Tensor Flow 是一个采用数据流图(data flow graphs),用于数值计算的开源软件库。节点(Nodes)在图中表示数学操作,图中的线(edges)则表示在节点间相互联系的多维数据数组,即张量(tensor)。
这是谷歌开源的一个强大的做深度学习的软件库,提供了C++ 和 Python 接口,下面给出用Tensor Flow 建立CNN 网络做笑脸识别的一个简单用例。
我们用到的数据库是GENKI4K,这个数据库有4000张图像,首先做人脸检测与剪切,将图像resize到
网络的基本结构如下:
input -> conv 1 -> pool 1 -> conv 2 -> pool 2 -> conv 3 -> pool 3 -> fc 1 -> out
input ->
conv 1 -> filter size:
pool 1 -> filter size:
conv 2 -> filter size:
pool 2 -> filter size:
conv 3 -> filter size:
pool 3 -> filter size:
fc 1 -> hidden nodes:
out ->
import string, os, sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.io
import random
import tensorflow as tf
# set the folder path
dir_name = 'GENKI4K/Feature_Data'
# set the file path
files = os.listdir(dir_name)
for f in files:
print (dir_name + os.sep + f)
file_path = dir_name + os.sep + files[10]
# get the data
dic_mat = scipy.io.loadmat(file_path)
data_mat = dic_mat['Face_64']
file_path2 = dir_name + os.sep + files[15]
dic_label = scipy.io.loadmat(file_path2)
label_mat = dic_label['Label']
file_path3 = dir_name + os.sep+files[16]
# get the label
label = label_mat.ravel()
label_y = np.zeros((4000, 2))
label_y[:, 0] = label
label_y[:, 1] = 1-label
T_ind=random.sample(range(0, 4000), 4000)
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
batch_size = 40
batch_num=4000/batch_size
train_epoch=100
# Network Parameters
n_input = 4096 # data input (img shape: 64*64)
n_classes = 2 # total classes (smile & non-smile)
dropout = 0.5 # Dropout, probability to keep units
# tf Graph input
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #dropout (keep probability)
# Create some wrappers for simplicity
def conv2d(x, W, b, strides=1):
# Conv2D wrapper, with bias and relu activation
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='VALID')
x = tf.nn.bias_add(x, b)
return tf.nn.relu(x)
def maxpool2d(x, k=2):
# MaxPool2D wrapper
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1],
padding='VALID')
# Create model
def conv_net(x, weights, biases, dropout):
# Reshape input picture
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 64, 64, 1])
# Convolution Layer
conv1 = conv2d(x, weights['wc1'], biases['bc1'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv1 = maxpool2d(conv1, k=2)
# Convolution Layer
conv2 = conv2d(conv1, weights['wc2'], biases['bc2'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv2 = maxpool2d(conv2, k=2)
# Convolution Layer
conv3 = conv2d(conv2, weights['wc3'], biases['bc3'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv3 = maxpool2d(conv3, k=2)
# Fully connected layer
# Reshape conv2 output to fit fully connected layer input
fc1 = tf.reshape(conv3, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['wd1']), biases['bd1'])
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
# Apply Dropout
# fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1, dropout)
# Output, class prediction
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['out']), biases['out'])
return out
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
# 5x5 conv, 1 input, 16 outputs
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 1, 16])),
# 7x7 conv, 16 inputs, 8 outputs
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7, 7, 16, 8])),
# 5x5 conv, 8 inputs, 16 outputs
'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 8, 16])),
# fully connected, 7*7*64 inputs, 1024 outputs
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*16, 100])),
# 1024 inputs, 10 outputs (class prediction)
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([100, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([16])),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([8])),
'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([16])),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([100])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
# Construct model
pred = conv_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)
# Define loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Evaluate model
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(0, train_epoch):
for batch in range (0, batch_num):
arr_3 = T_ind[batch * batch_size:(batch + 1) * batch_size]
batch_x = data_mat[arr_3, :]
batch_y = label_y[arr_3, :]
# Run optimization op (backprop)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y,
keep_prob: dropout})
# Calculate loss and accuracy
loss, acc = sess.run([cost, accuracy], feed_dict={x: data_mat,
y: label_y,
keep_prob: 1.})
print("Epoch: " + str(epoch) + ", Loss= " +
"{:.3f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " +
"{:.3f}".format(acc))
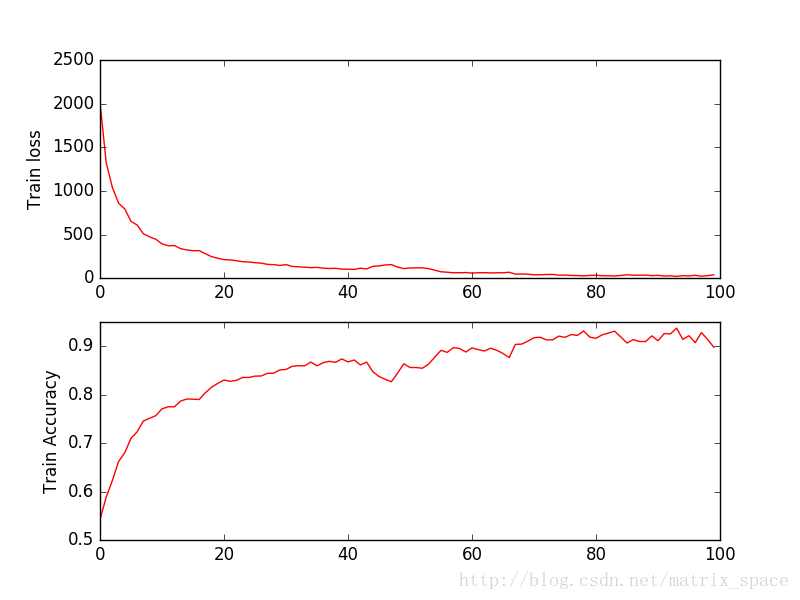
100个训练周期的结果: