论文阅读:Adaptive Fusion for RGB-D Salient Object Detection
这篇代码的创新点在于使用了SW层,使用SW_logits * img_logits + (1 - SW_logits) * (1 - depth_logits) 来获得最终的预测结果
另外一个关键点是使用了3种loss损失值
第一种损失值,即经过归一化的标签g_t 与 输出的结果logits的sigmoid的损失值
第二种损失值, 即将im_logits进行sigmoid转换为0, 1之间,然后使用sigmoid_im * label + (1 - sigmoid_im) * (1 - label) # 获得标签值与图片值的交叉熵损失值
将计算好的交叉熵损失函数与SW_map 计算-log的交叉熵损失函数,个人认为这个loss存在问题
第三种损失值,即edge_loss即边界的损失值
将预测的结果进行sigmoid操作,转换为(0, 1)
使用tf.reshape(tf.constant([-1, 0, 1], tf.float32), [1, 3, 1, 1]) 构造x方向的边界卷积
使用tf.reshape(x_weight, [3, 1, 1, 1]) # 构造y方向的边界卷积
使用tf.nn.conv2d(g_t, x_weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME') 进行标签的x轴方向和y轴方向上的边界卷积
使用tf.nn.conv2d(sigmoid_p, x_weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME') 进行预测结果的x轴方向和y轴方向上的边界卷积
最后使用tf.losses.mean_squre_error(xgrad_gt, xgrad_sal) + tf.losses.mean_squre_error(ygrad_gt, ygrad_sal) 获得最终的mse损失函数
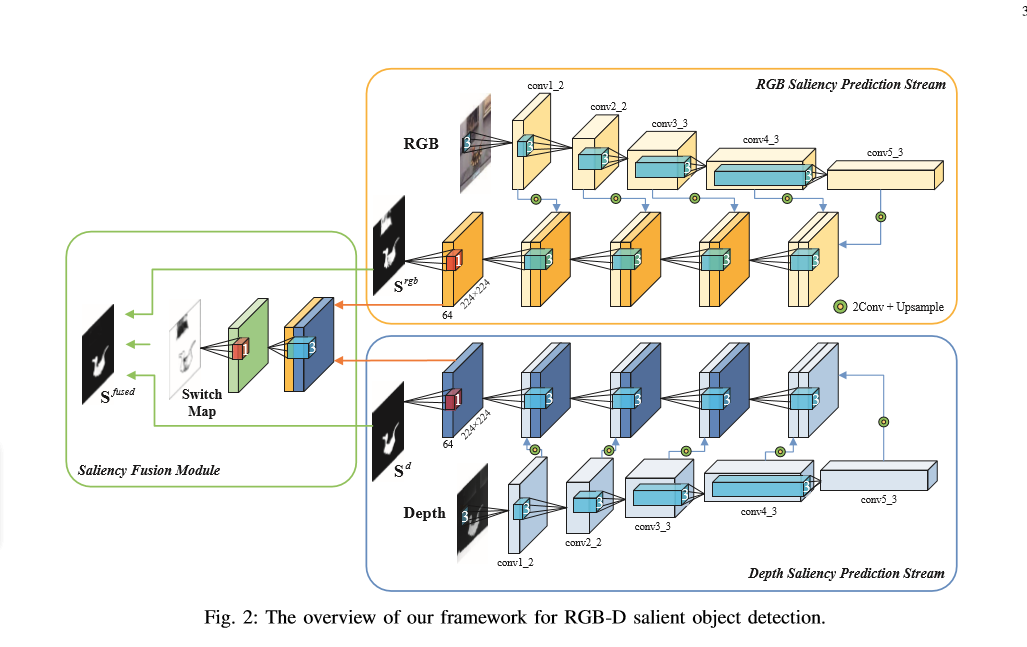
论文中的网络结构图
run_saliency.py 用于执行代码
from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import scipy.misc as misc import os import cv2 from net import * from loss import * FLAGS = tf.flags.FLAGS tf.flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', './data/', 'path to dataset') tf.flags.DEFINE_string('ckpt_file', './model/AF-Net', 'checkpoint file') tf.flags.DEFINE_string('save_dir', './result', 'path to prediction direction') tf.flags.DEFINE_string('train_data', './train_data/', 'path to train_data') IMAGE_SIZE = 224 BATCH_SIZE = 1 train_num = 1500 num_epoch = 1000 def _transform(filename, _channels=True): image = misc.imread(filename) if _channels and len(image.shape) < 3: image = np.array([image for _ in range(3)]) resize_image = misc.imresize(image, [IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE], interp='nearest') return image def main(argv=None, is_training=True): image = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3], name='input_image') depth_2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE], name='input_depth') depth = tf.expand_dims(depth_2, axis=3) processed_image = image - [123.64, 116.779, 103.939] # 减去最后一个维度的均值 gt_2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE], name='label') gt = tf.expand_dims(gt_2, axis=3) net_handler = NetHandler() logits, im_logits, SW_map = net_handler.RGBD_SW_net(processed_image, depth) pred_annotation = tf.sigmoid(logits) # 将其转换为0, 1 # 构造sal损失值 loss_sal = sigmoid_CEloss(logits, gt) # 构造SW损失值 loss_sw = SW_loss(im_logits, SW_map, gt) # 计算边缘损失值 loss_edge = edge_loss(logits, gt) # 计算总的损失值loss loss = loss_sal + loss_sw + loss_edge # 构造损失值的优化器 train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-6, beta1=0.5).minimize(loss) # 构造执行函数 sess = tf.Session() # 变量初始化 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 打印保存的参数的地址 print('Rreading params from {}'.format(FLAGS.ckpt_file)) # 如果已经保存了参数就加载 if tf.train.get_checkpoint_state('model'): saver = tf.train.Saver(None) saver.restore(sess, FLAGS.ckpt_file) # 进行图片结果的保存 if not os.path.exists(FLAGS.save_dir): os.makedirs(FLAGS.save_dir) if is_training == False: files = os.listdir(os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir + '/RGB/')) test_num = len(files) test_RGB = np.array([_transform(os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir + '/RGB/' + filename), _channels=True) for filename in files]) # 这里是不对的 test_depth = np.array([np.expand_dims(_transform(os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir + '/depth/' + filename), _channels=True) for filename in files)]) # 进行测试操作 for k in range(test_num): # 进行结果的预测,这里结果的范围为0,1之间 test_prediction = sess.run(pred_annotation, feed_dict={image:test_RGB[k], depth:test_depth[k]}) test_origin_RGB = misc.imread(os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir + '/RGB/' + files[k].split('.')