一、简介
最近马三在工作中经常使用到了lua 中的 os.date( ) 和 os.time( )函数,不过使用的时候都是不得其解,一般都是看项目里面怎么用,然后我就模仿写一下。今天正好稍微有点空闲时间就好好地收集了一下相关资料并学习了一下,并将学习结果记录成此博客。
二、os.time和os.date函数说明
1.os.time()函数
os.time()的函数原型与Lua官方的解释如下:

如果没有任何参数,就会返回当前时间。如果参数一个table,并且table的域必须有 year, month, day, 可有也可以没有 hour, min, sec, isdst,则会返回table所代表日期的时间,如果未定义后几项,默认时间为当天正午(12:00:00)。 返回值是一个 number ,其值取决于你的系统。返回值通常被用于 os.date 和 os.difftime。
具体的用法可以看下面几段代码样例:
print(os.time()) print(os.time({day=26,month=4,year=2018})) print(os.date("%y/%m/%d, %H:%M:%S",os.time({day=26,month=4,year=2018})))
其执行结果如下图所示:
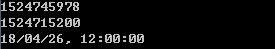
图1:os.time样例执行结果示意图
os.time()函数的源码如下,可以仔细研读一下,对提高代码水平有帮助:
1 static int os_time (lua_State *L) { 2 time_t t; 3 if (lua_isnoneornil(L, 1)) /* called without args? */ 4 t = time(NULL); /* get current time */ 5 else { 6 struct tm ts; 7 luaL_checktype(L, 1, LUA_TTABLE); 8 lua_settop(L, 1); /* make sure table is at the top */ 9 ts.tm_sec = getfield(L, "sec", 0); 10 ts.tm_min = getfield(L, "min", 0); 11 ts.tm_hour = getfield(L, "hour", 12); 12 ts.tm_mday = getfield(L, "day", -1); 13 ts.tm_mon = getfield(L, "month", -1) - 1; 14 ts.tm_year = getfield(L, "year", -1) - 1900; 15 ts.tm_isdst = getboolfield(L, "isdst"); 16 t = mktime(&ts); 17 } 18 if (t == (time_t)(-1)) 19 lua_pushnil(L); 20 else 21 lua_pushnumber(L, (lua_Number)t); 22 return 1; 23 }
2.os.date()函数
os.date()函数的原型与Lua官方解释如下:

第一个参数是时间的格式化参数,如果设置了则会按照固定的格式来格式化时间。若设置time参数,则按time指定的时间格式化,否则按当前时间格式化。如果format 以 ! 开始, date 会被格式化成协调世界时(Coordinated Universal Time) 。 *t 将返一个带year(4位), month(1-12), day (1--31), hour (0-23), min (0-59), sec (0-61), wday (星期几, 星期天为1), yday (年内天数), isdst (是否为日光节约时间true/false)的表。若没有*t则返回一个按C的strftime函数格式化的字符串 若不带参数,则按当前系统的设置返回格式化的字符串 os.date() <=> os.date("%c")。
对于format参数,马三在这里给大家提供了一个列表,分别列出了各种format参数和对应的含义:
%a - Abbreviated weekday name (eg. Wed) %A - Full weekday name (eg. Wednesday) %b - Abbreviated month name (eg. Sep) %B - Full month name (eg. September) %c - Date and time representation appropriate for locale (eg. 23/04/07 10:20:41) (Standard date and time string ) - see below for using os.setlocale to get the correct locale. %d - Day of month as decimal number (01 - 31) %H - Hour in 24-hour format (00 - 23) %I - Hour in 12-hour format (01 - 12) %j - Day of year as decimal number (001 - 366) %m - Month as decimal number (01 - 12) %M - Minute as decimal number (00 - 59) %p - Current locale’s A.M./P.M. indicator for 12-hour clock (eg. AM/PM) %S - Second as decimal number (00 - 59) %U - Week of year as decimal number, with Sunday as first day of week 1 (00 - 53) %w - Weekday as decimal number (0 - 6; Sunday is 0) %W - Week of year as decimal number, with Monday as first day of week 1 (00 - 53) %x - Date representation for current locale (Standard date string) %X - Time representation for current locale (Standard time string) %y - Year without century, as decimal number (00 - 99) (eg. 07) %Y - Year with century, as decimal number (eg. 2007) %Z - Time-zone name or abbreviation; no characters if time zone is unknown %% - Percent sign
具体的用法,我们依然可以参考下面的几段代码样例:
