原文地址:http://dangdangdotcom.github.io/elastic-job/post/1.x/user_guide/
开发指南
代码开发
作业类型
目前提供3种作业类型,分别是Simple, DataFlow和Script。
DataFlow类型用于处理数据流,它又提供2种作业类型,分别是ThroughputDataFlow和SequenceDataFlow。需要继承相应的抽象类。
Script类型用于处理脚本,可直接使用,无需编码。
方法参数shardingContext包含作业配置,分片和运行时信息。可通过getShardingTotalCount(), getShardingItems()等方法分别获取分片总数,运行在本作业服务器的分片序列号集合等。
Simple类型作业
Simple类型作业意为简单实现,未经任何封装的类型。需要继承AbstractSimpleElasticJob,该类只提供了一个方法用于覆盖,此方法将被定时执行。用于执行普通的定时任务,与Quartz原生接口相似,只是增加了弹性扩缩容和分片等功能。
public class MyElasticJob extends AbstractSimpleElasticJob { @Override public void process(JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext context) { // do something by sharding items } }
ThroughputDataFlow类型作业
ThroughputDataFlow类型作业意为高吞吐的数据流作业。需要继承AbstractIndividualThroughputDataFlowElasticJob并可以指定返回值泛型,该类提供3个方法可覆盖,分别用于抓取数据,处理数据和指定是否流式处理数据。可以获取数据处理成功失败次数等辅助监控信息。如果流式处理数据,fetchData方法的返回值只有为null或长度为空时,作业才会停止执行,否则作业会一直运行下去;非流式处理数据则只会在每次作业执行过程中执行一次fetchData方法和processData方法,即完成本次作业。流式数据处理参照TbSchedule设计,适用于不间歇的数据处理。
作业执行时会将fetchData的数据传递给processData处理,其中processData得到的数据是通过多线程(线程池大小可配)拆分的。如果采用流式作业处理方式,建议processData处理数据后更新其状态,避免fetchData再次抓取到,从而使得作业永远不会停止。processData的返回值用于表示数据是否处理成功,抛出异常或者返回false将会在统计信息中归入失败次数,返回true则归入成功次数。
public class MyElasticJob extends AbstractIndividualThroughputDataFlowElasticJob<Foo> { @Override public List<Foo> fetchData(JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext context) { Map<Integer, String> offset = context.getOffsets(); List<Foo> result = // get data from database by sharding items and by offset return result; } @Override public boolean processData(JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext context, Foo data) { // process data // ... // store offset for (int each : context.getShardingItems()) { updateOffset(each, "your offset, maybe id"); } return true; } }
SequenceDataFlow类型作业
SequenceDataFlow类型作业和ThroughputDataFlow作业类型极为相似,所不同的是ThroughputDataFlow作业类型可以将获取到的数据多线程处理,但不会保证多线程处理数据的顺序。如:从2个分片共获取到100条数据,第1个分片40条,第2个分片60条,配置为两个线程处理,则第1个线程处理前50条数据,第2个线程处理后50条数据,无视分片项;SequenceDataFlow类型作业则根据当前服务器所分配的分片项数量进行多线程处理,每个分片项使用同一线程处理,防止了同一分片的数据被多线程处理,从而导致的顺序问题。如:从2个分片共获取到100条数据,第1个分片40条,第2个分片60条,则系统自动分配两个线程处理,第1个线程处理第1个分片的40条数据,第2个线程处理第2个分片的60条数据。由于ThroughputDataFlow作业可以使用多于分片项的任意线程数处理,所以性能调优的可能会优于SequenceDataFlow作业。
public class MyElasticJob extends AbstractIndividualSequenceDataFlowElasticJob<Foo> { @Override public List<Foo> fetchData(JobExecutionSingleShardingContext context) { int offset = context.getOffset(); List<Foo> result = // get data from database by sharding items and by offset return result; } @Override public boolean processData(JobExecutionSingleShardingContext context, Foo data) { // process data // ... // store offset updateOffset(context.getShardingItem(), "your offset, maybe id"); return true; } }
Script类型作业
Script类型作业意为脚本类型作业,支持shell,python,perl等所有类型脚本。只需通过控制台/代码配置scriptCommandLine即可。执行脚本路径可以包含参数,最后一个参数为作业运行时信息.
#!/bin/bash
echo sharding execution context is $*
作业运行时输出
sharding execution context is {"shardingItems":[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9],"shardingItemParameters":{},"offsets":{},"jobName":"scriptElasticDemoJob","shardingTotalCount":10,"jobParameter":"","monitorExecution":true,"fetchDataCount":1}
批量处理
为了提高数据处理效率,数据流类型作业提供了批量处理数据的功能。之前逐条处理数据的两个抽象类分别是AbstractIndividualThroughputDataFlowElasticJob和AbstractIndividualSequenceDataFlowElasticJob,批量处理则使用另外两个接口AbstractBatchThroughputDataFlowElasticJob和AbstractBatchSequenceDataFlowElasticJob。不同之处在于processData方法的返回值从boolean类型变为int类型,用于表示一批数据处理的成功数量,第二个入参则转变为List数据集合。
异常处理
elastic-job在最上层接口提供了handleJobExecutionException方法,使用作业时可以覆盖此方法,并使用quartz提供的JobExecutionException控制异常后作业的声明周期。默认实现是直接将异常抛出。示例:
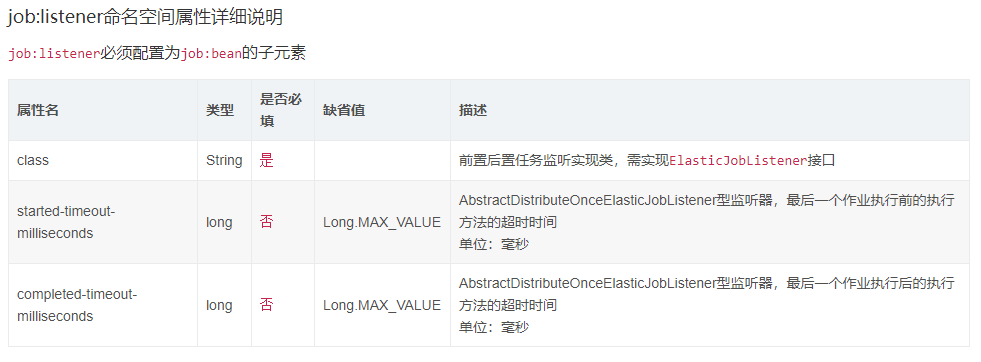
任务监听配置
可以通过配置多个任务监听器,在任务执行前和执行后执行监听的方法。监听器分为每台作业节点均执行和分布式场景中仅单一节点执行两种。
每台作业节点均执行的监听
若作业处理作业服务器的文件,处理完成后删除文件,可考虑使用每个节点均执行清理任务。此类型任务实现简单,且无需考虑全局分布式任务是否完成,请尽量使用此类型监听器。
步骤:
- 定义监听器
import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.api.JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext; import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.api.listener.ElasticJobListener; public class MyElasticJobListener implements ElasticJobListener { @Override public void beforeJobExecuted(final JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext shardingContext) { // do something ... } @Override public void afterJobExecuted(final JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext shardingContext) { // do something ... } }
- 将监听器作为参数传入
JobScheduler
public class JobMain { public static void main(final String[] args) { new JobScheduler(regCenter, jobConfig, new MyElasticJobListener()).init(); } }
分布式场景中仅单一节点执行的监听
若作业处理数据库数据,处理完成后只需一个节点完成数据清理任务即可。此类型任务处理复杂,需同步分布式环境下作业的状态同步,提供了超时设置来避免作业不同步导致的死锁,请谨慎使用。
步骤:
- 定义监听器
import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.api.JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext; import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.api.listener.AbstractDistributeOnceElasticJobListener; public final class TestDistributeOnceElasticJobListener extends AbstractDistributeOnceElasticJobListener { public TestDistributeOnceElasticJobListener(final long startTimeoutMills, final long completeTimeoutMills) { super(startTimeoutMills, completeTimeoutMills); } @Override public void doBeforeJobExecutedAtLastStarted(final JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext shardingContext) { // do something ... } @Override public void doAfterJobExecutedAtLastCompleted(final JobExecutionMultipleShardingContext shardingContext) { // do something ... } }
- 将监听器作为参数传入
JobScheduler
public class JobMain { public static void main(final String[] args) { long startTimeoutMills = 5000L; long completeTimeoutMills = 10000L; new JobScheduler(regCenter, jobConfig, new MyDistributeOnceElasticJobListener(startTimeoutMills, completeTimeoutMills)).init(); } }
作业配置
与Spring容器配合使用作业,可以将作业Bean配置为Spring Bean,可在作业中通过依赖注入使用Spring容器管理的数据源等对象。可用placeholder占位符从属性文件中取值。
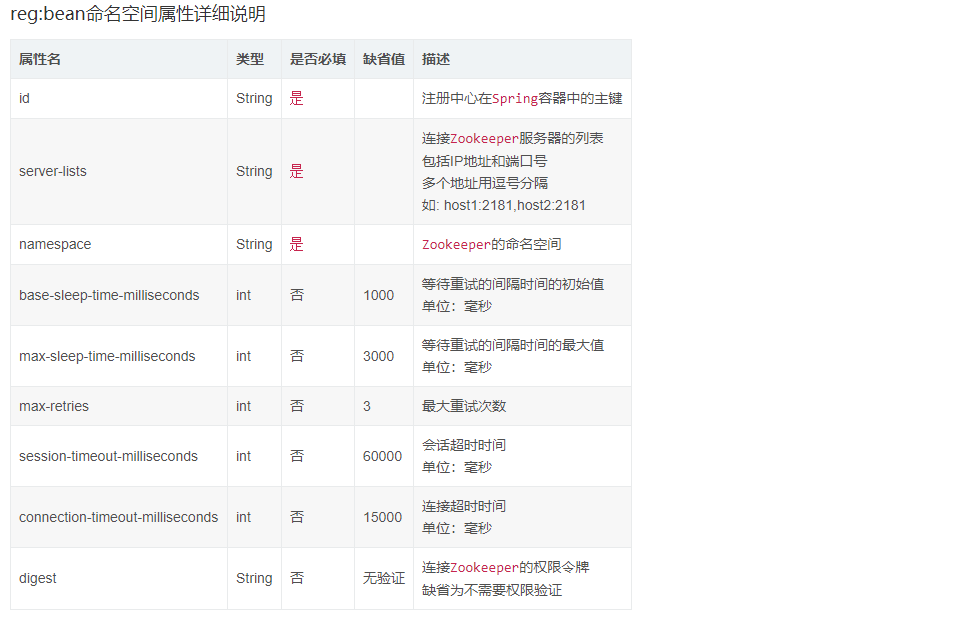
Spring命名空间配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:reg="http://www.dangdang.com/schema/ddframe/reg" xmlns:job="http://www.dangdang.com/schema/ddframe/job" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.dangdang.com/schema/ddframe/reg http://www.dangdang.com/schema/ddframe/reg/reg.xsd http://www.dangdang.com/schema/ddframe/job http://www.dangdang.com/schema/ddframe/job/job.xsd "> <!--配置作业注册中心 --> <reg:zookeeper id="regCenter" server-lists=" yourhost:2181" namespace="dd-job" base-sleep-time-milliseconds="1000" max-sleep-time-milliseconds="3000" max-retries="3" /> <!-- 配置简单作业--> <job:simple id="simpleElasticJob" class="xxx.MySimpleElasticJob" registry-center-ref="regCenter" cron="0/10 * * * * ?" sharding-total-count="3" sharding-item-parameters="0=A,1=B,2=C" /> <!-- 配置数据流作业--> <job:dataflow id="throughputDataFlow" class="xxx.MyThroughputDataFlowElasticJob" registry-center-ref="regCenter" cron="0/10 * * * * ?" sharding-total-count="3" sharding-item-parameters="0=A,1=B,2=C" process-count-interval-seconds="10" concurrent-data-process-thread-count="10" /> <!-- 配置脚本作业--> <job:script id="scriptElasticJob" registry-center-ref="regCenter" cron="0/10 * * * * ?" sharding-total-count="3" sharding-item-parameters="0=A,1=B,2=C" script-command-line="/your/file/path/demo.sh" /> <!-- 配置带监听的简单作业--> <job:simple id="listenerElasticJob" class="xxx.MySimpleListenerElasticJob" registry-center-ref="regCenter" cron="0/10 * * * * ?" sharding-total-count="3" sharding-item-parameters="0=A,1=B,2=C"> <job:listener class="xx.MySimpleJobListener"/> <job:listener class="xx.MyOnceSimpleJobListener" started-timeout-milliseconds="1000" completed-timeout-milliseconds="2000" /> </job:simple> </beans>
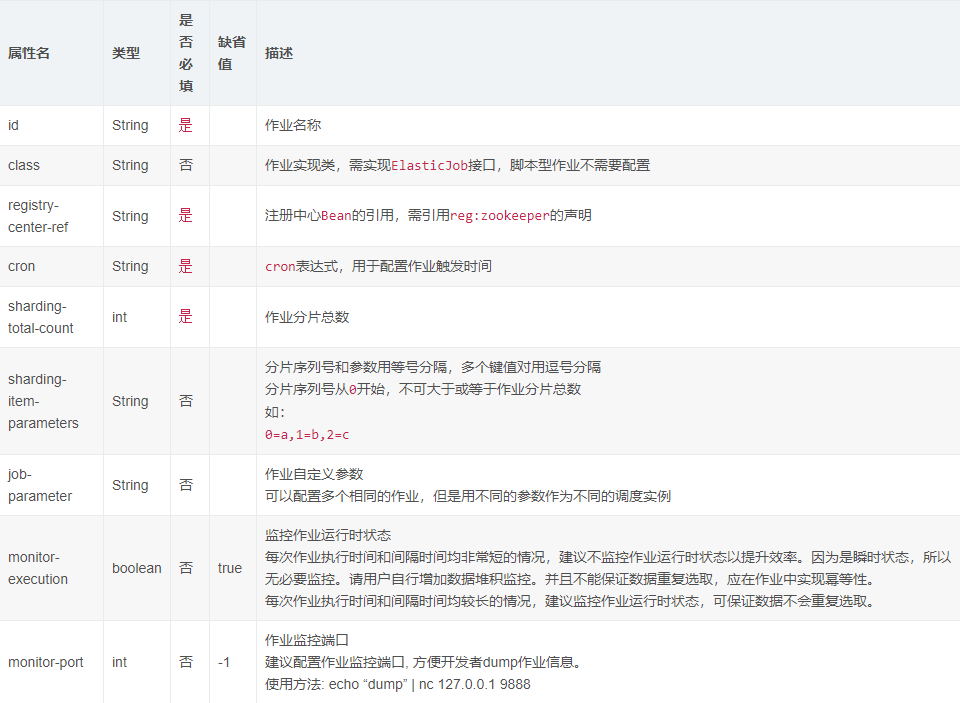
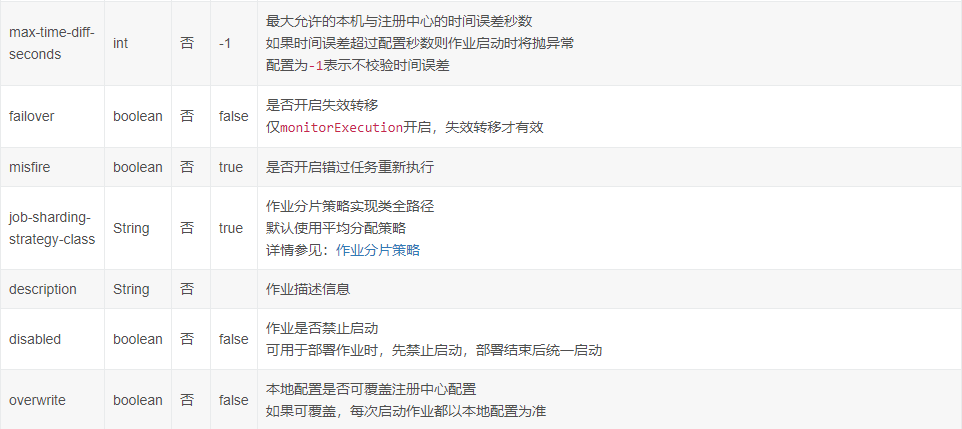
job:simple命名空间属性详细说明
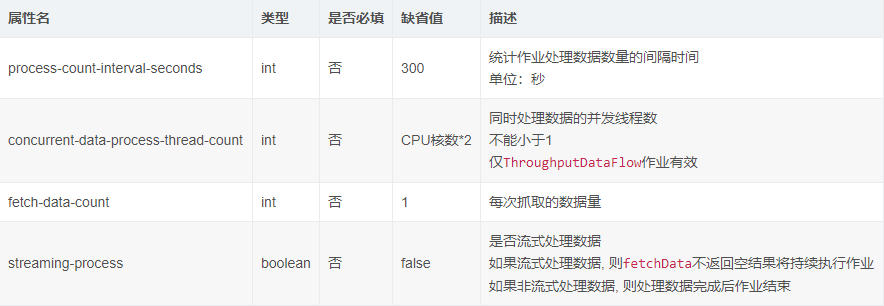
job:dataflow命名空间属性详细说明
job:dataflow命名空间拥有job:simple命名空间的全部属性,以下仅列出特有属性
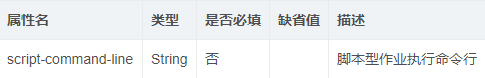
job:script命名空间属性详细说明,基本属性参照job:simple命名空间属性详细说明
job:script命名空间拥有job:simple命名空间的全部属性,以下仅列出特有属性
不使用Spring配置
如果不使用Spring框架,可以用如下方式启动作业。
import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.api.config.JobConfiguration; import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.api.JobScheduler; import com.dangdang.ddframe.reg.base.CoordinatorRegistryCenter; import com.dangdang.ddframe.reg.zookeeper.ZookeeperConfiguration; import com.dangdang.ddframe.reg.zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistryCenter; import com.dangdang.example.elasticjob.core.job.SimpleJobDemo; import com.dangdang.example.elasticjob.core.job.ThroughputDataFlowJobDemo; import com.dangdang.example.elasticjob.core.job.SequenceDataFlowJobDemo; import com.dangdang.ddframe.job.plugin.job.type.integrated.ScriptElasticJob; public class JobDemo { // 定义Zookeeper注册中心配置对象 private ZookeeperConfiguration zkConfig = new ZookeeperConfiguration("localhost:2181", "elastic-job-example", 1000, 3000, 3); // 定义Zookeeper注册中心 private CoordinatorRegistryCenter regCenter = new ZookeeperRegistryCenter(zkConfig); // 定义简单作业配置对象 private final SimpleJobConfiguration simpleJobConfig = JobConfigurationFactory.createSimpleJobConfigurationBuilder("simpleElasticDemoJob", SimpleJobDemo.class, 10, "0/30 * * * * ?").build(); // 定义高吞吐流式处理的数据流作业配置对象 private final DataFlowJobConfiguration throughputJobConfig = JobConfigurationFactory.createDataFlowJobConfigurationBuilder("throughputDataFlowElasticDemoJob", ThroughputDataFlowJobDemo.class, 10, "0/5 * * * * ?").streamingProcess(true).build(); // 定义顺序的数据流作业配置对象 private final DataFlowJobConfiguration sequenceJobConfig = JobConfigurationFactory.createDataFlowJobConfigurationBuilder("sequenceDataFlowElasticDemoJob", SequenceDataFlowJobDemo.class, 10, "0/5 * * * * ?").build(); // 定义脚本作业配置对象 private final ScriptJobConfiguration scriptJobConfig = JobConfigurationFactory.createScriptJobConfigurationBuilder("scriptElasticDemoJob", 10, "0/5 * * * * ?", "test.sh").build(); public static void main(final String[] args) { new JobDemo().init(); } private void init() { // 连接注册中心 regCenter.init(); // 启动简单作业 new JobScheduler(regCenter, simpleJobConfig).init(); // 启动高吞吐流式处理的数据流作业 new JobScheduler(regCenter, throughputJobConfig).init(); // 启动顺序的数据流作业 new JobScheduler(regCenter, sequenceJobConfig).init(); // 启动脚本作业 new JobScheduler(regCenter, scriptJobConfig).init(); } }