一、Springboot诞生的技术基础
Spring的发展历史
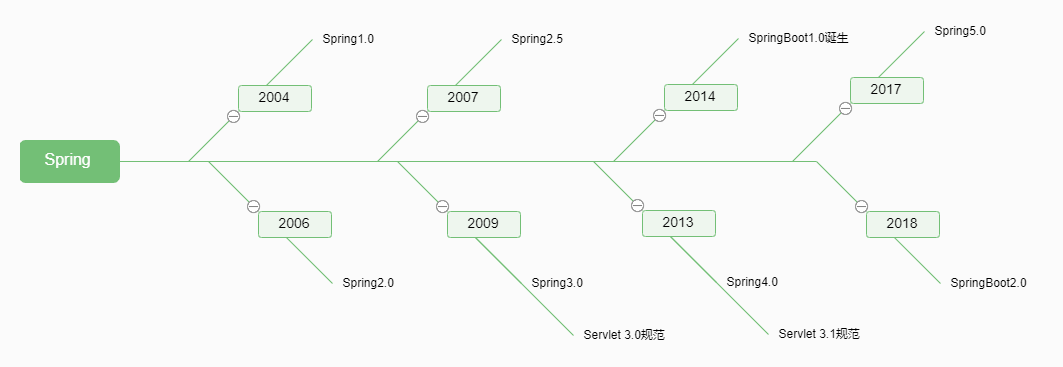
(1)spring1.0时代
Spring的诞生大大促进了JAVA的发展。也降低了企业java应用开发的技术和时间成本。
(2)spring2.0时代
对spring1.0在繁杂的xml配置文件上做了一定的优化,让配置看起来越来越简单,但是并没语完全解决xml冗余的问题。
(3)spring3.0时代
可以使用spring提供的java注解来取代曾经xml配置上的问题,似乎我们曾经忘记了发生什么,spring变得前所未有的简单。Spring3.0奠定了SpringBoot自动装配的基础。3.0提供的java注解使得我们可以通过注解的方式来配置spring容器。省去了使用类似于spring-context.xml的配置文件。
同年,Servlet3.0规范的诞生为SpringBoot彻底去掉xml(web.xml)奠定了了理论基础(对于servlet3.0来说,web.xml不再是必需品。但是Servlet3.0规范还是建议保留web.xml)。
(4)spring4.0时代
4.0 时代我们甚至连xml配置文件都不需要了完全使用java源码级别的配置与spring提供的注解就能快速的开发spring应用程序,但仍然无法改变Java Web应用程序的运行模式,我们仍然需要将war部署到Web Server 上,才能对外提供服务。
4.0开始全面支持java8.0
同年,Servlet3.1规范诞生(tomcat8开始采用Servlet3.1规范)。
Servlet3.0奠定了SpringBoot 零xml配置的基础
分析SpringBoot如何省去web.xml还得从Servlet3.0的规范说起。Servlet3.0规范规定如下(摘自穆茂强 张开涛翻译的Servlet3.1规范,3.0和3.1在这一点上只有一些细节上的变换):
ServletContainerInitializer类通过jar services API查找。对于每一个应用,应用启动时,由容器创建一个ServletContainerInitializer 实例。 框架提供的ServletContainerInitializer实现必须绑定在 jar 包 的META-INF/services 目录中的一个叫做 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 的文件,根据 jar services API,指定 ServletContainerInitializer 的实现。除 ServletContainerInitializer 外,我们还有一个注解@HandlesTypes。在 ServletContainerInitializer 实现上的@HandlesTypes注解用于表示感兴趣的一些类,它们可能指定了 HandlesTypes 的 value 中的注解(类型、方法或自动级别的注解),或者是其类型的超类继承/实现了这些类之一。无论是否设置了 metadata-complete,@HandlesTypes 注解将应用。当检测一个应用的类看是否它们匹配 ServletContainerInitializer 的 HandlesTypes 指定的条件时,如果应用的一个或多个可选的 JAR 包缺失,容器可能遇到类装载问题。由于容器不能决定是否这些类型的类装载失败将阻止应用正常工作,它必须忽略它们,同时也提供一个将记录它们的配置选项。如果ServletContainerInitializer 实现没有@HandlesTypes 注解,或如果没有匹配任何指定的@HandlesType,那么它会为每个应用使用 null 值的集合调用一次。这将允许 initializer 基于应用中可用的资源决定是否需要初始化 Servlet/Filter。在任何 Servlet Listener 的事件被触发之前,当应用正在启动时,ServletContainerInitializer 的 onStartup 方法将被调用。ServletContainerInitializer’s 的onStartup 得到一个类的 Set,其或者继承/实现 initializer 表示感兴趣的类,或者它是使用指定在@HandlesTypes 注解中的任意类注解的。
这个规范如何理解呢?
