解题报告 之 HDU5288 OO' s Sequence
Description
OO has got a array A of size n ,defined a function f(l,r) represent the number of i (l<=i<=r) , that there's no j(l<=j<=r,j<>i) satisfy a imod a j=0,now OO want to know

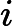

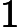


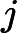

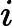

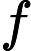
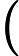
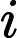




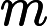
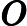

 (
(

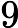

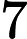 )
)

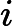

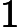


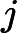

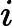

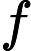
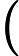
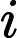




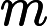


 (
(

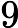

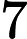 )
)
Input
There are multiple test cases. Please process till EOF.
In each test case:
First line: an integer n(n<=10^5) indicating the size of array
Second line:contain n numbers a i(0<a i<=10000)
In each test case:
First line: an integer n(n<=10^5) indicating the size of array
Second line:contain n numbers a i(0<a i<=10000)
Output
For each tests: ouput a line contain a number ans.
Sample Input
5 1 2 3 4 5
Sample Output
23
题目大意:给你n个数的序列(当中数可能反复)。对于每个子区间,求该子区间中没有因子也在该子区间的的个数。再把全部子区间内这种数的数量求和。比方例子中的 1
2 3 4 5,那么子区间[1,2,3]中这种数就是1。2,3三个。然后对于子区间2 3 4,这种数就仅仅有两个,由于4有因子2也在该子区间中。
分析:非常自然的想法是遍历每个子区间,再统计有多少个数,再加起来。但这样做是不可行的。这样就中了题目的陷阱,被那个公式给误导了,所以我们必需要跳出惯性思维。将关注的单位从子区间变到每个数。
考虑一个数。它能被统计多少次取决于什么呢?取决于它在多少个子区间内可以做到没有因子。所以我们非常自然的去关注离他近期的左右两个因子。由于这两个因子范围以外的子区间都没有卵用。
。
。比方5 5 2 3 3 4 3 2 5 5。那么对于4来说,我们找到左右两个因子2之后,就能够发现从5開始和结束的子区间都不会算到4。由于有2在那里杵着。
至此,问题转化为,找到每个数左右离它近期的因子。然后就行非常easy的知道这个数可以被统计多少次了。那么怎么去寻找左右两边的因子呢?有两种做法,首先介绍我的方法。注意到可能的数字一共仅仅有1e4个。先从左到右扫描依次更新两个数据,一是这个数最后出现的位置,用loc数组表示,还有一个是这个数左边离它近期的因子的位置则用该数的每个因子(遍历),求全部因子中最后出现的最大值。
然后再从右到左扫描,原理一样的。完毕之后再遍历序列,对于每个数求它被统计多少次就可以。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 10;
const int MAXM = 1e4 + 10;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int nums[MAXN]; //序列中的数
int lb[MAXN], rb[MAXN]; //序列中的数左右离他近期的因子的位置
int latest[MAXM];//某个数字最后出现的位置
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf( "%d", &n ) == 1)
{
memset( lb, 0, sizeof lb );
memset( rb, INF, sizeof rb );
//reset
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf( "%d", &nums[i] );
}//input
for(int i = 0; i < MAXM; i++) latest[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= sqrt( nums[i] ); j++)
{//遍历每一个因子
if(nums[i] % j == 0)
{
lb[i] = max( lb[i], latest[j] );
lb[i] = max( lb[i], latest[nums[i] / j] );
}
}
latest[nums[i]] = i; //更新位置。注意要遍历后更新,由于本身也是自己的因子
}// tackle 1
for(int i = 0; i < MAXM; i++) latest[i] = n + 1;
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= sqrt( nums[i] ); j++)
{
if(nums[i] % j == 0)
{
rb[i] = min( rb[i], latest[j] );
rb[i] = min( rb[i], latest[nums[i] / j] );
}
}
latest[nums[i]] = i;
}// tackle 2 同理
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ans = (ans + (i - lb[i])*(rb[i] - i)) % MOD;
//统计序列中每一个数被统计的次数。能够理解为范围内左边选一个数的选法*右边选一个数的选法。
}
printf( "%lld
", ans );
}
return 0;
}另一种方法是,记录每一个数字出现的位置,每次更新的时候用二分去找距离它近期的因子的位置。可是非常麻烦也更慢。