对象池技术其实蛮常见的,比如线程池、数据库连接池
他们的特点是:对象创建代价较高、比较消耗资源、比较耗时;
比如 mysql数据库连接建立就要先建立 tcp三次握手、发送用户名/密码、进行身份校验、权限校验等很多步骤才算是 db连接建立成功;要是每次使用的时候才去创建会比较影响性能,而且也不能无限制的创建太多
所以,这种对象使用完后不立即释放资源,一般是先放到一个池子里暂存起来,下次就能直接从池子里拿出现成可用的对象
对象池需要具备的能力
所以,为了让这类资源对象的使用方能够复用资源、快速获取可用对象,这个池子得具备的能力有哪些?
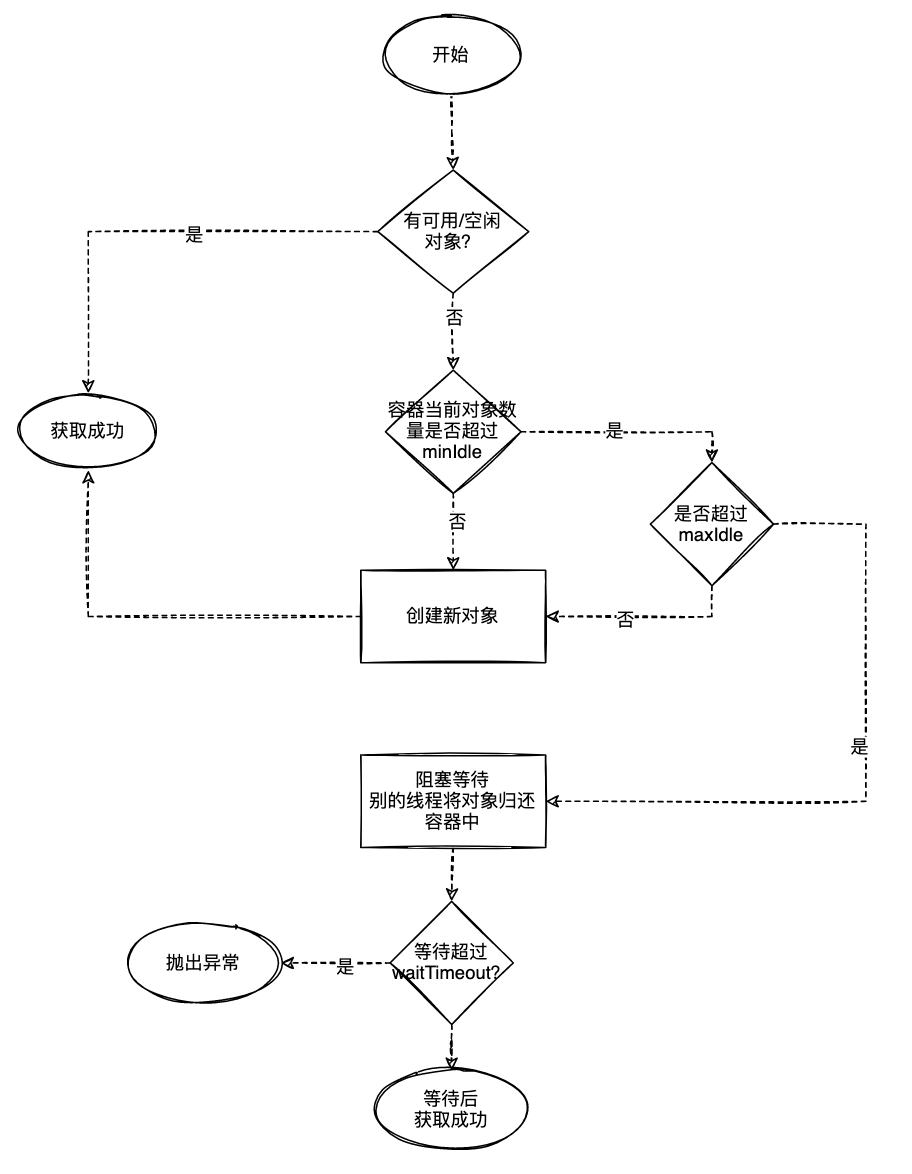
- 首先有个容器的数据结构,能存放多个对象,也有数量上限
- 维持一定数量的常驻对象,这个数量如果和
qps * rt匹配的话,业务处理就都能直接获取可用对象,不需要消耗对象创建的时间了 - 能应对突发流量
- 超时获取,一定时间没有获取成功就抛出异常,不卡死业务线程
- 具有活性检测机制, 从容器拿出来的对象得是可用的
1 核心流程
1.1对象获取流程
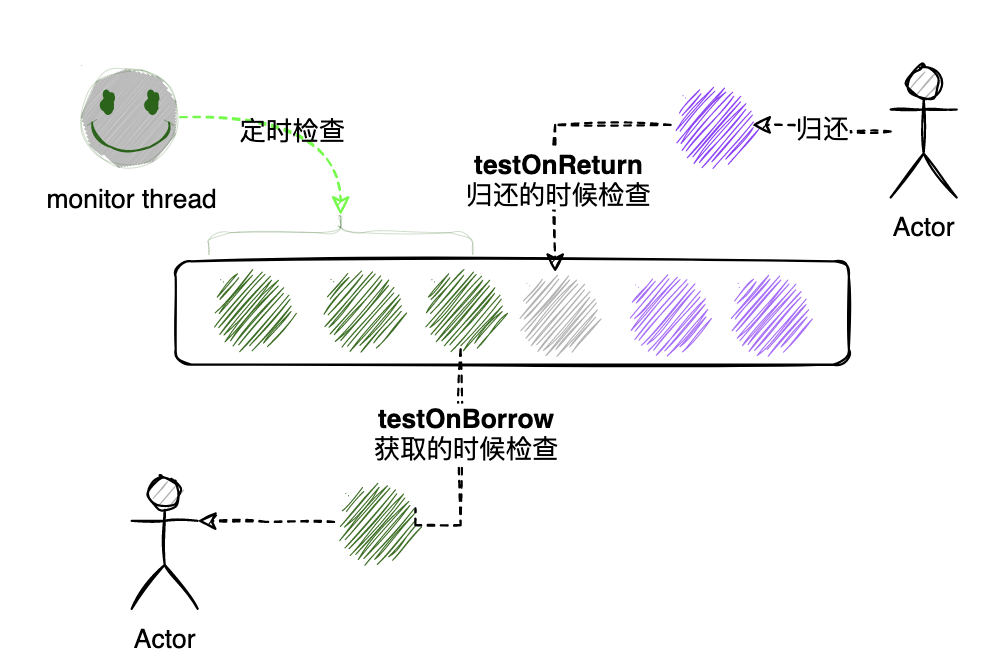
1.2 活性检测
2 实现
为了实现前面提到的容器具备的能力,以及对象获取流程,需要考虑几个东西:
-
容器的数据结构选择
用 List、 Map 还是 Queue ?亦或是组合起来用? -
空闲对象要不要单独用要给集合存一份?方便判断是否空、阻塞等待?
比如将空闲对象,用一个blockingqueue存一下,就能利用阻塞队列的能力实现超时等待 -
检测机制
- 在什么时候检测:常见的有 testOnBorrow 在申请到的时候检测、testOnReturn在归还的时候检测 这两个对性能有些影响; 单独开个检查线程,定时去扫描检查,这个是异步的 不会有testOnBorrow和testOnReturn的性能影响
- 检测哪些对象: 比如空闲超过 500ms 的对象
- 如何检查:这个需要根据具体对象的类型来,比如db连接的话一般是发送 “select 1” 看是否能正常执行
3 一个通用实现 apache commons pool
通过前面的介绍,可以知道对象池技术的核心过程大同小异,可以将对象获取流程、活性检测机制等封装成一个通用的工具,将对象本身的创建、活性检测逻辑开放给具体的对象实现来完成; apache commons pool 就是这么个工具, jedis底层的连接池就是直接用的这个
3.1 核心数据结构
LinkedBlockingDeque<PooledObject<T>> idleObjects空闲对象双向阻塞队列Map<IdentityWrapper<T>, PooledObject<T>> allObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();所有对象的map
apache commons pool 的容器用的 ConcurrentHashMap,并且将空闲的对象用一个双向阻塞队列单独连接起来;
这样他就能利用这个阻塞队列本身的特性,达到阻塞获取的逻辑,如果 idleObjects 是空的,就能 take()/poll(timeout) 阻塞在这里,等待其他线程归还对象队列里
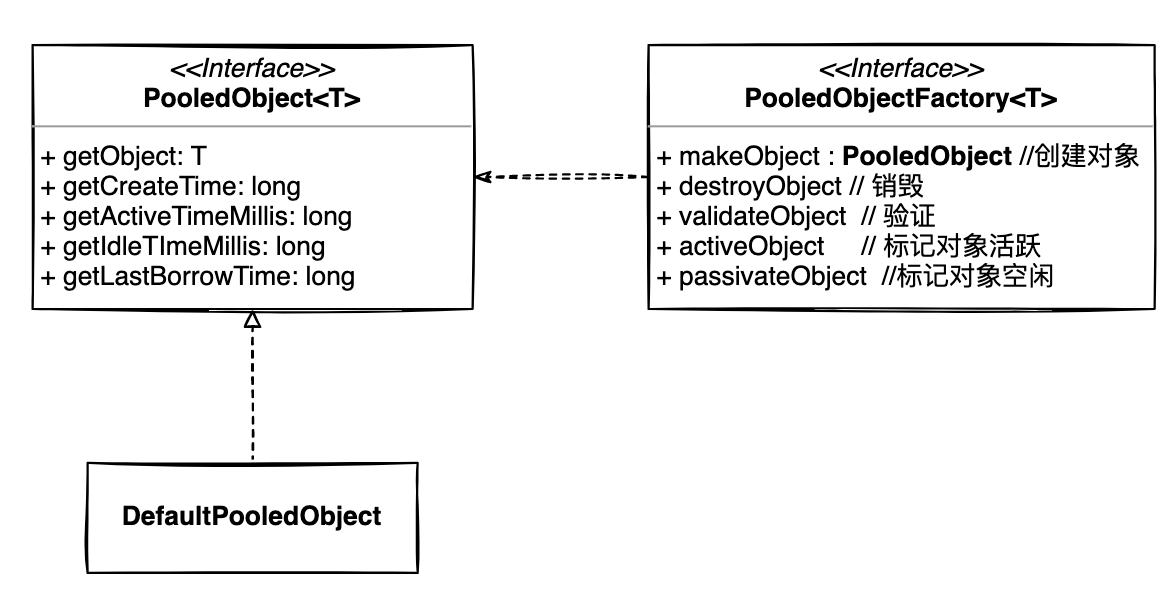
3.2 核心对象定义
- PooledObject 可池化的对象:包含真实对象、状态扭转及其创建时间、取出时间、空闲时间等指标信息
- PooledObjectFactory 对象工厂,负责对象的创建、销毁、检查等逻辑;它有个默认实现
DefaultPooledObject 提供了基本的实现,一般只要继承它重写对象创建和验活逻辑就可以了 - GenericObjectPool 就是对象容器了
3.3 代码细节
从池子中获取对象
T borrowObject(final long borrowMaxWaitMillis) {
//省略一些代码 ...
PooledObject<T> p = null;
// Get local copy of current config so it is consistent for entire
// method execution
final boolean blockWhenExhausted = getBlockWhenExhausted();
boolean create;
final long waitTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (p == null) {
create = false;
// 空闲队列 队首如果是空的,则创建一个新的对象
// 创建的逻辑里会校验是否超过最大连接数,然后利用 PooledObjectFactory创建对象
p = idleObjects.pollFirst();
if (p == null) {
p = create();
if (p != null) {
create = true;
}
}
// 阻塞从 idleObject 空闲阻塞队列获取对象
if (blockWhenExhausted) {
if (p == null) {
if (borrowMaxWaitMillis < 0) {
p = idleObjects.takeFirst();
} else {
//超时等待
p = idleObjects.pollFirst(borrowMaxWaitMillis,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
if (p == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException(
"Timeout waiting for idle object");
}
} else {
if (p == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Pool exhausted");
}
}
// 状态转换为已分配 ALLOCATE,记录借出时间等信息
if (!p.allocate()) {
p = null;
}
if (p != null) {
try {
// 允许 PooledObjectFactory 在成功获取到对象后做一些事,
// 比如jedis连接池获取到连接后会执行 select db 切换db
factory.activateObject(p);
} catch (final Exception e) {
try {
destroy(p);
} catch (final Exception e1) {
// Ignore - activation failure is more important
}
p = null;
if (create) {
final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException(
"Unable to activate object");
nsee.initCause(e);
throw nsee;
}
}
// 如果 testOnBorrow=true, 或者 testOnCreate=true + 此次对象是新建的
// 则会去校验对象的有效性 PooledObjectFactory#validateObject()
if (p != null && (getTestOnBorrow() || create && getTestOnCreate())) {
boolean validate = false;
Throwable validationThrowable = null;
try {
validate = factory.validateObject(p);
} catch (final Throwable t) {
PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t);
validationThrowable = t;
}
// 如果对象有效性校验失败,则销毁掉
if (!validate) {
try {
destroy(p);
destroyedByBorrowValidationCount.incrementAndGet();
} catch (final Exception e) {
// Ignore - validation failure is more important
}
p = null;
if (create) {
final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException(
"Unable to validate object");
nsee.initCause(validationThrowable);
throw nsee;
}
}
}
}
}
updateStatsBorrow(p, System.currentTimeMillis() - waitTime);
return p.getObject();
}
归还对象
public void returnObject(final T obj) {
// 校验下对象是否还存在
final PooledObject<T> p = allObjects.get(new IdentityWrapper<>(obj));
if (p == null) {
if (!isAbandonedConfig()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Returned object not currently part of this pool");
}
return; // Object was abandoned and removed
}
// 状态标记为 “归还中”
synchronized(p) {
final PooledObjectState state = p.getState();
if (state != PooledObjectState.ALLOCATED) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Object has already been returned to this pool or is invalid");
}
p.markReturning(); // Keep from being marked abandoned
}
final long activeTime = p.getActiveTimeMillis();
// 如果 testOnReturn=true,则在归回时校验对象是否还有效,如果无效了就销毁掉
if (getTestOnReturn()) {
if (!factory.validateObject(p)) {
try {
destroy(p);
} catch (final Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
try {
ensureIdle(1, false);
} catch (final Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
updateStatsReturn(activeTime);
return;
}
}
try {
factory.passivateObject(p);
} catch (final Exception e1) {
swallowException(e1);
try {
destroy(p);
} catch (final Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
try {
ensureIdle(1, false);
} catch (final Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
updateStatsReturn(activeTime);
return;
}
if (!p.deallocate()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Object has already been returned to this pool or is invalid");
}
// 如果此时对象池已经关闭了, 或者当前空闲对象数量大于maxIdle(最大空闲数量)则直接销毁掉
final int maxIdleSave = getMaxIdle();
if (isClosed() || maxIdleSave > -1 && maxIdleSave <= idleObjects.size()) {
try {
destroy(p);
} catch (final Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
} else {
if (getLifo()) {
idleObjects.addFirst(p);
} else {
idleObjects.addLast(p);
}
if (isClosed()) {
// Pool closed while object was being added to idle objects.
// Make sure the returned object is destroyed rather than left
// in the idle object pool (which would effectively be a leak)
clear();
}
}
updateStatsReturn(activeTime);
}
开启定期检查任务
final void startEvictor(final long delay) {
synchronized (evictionLock) {
// 关闭前已有的清理任务
if (null != evictor) {
EvictionTimer.cancel(evictor, evictorShutdownTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
evictor = null;
evictionIterator = null;
}
// 间隔时间大于0的话(默认为-1),才创建定时清理任务Evictor
// Evictor 是一个 Runable任务, 它会检查空闲队列里的对象数量是否超过 maxIdle,空闲时长是否超过 minEvictableTimeMillis
if (delay > 0) {
evictor = new Evictor();
EvictionTimer.schedule(evictor, delay, delay);
}
}
}
总结
apache commons pool 的对象池实现,比较通用,在性能要求不是太苛刻的情况下可以直接使用;
但是默认的对象实现在状态扭转等地方是用 synchronized 加锁来处理并发的,如果对性能要求比较高的话,需要考虑自定义其他实现方式,比如用 cas + retry 或 threadlocal 等方式减少并发冲突