简单来说,当实现了Servlet3.0规范的容器(比如tomcat7及以上版本)启动时,通过SPI扩展机制自动扫描所有已添加的jar包下的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer中指定的全路径的类,并实例化该类,然后回调META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件中指定的ServletContainerInitializer的实现类的onStartup方法。 如果该类存在@HandlesTypes注解,并且在@HandlesTypes注解中指定了我们感兴趣的类,所有实现了这个类的onStartup方法将会被调用。
再直白一点来说,存在web.xml的时候,Servlet容器会根据web.xml中的配置初始化我们的jar包(也可以说web.xml是我们的jar包和Servlet联系的中介)。而在Servlet3.0容器初始化时会调用jar包META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer中指定的类的实现(javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer中的实现替代了web.xml的作用,而所谓的在@HandlesTypes注解中指定的感兴趣的类,可以理解为具体实现了web.xml的功能,当然也可以有其他的用途)。
二、从Spring源码中分析SpringBoot如何省去web.xml
META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer
如下图所示,在org.springframework:spring-web工程下,META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件中,指定了将会被Servlet容器启动时回调的类。
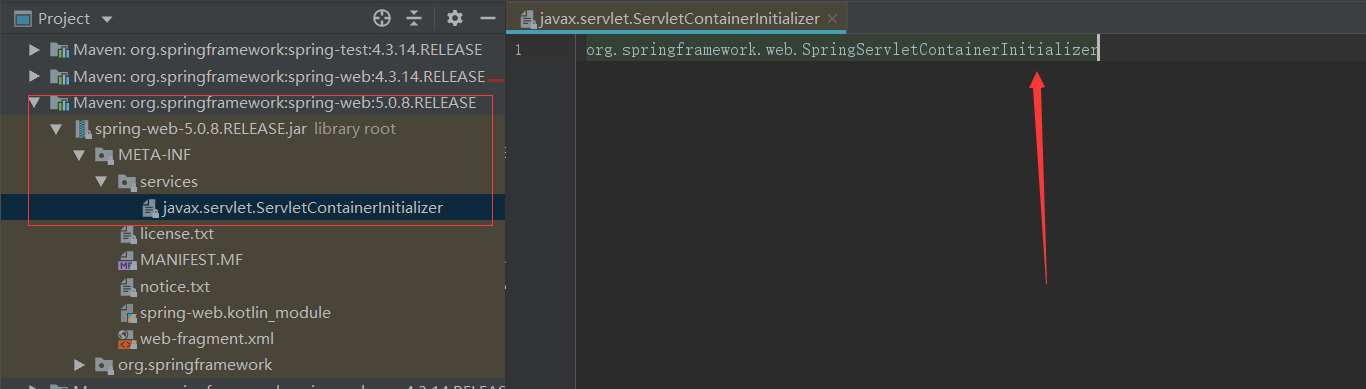
SpringServletContainerInitializer
查看 SpringServletContainerInitializer 类的源码,发现确实如如上文所说,实现了 ServletContainerInitializer ,并且也在 @HandlesTypes 注解中指定了,感兴趣的类 WebApplicationInitializer
可以看到onStartup方法上有一大段注释,翻译一下大致意思:
servlet 3.0+容器启动时将自动扫描类路径以查找实现Spring的webapplicationinitializer接口的所有实现,将其放进一个Set集合中,提供给 SpringServletContainerInitializer onStartup的第一个参数。
在Servlet容器初始化的时候会调用 SpringServletContainerInitializer 的onStartup方法,继续看onStartup方法的代码逻辑,在该onStartup方法中利用逐个调用webapplicationinitializer所有实现类中的onStartup方法。
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer { /** * Delegate the {@code ServletContext} to any {@link WebApplicationInitializer} * implementations present on the application classpath. * <p>Because this class declares @{@code HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)}, * Servlet 3.0+ containers will automatically scan the classpath for implementations * of Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer} interface and provide the set of all * such types to the {@code webAppInitializerClasses} parameter of this method. * <p>If no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations are found on the classpath, * this method is effectively a no-op. An INFO-level log message will be issued notifying * the user that the {@code ServletContainerInitializer} has indeed been invoked but that * no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations were found. * <p>Assuming that one or more {@code WebApplicationInitializer} types are detected, * they will be instantiated (and <em>sorted</em> if the @{@link * org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is present or * the {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} interface has been * implemented). Then the {@link WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)} * method will be invoked on each instance, delegating the {@code ServletContext} such * that each instance may register and configure servlets such as Spring's * {@code DispatcherServlet}, listeners such as Spring's {@code ContextLoaderListener}, * or any other Servlet API componentry such as filters. * @param webAppInitializerClasses all implementations of * {@link WebApplicationInitializer} found on the application classpath * @param servletContext the servlet context to be initialized * @see WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext) * @see AnnotationAwareOrderComparator */ @Override public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>(); if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) { for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) { // Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes, // no matter what @HandlesTypes says... if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) { try { initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex); } } } } if (initializers.isEmpty()) { servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath"); return; } servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath"); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers); for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) { initializer.onStartup(servletContext); } } }
WebApplicationInitializer
查看 WebApplicationInitializer接口,这个接口也就是上文中所说的Servlet3.0规范中 @HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) 注解中所指定的感兴趣的类。
截取一段很重要的注释。这段注释告诉我们实现该接口的类主要需要实现的功能就是web.xml中配置文件中配置的内容。
/* * <servlet> * <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> * <servlet-class> * org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet * </servlet-class> * <init-param> * <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> * <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml</param-value> * </init-param> * <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> * </servlet> * * <servlet-mapping> * <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> * <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> * </servlet-mapping>}</pre> * */ public interface WebApplicationInitializer { void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException; }
SpringBoot的 WebApplicationInitializer 的实现
查看SpringBoot SpringBootServletInitializer 源码,该类在spring-boot依赖包中。
仔细看下面的标蓝的代码。不难发现这正是Servlet容器(tomcat)如何找到SpringBoot并启动它的。
package org.springframework.boot.web.support; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.Servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer; import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer; import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.context.support.StandardServletEnvironment; /** * An opinionated {@link WebApplicationInitializer} to run a {@link SpringApplication} * from a traditional WAR deployment. Binds {@link Servlet}, {@link Filter} and * {@link ServletContextInitializer} beans from the application context to the servlet * container. * <p> * To configure the application either override the * {@link #configure(SpringApplicationBuilder)} method (calling * {@link SpringApplicationBuilder#sources(Object...)}) or make the initializer itself a * {@code @Configuration}. If you are using {@link SpringBootServletInitializer} in * combination with other {@link WebApplicationInitializer WebApplicationInitializers} you * might also want to add an {@code @Ordered} annotation to configure a specific startup * order. * <p> * Note that a WebApplicationInitializer is only needed if you are building a war file and * deploying it. If you prefer to run an embedded container then you won't need this at * all. * * @author Dave Syer * @author Phillip Webb * @author Andy Wilkinson * @since 1.4.0 * @see #configure(SpringApplicationBuilder) */ public abstract class SpringBootServletInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { protected Log logger; // Don't initialize early private boolean registerErrorPageFilter = true; /** * Set if the {@link ErrorPageFilter} should be registered. Set to {@code false} if * error page mappings should be handled via the Servlet container and not Spring * Boot. * @param registerErrorPageFilter if the {@link ErrorPageFilter} should be registered. */ protected final void setRegisterErrorPageFilter(boolean registerErrorPageFilter) { this.registerErrorPageFilter = registerErrorPageFilter; } @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { // Logger initialization is deferred in case a ordered // LogServletContextInitializer is being used this.logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext( servletContext); if (rootAppContext != null) { servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext) { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { // no-op because the application context is already initialized } }); } else { this.logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " + "createRootApplicationContext() did not " + "return an application context"); } } protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext( ServletContext servletContext) { SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder(); StandardServletEnvironment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment(); environment.initPropertySources(servletContext, null); builder.environment(environment); builder.main(getClass()); ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext); if (parent != null) { this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent)."); servletContext.setAttribute( WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null); builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent)); } builder.initializers( new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext)); builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class); builder = configure(builder); SpringApplication application = builder.build(); if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils .findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) { application.getSources().add(getClass()); } Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(), "No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the " + "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation"); // Ensure error pages are registered if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) { application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class); } return run(application); } /** * Returns the {@code SpringApplicationBuilder} that is used to configure and create * the {@link SpringApplication}. The default implementation returns a new * {@code SpringApplicationBuilder} in its default state. * @return the {@code SpringApplicationBuilder}. * @since 1.3.0 */ protected SpringApplicationBuilder createSpringApplicationBuilder() { return new SpringApplicationBuilder(); } /** * Called to run a fully configured {@link SpringApplication}. * @param application the application to run * @return the {@link WebApplicationContext} */ protected WebApplicationContext run(SpringApplication application) { return (WebApplicationContext) application.run(); } private ApplicationContext getExistingRootWebApplicationContext( ServletContext servletContext) { Object context = servletContext.getAttribute( WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE); if (context instanceof ApplicationContext) { return (ApplicationContext) context; } return null; } /** * Configure the application. Normally all you would need to do is to add sources * (e.g. config classes) because other settings have sensible defaults. You might * choose (for instance) to add default command line arguments, or set an active * Spring profile. * @param builder a builder for the application context * @return the application builder * @see SpringApplicationBuilder */ protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) { return builder; } }
查看Spring官方文档
查看Spring 5.0.14官方文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.0.14.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/web.html#spring-web
文档中给出在传统的springMVC中在web.xml中的配置内容
<web-app> <!-- 初始化Spring上下文 --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 指定Spring的配置文件 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/app-context.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!-- 初始化DispatcherServlet --> <servlet> <servlet-name>app</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value></param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>app</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/app/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
文档中提供了一个如何使用基于java代码的方式配置Servlet容器example
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext servletCxt) { // Load Spring web application configuration //通过注解的方式初始化Spring的上下文 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); //注册spring的配置类(替代传统项目中xml的configuration) ac.register(AppConfig.class); ac.refresh(); // Create and register the DispatcherServlet //基于java代码的方式初始化DispatcherServlet DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(ac); ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletCxt.addServlet("app", servlet); registration.setLoadOnStartup(1); registration.addMapping("/app/*"); } }
对比官方文档给出的example,不难发现上面这段java代码就是SpringBoot省去web.xml的具体实现方法。上面 MyWebApplicationInitializer 正是 WebApplicationInitializer ( @HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) ) 接口的实现。
官方文档提供的 MyWebApplicationInitializer 类正是SpringBoot不依赖与web.xml的关键代码。
SpringBoot中具体实现web.xml中配置的代码没有官方文档中的example这么简单,SpringBoot中具体初始化 DispatcherServlet 的类是 DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration 。感兴趣的话可以断点调试一下。
转自: