LinkedHashMap源码分析
为什么要有LinkedHashMap?
在分析HashMap的时候提到了HashMap是无序的,即添加节点的顺序和遍历的顺序不一致
@Test
public void test1() {
HashMap<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<String, String>();
hashMap.put("tom", "american");
hashMap.put("jack", "chainese");
hashMap.put("mary", "japanese");
Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = hashMap.entrySet();
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+":"+value);
}
}
输出:
tom:american
mary:japanese
jack:chainese
LinkedHashMap保证节点的顺序,这也是LinkedHashMap和HashMap的主要区别
@Test
public void test2() {
LinkedHashMap<String,String> linkedHashMap=new LinkedHashMap();
linkedHashMap.put("tom", "american");
linkedHashMap.put("jack", "chainese");
linkedHashMap.put("mary", "japanese");
Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = linkedHashMap.entrySet();
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+":"+value);
}
}
输出:
tom:american
jack:chainese
mary:japanese
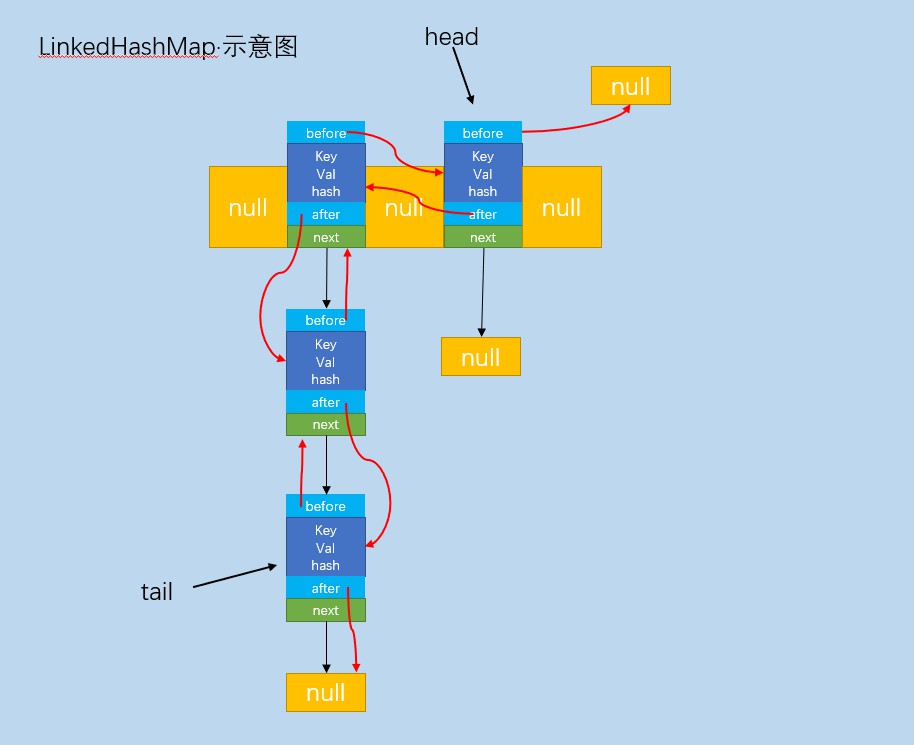
存储示意图
类结构
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类,它对HashMap做了一些增强
节点
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {//LinkedHashMap的Entry节点是HashMap的Node节点的子类
Entry<K,V> before, after;//新增了before、after分别指向前驱和后继
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
//直接使用HashMap的Node节点构造方法
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
属性
//头指针指向第一个添加节点
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
//尾指针指向最后一个添加节点
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
//排序规则,true的话按照访问顺序排序,最近访问的放到最后,false也是默认按照插入顺序排序
final boolean accessOrder;
构造方法
//指定初始化容量和加载因子
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
//指定初始化容量
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
//无参构造方法
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
//使用Map初始化
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
//指定初始化容量、加载因子、排序规则
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
方法
LinkedHashMap中并没有put方法,所以使用的是父类HashMap的put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//当根据hash计算的下标位置没放节点,调用LinkedHashMap的newNode方法
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
//如果是指定访问顺序排序,那么替换后,把节点移动到最后
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
//保存LinkedHashMap的为指针
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)//尾指针为null说明LinkedHashMap中没元素
head = p;
else {//有元素
//新节点的前驱指向添加之前的尾指针
p.before = last;
//添加之前的尾指针节点的后继指向新节点
last.after = p;
}
}
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {//如果指定了按访问顺序排序且替换的节点不是最末尾的节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {//removeEldestEntry方法返回false所以不会进入if
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
get(Object)根据key获取值
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)//调用HashMap的方法拿到值
return null;
if (accessOrder)//如果是按照访问顺序排序的话
//访问过后要修改顺序
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
//把访问的节点移动到链表的最末端
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {//按访问顺序排序并且访问节点不是最后一个节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
remove(Object)方法是调用父类HashMap的方法
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
//调用LinkedHashMap·的方法来实现双链的删除
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
//把要移除节点的前驱后继置为null
p.before = p.after = null;
if (b == null)//b为null即移除的就是第一个元素
//头指针指向移除元素的后继
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a == null)//a为null即移除的元素是最后一个元素
//尾指针指向移除元素的前驱
tail = b;
else
a.before = b;
}