1 print("=================os.date test===============") 2 print(os.date()) 3 print(os.date("%x",os.time())) 4 print(os.date("*t")) 5 print(os.date("*t").year) 6 print(os.date("*t").month) 7 print(os.date("*t").day) 8 print(os.date("*t").hour) 9 print(os.date("*t").wday) 10 -- 显示当前年份 11 print(os.date("%Y")) 12 -- 显示当前是一年中的第几周 13 print(os.date("%U")) 14 -- 组合格式化时间 15 print(os.date("%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M:%S",os.time()))
其执行结果如下图所示:
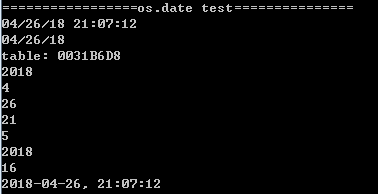
图2:os.date()样例函数执行结果示意图
os.date( )函数源码如下:
1 static int os_date (lua_State *L) { 2 size_t slen; 3 const char *s = luaL_optlstring(L, 1, "%c", &slen); 4 time_t t = luaL_opt(L, l_checktime, 2, time(NULL)); 5 const char *se = s + slen; /* 's' end */ 6 struct tm tmr, *stm; 7 if (*s == '!') { /* UTC? */ 8 stm = l_gmtime(&t, &tmr); 9 s++; /* skip '!' */ 10 } 11 else 12 stm = l_localtime(&t, &tmr); 13 if (stm == NULL) /* invalid date? */ 14 luaL_error(L, "time result cannot be represented in this installation"); 15 if (strcmp(s, "*t") == 0) { 16 lua_createtable(L, 0, 9); /* 9 = number of fields */ 17 setallfields(L, stm); 18 } 19 else { 20 char cc[4]; /* buffer for individual conversion specifiers */ 21 luaL_Buffer b; 22 cc[0] = '%'; 23 luaL_buffinit(L, &b); 24 while (s < se) { 25 if (*s != '%') /* not a conversion specifier? */ 26 luaL_addchar(&b, *s++); 27 else { 28 size_t reslen; 29 char *buff = luaL_prepbuffsize(&b, SIZETIMEFMT); 30 s++; /* skip '%' */ 31 s = checkoption(L, s, se - s, cc + 1); /* copy specifier to 'cc' */ 32 reslen = strftime(buff, SIZETIMEFMT, cc, stm); 33 luaL_addsize(&b, reslen); 34 } 35 } 36 luaL_pushresult(&b); 37 } 38 return 1; 39 }
3.计算时间差
在开发过程中我们经常遇到需要计算两个时间t1,t2的时间差这种需求,我们可以直接使用os.difftime( )这个自带的函数来完成,当然我们也可以自己实现一个符合自己要求的函数。例如,策划经常会在表格中配置一些活动/玩法的开启时间等,样式如下图所示:
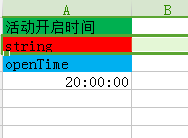
图3:时间差数据表示意图
然后我们就可以利用下面的代码实现求时间差了,它会返回当前时间和配置时间相差的秒数:
1 Split = function(szFullString,szSeprator) 2 local nFindStartIndex = 1 3 local nSplitIndex = 1 4 local nSplitArray = {} 5 while true do 6 local nFindLastIndex = string.find(szFullString,szSeprator,nFindStartIndex) 7 if not nFindLastIndex then 8 nSplitArray[nSplitIndex] = string.sub(szFullString,nFindStartIndex,string.len(szFullString)) 9 break 10 end 11 nSplitArray[nSplitIndex] = string.sub(szFullString,nFindStartIndex,nFindLastIndex - 1) 12 nFindStartIndex = nFindLastIndex + string.len(szSeprator) 13 nSplitIndex = nSplitIndex + 1 14 end 15 return nSplitArray 16 end 17 18 formatTime = function( timeStr ) 19 local splited = Split(timeStr, ":") 20 local h = splited[1] 21 local m = splited[2] 22 return tonumber(h), tonumber(m) 23 end 24 25 getRemainTime = function(timeStr) 26 local h1, m1 = formatTime(timeStr) 27 local curTime = os.date("*t", os.time()) 28 local curH = curTime.hour 29 local curM = curTime.min 30 31 local remainH = h1 - curH 32 local remainM = m1 - curM 33 local totalRemainSeCond = remainH * 3600 + remainM * 60 34 return totalRemainSeCond 35 end
三、总结
对于一些lua中的源码我们可以到这里去下载并查看学习:传送门 。最近项目实在是太忙了,忙得晕头转向的,天天加班到深夜,真是哔了狗了。今天好不容易挤出点时间更新点东西,真鸡儿难受~
本篇博客中的代码已经同步到Github:https://github.com/XINCGer/Unity3DTraining/tree/master/SomeTest/os_time 欢迎fork!
作者:马三小伙儿
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/msxh/p/8955150.html
请尊重别人的劳动成果,让分享成为一种美德,欢迎转载。另外,文章在表述和代码方面如有不妥之处,欢迎批评指正。留下你的脚印,欢迎评论!