残差网络:将输入层与输出层进行连接,保证了经过这层网路结构,网络的运算能力不会出现较大的改变
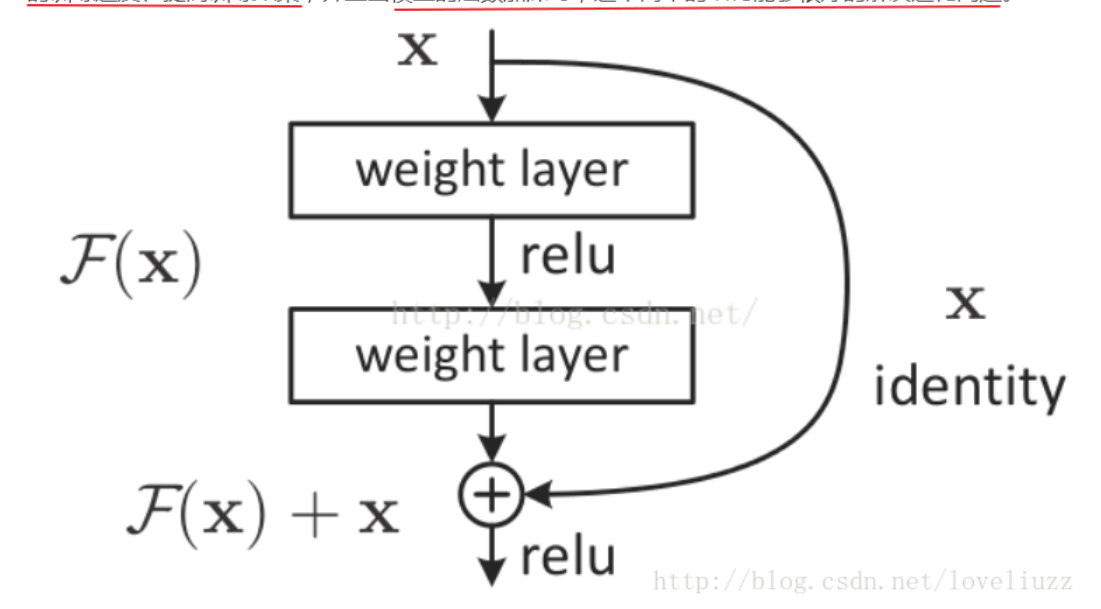
网络解析:
第一层网络: 输入网络经过一个卷积层,再经过一个batch_normalize, 再经过一个relu层
第二层网络;经过一层卷积层,将卷积后的网络与原输入数据进行对应位置相加操作, 将加和后的网络进行batch_normalize, 再经过一层relu
import torch from torch import nn def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1): return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) # 定义卷积层 class BasicBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, inplanes, outplanes, stride, downsample=None): super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, outplanes, stride=stride) # 第一个卷积 self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(outplanes) # 定义batch_norm层 self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 定义激活层 self.conv2 = conv3x3(outplanes, outplanes, stride=stride) # 第二个卷积 self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(outplanes) # 进行标准化操作 self.downsample = downsample # 进行维度的降低, 通常使用卷积操作来进行维度的降低 def forward(self, x): residual = x # 原始的残差模块 x = self.conv1(x) # 第一次卷积 x = self.bn(x) # 归一化操作 x = self.relu(x) # 激活操作 x = self.conv2(x) # 第二次卷积 out = self.bn2(x) # 归一化操作 if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) # 是否需要对原始的样本做降采样操作 out += residual # 进行加和操作 out = self.relu(out) # 进行激活操作 return out