今天我们用python进行体育竞技分析,预测球队成绩
一.体育竞技分析的IPO模式:
输入I(input):两个球员的能力值,模拟比赛的次数(其中,运动员的能力值,可以通过发球方赢得本回合的概率来表示,
一个能力值为0.8的球员,在他发球时,有80%的可能性赢得1分)
处理P(process):模拟比赛过程
输出O(output):两个球员获胜的概率
该体育竞技程序,我们采用自顶向下的设计方法。
自顶向下的设计是一种解决复杂问题的行之有效的方法。其步骤如下
自顶向下设计的基本思想,如下图:

二.我们首先采用兵乓球的比赛规则
一局比赛中,先得11分的一方为胜方,如果10平后,则比对方多得两分为胜方
一场比赛中,采用7局四胜的方式
代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed May 15 12:49:17 2019 @author: moyulin """ from random import random def printIntro(): print("BY 2018310143103") print("这个程序模拟两个选手A和B的兵乓球比赛") print("程序运行需要A和B的能力值(以0到1之间的小数表示)") def getInputs(): a = eval(input("请输入选手A的能力值(0-1): ")) b = eval(input("请输入选手B的能力值(0-1): ")) n = eval(input("请输入模拟比赛的局数: ")) return a, b, n def simNGames(n, probA, probB): WinsA, WinsB = 0, 0 winsA, winsB = 0, 0 for i in range(1,n+1): scoreA, scoreB = simOneGame(probA, probB) if scoreA > scoreB: winsA += 1 else: winsB += 1 if i%7==0: if winsA>winsB: WinsA+=1 print("单打第{}场胜利的为A".format(int(i/7))) else: WinsB+=1 print("单打第{}场胜利的为B".format(int(i/7))) winsA,winsB=0,0 return WinsA, WinsB def gameOver(a,b): if a>=10 and b>=10: if abs(a-b)==2: return True if a<10 or b<10: if a==11 or b==11: return True else: return False def simOneGame(probA, probB): scoreA, scoreB = 0, 0 serving = "A" while not gameOver(scoreA, scoreB): if serving == "A": if random() < probA: scoreA += 1 else: scoreB +=1 serving="B" else: if random() < probB: scoreB += 1 else: scoreA += 1 serving="A" return scoreA, scoreB def printSummary(winsA, winsB): n = winsA + winsB print("竞技分析开始,共模拟{}场比赛".format(n)) print("选手A获胜{}场比赛,占比{:0.1%}".format(winsA, winsA/n)) print("选手B获胜{}场比赛,占比{:0.1%}".format(winsB, winsB/n)) def main(): printIntro() probA, probB, n = getInputs() WinsA, WinsB = simNGames(n, probA, probB) printSummary(WinsA, WinsB) main()
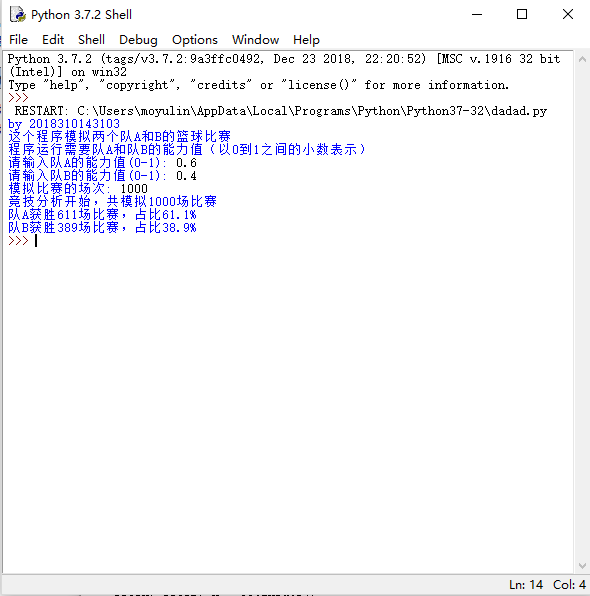
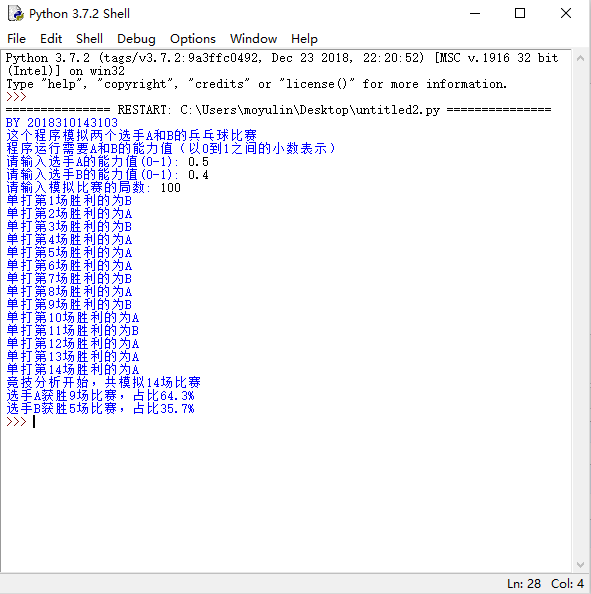
运行结果如下:
三.运用pyinstaller打包应用程序,使之可运行
win+cmd打开命令行
1.安装pyinstaller库
pip install pyinstaller
安装完成后就可以使用了,下面介绍pyinstaller的部分使用方法
-F, –onefile 打包一个单个文件,如果你的代码都写在一个.py文件的话,可以用这个,如果是多个.py文件就别用
-D, –onedir 打包多个文件,在dist中生成很多依赖文件,适合以框架形式编写工具代码,我个人比较推荐这样,代码易于维护
-K, –tk 在部署时包含 TCL/TK
-a, –ascii 不包含编码.在支持Unicode的python版本上默认包含所有的编码.
-d, –debug 产生debug版本的可执行文件
-w,–windowed,–noconsole 使用Windows子系统执行.当程序启动的时候不会打开命令行(只对Windows有效)
-c,–nowindowed,–console
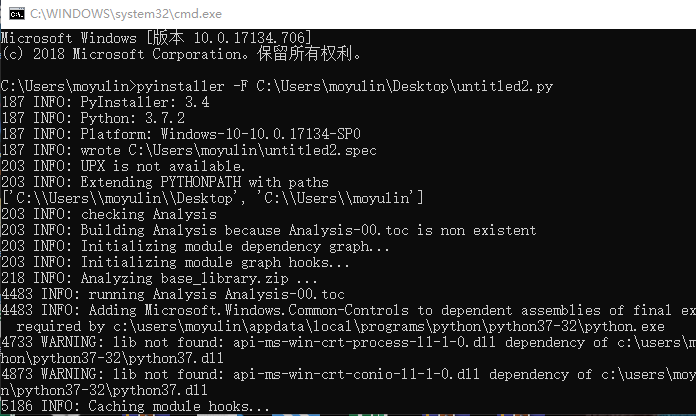
2.打开命令行使用
输入
pyinstaller -F C:#py文件地址
图例
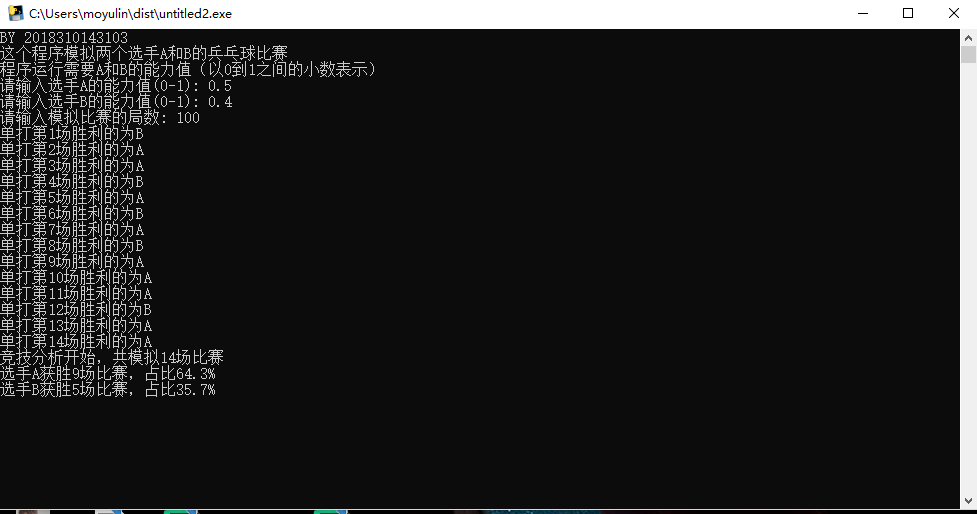
最后回到根目录上会看到dist文件夹,里面有个exe文件,直接运行即可,如图
四.模拟体育竞技分析之篮球
假设谁先获得100分谁胜利
代码如下
from random import random def printIntro(): print("by 2018310143103") print("这个程序模拟两个队A和B的篮球比赛") print("程序运行需要队A和队B的能力值(以0到1之间的小数表示)") def getInputs(): a = eval(input("请输入队A的能力值(0-1): ")) b = eval(input("请输入队B的能力值(0-1): ")) n = eval(input("模拟比赛的场次: ")) return a, b, n def simNGames(n, probA, probB): winsA, winsB = 0, 0 for i in range(n): scoreA, scoreB = simOneGame(probA, probB) if scoreA > scoreB: winsA += 1 else: winsB += 1 return winsA, winsB def gameOver(a,b): return a==100 or b==100 def simOneGame(probA, probB): scoreA, scoreB = 0, 0 serving = "A" while not gameOver(scoreA, scoreB): if serving == "A": if random() < probA: scoreA += 1 else: scoreB += 1 else: if random() < probB: scoreB += 1 else: scoreA += 1 return scoreA, scoreB def printSummary(winsA, winsB): n = winsA + winsB print("竞技分析开始,共模拟{}场比赛".format(n)) print("队A获胜{}场比赛,占比{:0.1%}".format(winsA, winsA/n)) print("队B获胜{}场比赛,占比{:0.1%}".format(winsB, winsB/n)) def main(): printIntro() probA, probB, n = getInputs() winsA, winsB = simNGames(n, probA, probB) printSummary(winsA, winsB) main()
运行结果如下