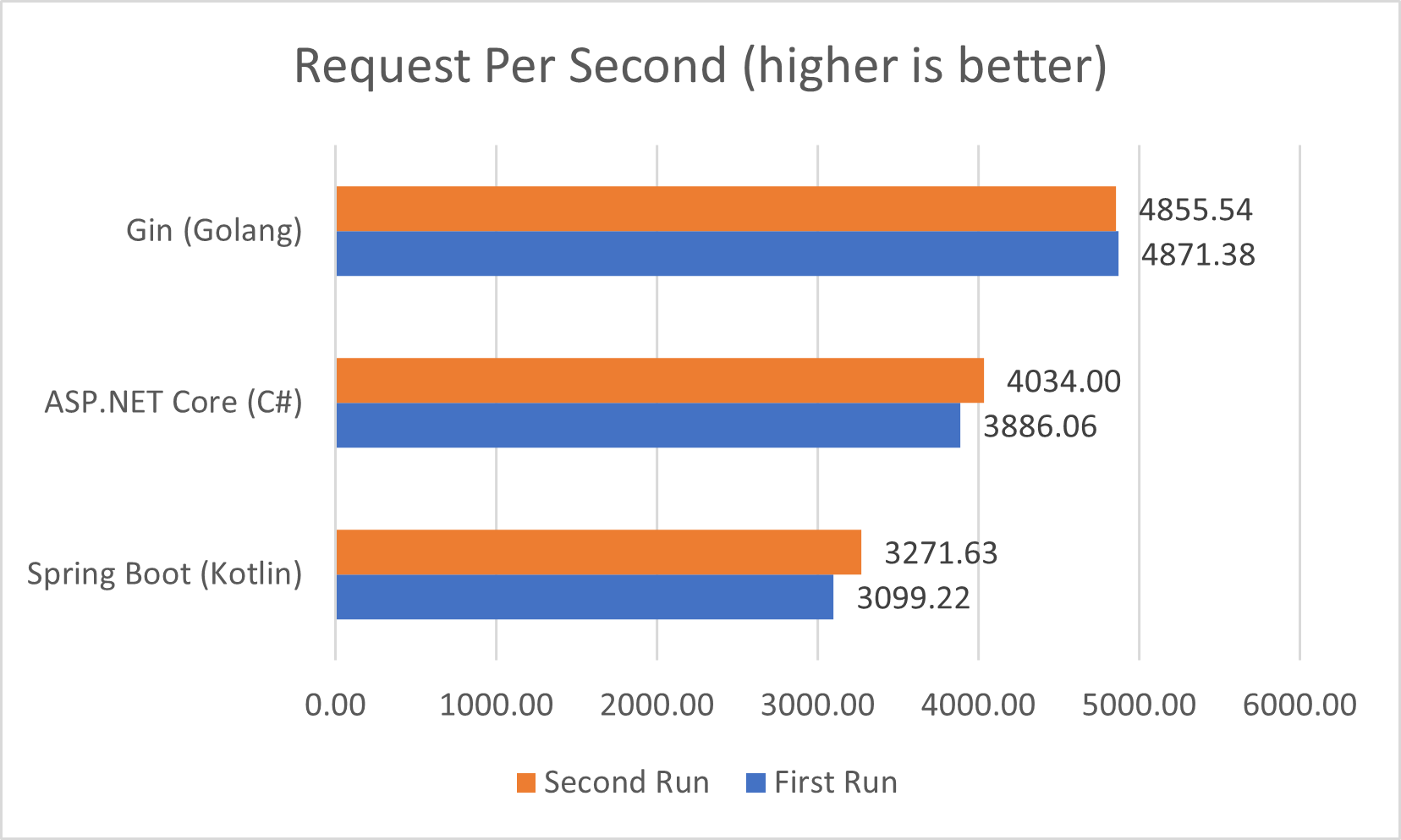
显然,Golang 是最快的,我检查了两者都执行了查询优化,确认没有 N+1 问题,所以在 qps 上 .NET Core 胜出。
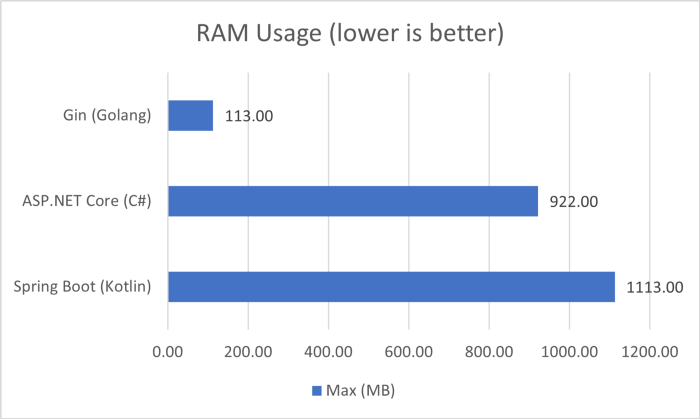
在内存使用方面,Golang 当然是最小的(只有 113 MB!),其次是 .NET Core, 最后就是超过1 GB 内存的 Spring Boot, 另外我观察到的有趣的事情是,测试完成后,Golang 和 .NET Core 的内存消耗分别减少到 10 MB 和 100 MB 左右,而 Spring Boot 保持在 1 GB 以上,直到我终止进程。
最后,Spring Boot 和 ASP.NET Core 都是非常成熟的框架,您都可以考虑使用, 希望对您有用!
原文作者:Putu Prema
原文链接: https://medium.com/@putuprema/spring-boot-vs-asp-net-core-a-showdown-1d38b89c6c2d