[0] + '.jpg')) image_shape = test_origin_RGB.shape # 将图片转换为原来的图片的大小 test_pred = misc.imresize(test_prediction[0, :, :, 0], image_shape, interp='bilinear') misc.imsave('{}/{}'.format(FLAGS.save_dir, files[k].split('.')[0] + '.jpg'), test_pred.astype(np.uint8)) print('Save results in to %s' % (FLAGS.save_dir)) else: iter = 0 for epoch in range(num_epoch): # 载入数据 for i in range(train_num // BATCH_SIZE): deep_img, GT_image, Img_img = read_data_some('train_data.npy', BATCH_SIZE) _, _loss = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict={image:Img_img, depth_2:deep_img, gt_2:GT_image}) if iter % 100 == 0 and iter != 0: print('iter', iter, 'loss', _loss) saver = tf.train.Saver() if epoch % 10 == 0: saver.save(sess, FLAGS.ckpt_file, write_meta_graph=FLAGS) test_deep, test_GT, test_RGB = read_data_some('test_data.npy', 1) test_prediction = sess.run(pred_annotation, feed_dict={image:test_RGB, depth_2:test_deep, gt_2:test_GT}) # 进行图片保存 cv2.imwrite('train_result/deep.png', test_deep) cv2.imwrite('train_result/GT.png', test_GT) cv2.imwrite('train_result/RGB.png', test_RGB) cv2.imwrite('train_result/pred.png', test_prediction) iter += 1 if __name__ == '__main__': tf.app.run()
net.py 网络结构
import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim class NetHandler(object): def __int__(self, weights_initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(), weight_decay = 0.0001, padding='SAME'): self.padding = padding self.weight_initializer = weights_initializer self.weight_decay = weight_decay def vgg16_net(self, inputs, depth_suf = ''): layers = ( 'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1', 'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2', 'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3', 'relu3_3', 'pool3', 'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3', 'relu4_3', 'pool4', 'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3', 'relu5_3', 'pool5' ) kernel_size = 3 num_outputs = 64 net = {} current = inputs # 当前输入 for i, name in enumerate(layers): if depth_suf == '_d' and i == 0: current = slim.conv2d(current, 64, [3, 3], weights_initializer=self.weight_initializer, padding=self.padding, stride=1, activation_fn=None) net[name] = current continue kind = name[:4] if kind == 'conv': if name[:5] == 'conv1': num_outputs = 64 # 构造第一个卷积的输出fiter elif name[:5] == 'conv2': num_outputs = 128 elif name[:5] == 'conv3': num_outputs = 256 elif name[:5] == 'conv4': num_outputs = 512 elif name[:5] == 'conv5': num_outputs = 512 _, _, _, c = current.get_shape() kernels = tf.get_variable(name=name + '_w' + depth_suf, shape=[kernel_size, kernel_size, c, num_outputs], initializer=self.weight_initializer, regularizer=tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(self.weight_decay), trainable=True) _, _, _, bias_size = kernels.get_shape() bias = tf.get_variable(name=name + '_b' + depth_suf, shape=[bias_size], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), trainable=True) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(current, kernels, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=self.padding) current = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, bias) elif kind == 'relu': current = tf.nn.relu(current, name=name) elif kind == 'pool': current = tf.nn.max_pool(current, kernel_size=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=self.padding) net[name] = current return net def RGBD_SW_net(self, image, depth): image_net = self.vgg16_net(image) depth_net = self.vgg16_net(depth, depth_suf='_d') conv_5 = image_net['relu5_3'] # 获得第一层到最后一层卷积的结果 conv_4 = image_net['relu4_3'] conv_3 = image_net['relu3_3'] conv_2 = image_net['relu2_2'] conv_1 = image_net['relu1_2'] depth_5 = depth_net['relu5_3'] depth_4 = depth_net['relu4_3'] depth_3 = depth_net['relu3_3'] depth_2 = depth_net['relu2_2'] depth_1 = depth_net['relu1_2'] with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], weights_initializer=self.weight_initializer, weight_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(self.weight_decay), padding=self.padding, stride=1, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu): conv5 = slim.repeat(conv_5, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv5') # 2表示进行了两次的卷积操作 conv4 = slim.repeat(conv_4, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv4') # 进行两次卷积 conv3 = slim.repeat(conv_3, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv3') # conv2 = slim.repeat(conv_2, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv2') conv1 = slim.repeat(conv_1, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1') depth5 = slim.repeat(depth_5, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='depth5') depth4 = slim.repeat(depth_4, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='depth4') depth3 = slim.repeat(depth_3, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='depth3') depth2 = slim.repeat(depth_2, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='depth2') depth1 = slim.repeat(depth_1, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='depth1') conv5_up = tf.image.resize_images(conv5, [224, 224]) conv4_up = tf.image.resize_images(conv4, [224, 224]) conv3_up = tf.image.resize_images(conv3, [224, 224]) conv2_up = tf.image.resize_images(conv2, [224, 224]) depth5_up = tf.image.resize_images(depth5, [224, 224]) depth4_up = tf.image.resize_images(depth4, [224, 224]) depth3_up = tf.image.resize_images(depth3, [224, 224]) depth2_up = tf.image.resize_images(depth2, [224, 224]) # 将卷积层进行维度变化,卷积后的结果输入到下一层 concat4_im = tf.concat([conv5_up, conv4_up], 3) feat4_im = slim.conv2d(concat4_im, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat4_im') concat3_im = tf.concat([feat4_im, conv3_up], 3) feat3_im = slim.conv2d(concat3_im, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat3_im') concat2_im = tf.concat([feat3_im, conv2_up], 3) feat2_im = slim.conv2d(concat2_im, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat2_im') concat1_im = tf.concat([feat2_im, conv1], 3) feat1_im = slim.conv2d(concat1_im, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat1_im') # # 同理对深度图做相同的操作 concat4_d = tf.concat([depth4_up, depth5_up], 3) feat4_d = slim.conv2d(concat4_d, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat4_d') concat3_d = tf.concat([feat4_d, depth3]) feat3_d = slim.conv2d(concat3_d, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat3_d') concat2_d = tf.concat([feat3_d, depth2]) feat2_d = slim.conv2d(concat2_d, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat2_d') concat1_d = tf.concat([feat2_d, depth]) feat1_d = slim.conv2d(concat1_d, 64, [3, 3], scope='feat1_d') # 进行1*1的卷积, 时期维度变化为1 conv1_im_logits = slim.conv2d(feat1_im, 1, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, scope='conv1_im_logits') conv1_d_logits = slim.conv2d(feat1_d, 1, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, scope='conv1_d_logits') # 将图像卷积图与深度卷积图合并 feat1 = slim.conv2d(tf.concat([feat1_im, feat1_d], 3), 64, [3, 3], scope='feat1') SW_map = tf.nn.sigmoid(slim.conv2d(feat1, 1, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, scope='feat1_attn')) conv1_fused_logits = SW_map * conv1_im_logits + (1 - SW_map) * conv1_d_logits return conv1_fused_logits, conv1_im_logits, SW_map
loss.py 定义的损失值
import tensorflow as tf def sigmoid_CEloss(logits, gt): loss = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=tf.cast(gt, tf.float32)) ) def SW_loss(im_logits, SW_map, gt): label = tf.cast(gt, tf.float32) sigmoid_im = tf.nn.sigmoid(im_logits) SW_gt = label * sigmoid_im + (1 - label) * (1 - sigmoid_im) cost = -SW_gt * tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(SW_map, 1e-8, 1.0)) - (1 - SW_gt) * tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(1 - SW_map, 1e-8, 1.0)) return tf.reduce_mean(cost) # 边缘轮廓的损失值 def edge_loss(logits, gt): gt = tf.cast(gt, tf.float32) sigmoid_p = tf.nn.sigmoid(logits) x_weight = tf.reshape(tf.constant([-1, 0, +1], tf.float32), [1, 3, 1, 1]) # 构造了一个卷积核 y_weight = tf.reshape(x_weight, [3, 1, 1, 1]) # 构造了卷积核 # 获得其标签边缘的梯度值,获得x边缘的损失值 xgrad_gt = tf.nn.conv2d(gt, x_weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME') ygrad_gt = tf.nn.conv2d(gt, y_weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME') # 获得输出结果的边缘梯度值 xgrad_sal = tf.nn.conv2d(sigmoid_p, x_weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME') ygrad_sal = tf.nn.conv2d(sigmoid_p, y_weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME') # 计算平方根误差 loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(xgrad_gt, xgrad_sal) + tf.losses.mean_squared_error(ygrad_gt, ygrad_sal) return loss
read_data 读取一个batch_size的数据
import numpy as np import cv2 def read_data_some(path, bacth_size): data = np.array(np.load('npy/' + path)) num = len(data) indx = np.random.randint(0, num, bacth_size) deep_img, GT_img, Img_imgs = data[indx][:, 0], data[indx][:, 1], data[indx][:, 2] deep_imgs = [] GT_imgs = [] for i in range(bacth_size): deep_imgs.append(cv2.cvtColor(deep_img[i], cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)) GT_imgs.append(cv2.cvtColor(GT_img[i], cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)) return deep_imgs, GT_imgs, Img_imgs if __name__ == '__main__': read_train_data(64)
save_data 保存数据为.npy
import random import os import cv2 import numpy as np import glob def save_data(path): data = [] for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path): if len(dirs) != 0: file_names = glob.glob(path + dirs[0] + '/*.png') for deep_name in file_names: GT_name = deep_name.replace('deep', 'GT') Img_name = deep_name.replace('deep', 'Img').replace('png', 'jpg') # 图片的读取 deep_img = cv2.imread(deep_name) deep_img = cv2.resize(deep_img, (224, 224)) GT_img = cv2.imread(GT_name) GT_img = cv2.resize(GT_img, (224, 224)) Img_img = cv2.imread(Img_name) Img_img = cv2.resize(Img_img, (224, 224)) data.append((deep_img, GT_img, Img_img)) # 进行数据的清洗 random.shuffle(data) np.save('npy/' + path[:-1] + '.npy', data)