基本概念
Spring 把所有能记录信息的载体,如各种类型的文件、二进制流等都称为资源。
对 Spring 开发者来说,最常用的资源就是 Spring 配置文件(通常是一份 XML 格式的文件)。
Spring 为资源访问提供了一个 Resource 接口,利用该接口来表示不同类型的资源。并且 Spring 框架本身大量使用了 Resource 接口来访问底层资源。
Resource 接口是具体资源访问策略的抽象,也是所有资源访问类所实现的接口。
内部构造
Resource 接口继承了 InputStreamSource 接口,通过该接口,可以将任意形式的资源转成流来操作。
下面来看它的源码:
- InputStreamSource
public interface InputStreamSource {
// 表示任意形式的资源都可以被转换成输入流
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}- Resoure
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
// 资源是否存在,true 表示存在
boolean exists();
// 资源是否可读,true 表示存在
boolean isReadable();
// 资源是否打开,true 表示资源只能被读取一次然后关闭以避免资源泄露
boolean isOpen();
// 当前资源能由 java.util.URL 代表时,则返回该 URL,否则抛出异常
URL getURL() throws IOException;
// 当前资源能由 java.util.URI 代表时,则返回该 URI,否则抛出异常
URI getURI() throws IOException;
// 当前资源能由 java.io.File 代表时,则返回该 File,否则抛出异常
File getFile() throws IOException;
// 资源的长度,一般是值代表的文件资源的长度
long contentLength() throws IOException;
// 资源的最后修改时间
long lastModified() throws IOException;
// 创建相对于当前资源代表的资源
// 比如当前资源代表文件资源 [d:/test/] 则 [createRelative("test.txt")] 将返回文件资源 [d:/test/test.txt]
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
// 资源的文件路径,比如 File 资源就返回它的文件路径,URL 资源则返回空
String getFilename();
// 资源的描述符,通常就是资源的全路径(实际文件名或实际URL地址)。
String getDescription();
}Resource 接口是 Spring 资源访问策略的抽象,它本身并不提供任何资源访问实现,具体的资源访问由该接口的实现类完成——每个实现类代表一种资源访问策略。
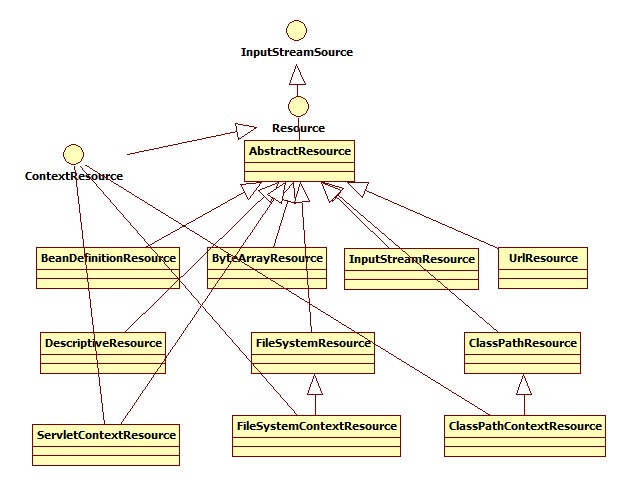
在 Spring 中存在这大量的 Resource 实现类来表示不同形式的资源。具体如下图所示:
- 继承关系
- 常见的资源类型
资源类型
Resource 实现类针对不同的的底层资源,提供了相应的资源访问逻辑,并提供便捷的包装,以利于客户端程序的资源访问。这其实也是典型的策略模式。下面来看几种常见的资源类型以及对应的访问方法。
1.ByteArrayResource
访问字节数组资源的实现类。它在其内部维护着一个字节数组,并该资源一旦创建就表示其一定存在,因此 exists 方法默认返回 true。我们可以通过将字节数组转换成 ByteArrayInputStream 来实现对它的访问。具体源码如下:
public class ByteArrayResource extends AbstractResource {
// 字节数组
private final byte[] byteArray;
// 描述,可由开发者自定义,为空时则为默认值
private final String description;
// 构造函数
public ByteArrayResource(byte[] byteArray) {
this(byteArray, "resource loaded from byte array");
}
// 构造函数
public ByteArrayResource(byte[] byteArray, String description) {
if (byteArray == null) {
// 抛出异常
}
this.byteArray = byteArray;
this.description = (description != null ? description : "");
}
// 关键 -> 将数组转换成 ByteArrayInputStream
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new ByteArrayInputStream(this.byteArray);
}
// 关键 -> 默认返回 true,表示该资源一旦被创建就默认存在
public boolean exists() {
return true;
}
//省略部分源码...
}接着来看如何使用 ByteArrayResource 访问字节数组:
// 定义流读取方法
public static void readResource(Resource resource) throws IOException{
InputStream is = resource.getInputStream();
byte[ ] buf = new byte[1024];
int len =0;
while((len=is.read(buf)) !=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len) );
}
}
public static void main(String [ ] args) throws IOException {
Resource resouce = new ByteArrayResource("hello".getBytes());
readResource(resouce);
}2.InputStreamResource
访问输入流资源的实现类。在其内部维护着一个输入流,因此我们可以直接取得该输入流并对其进行访问。值得注意的是,该输入流只允许读取一次(对应它的 isOpen 方法),若再次读取则会抛出异常。
public class InputStreamResource extends AbstractResource {
// 字符输入流
private final InputStream inputStream;
// 描述
private final String description;
// 表示是否可读
private boolean read = false;
public InputStreamResource(InputStream inputStream) {
this(inputStream, "resource loaded through InputStream");
}
public InputStreamResource(InputStream inputStream, String description) {
if (inputStream == null) {
// 抛出异常...
}
this.inputStream = inputStream;
this.description = (description != null ? description : "");
}
// 关键--> 直接取得输入流(本身就是流,无需再转换)
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException, IllegalStateException {
// 表示只能读取一次,对应 isOpen
if (this.read) {
// 抛出异常...
}
this.read = true;
return this.inputStream;
}
// 为 ture 表示只能读取一次
public boolean isOpen() {
return true;
}
// 关键 -> 默认返回 ture
public boolean exists() {
return true;
}
}接着来看如何使用 InputStreamResource 访问字符输入流:
// 用 bis 表示输入流
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("hello".getBytes());
InputStreamResource resource = new InputStreamResource(bis);
readByteArrayResource(resource);
// 关键-> 再次读取资源,抛出异常
readResource(resource);3.FileSystemResource
访问文件系统里资源的实现类。该类访问的资源为 java.io.File,即文件对象。它通过 file 的路径找到指定的文件。并且可以将其转成 FileInputStream 来操作。
isOpen 方法继承自父类 AbstractResource ,返回 false,表示该资源可以被多次读取。
public class FileSystemResource extends AbstractResource implements WritableResource {
// 文件
private final File file;
// 文件路径
private final String path;
public FileSystemResource(File file) {
Assert.notNull(file, "File must not be null");
this.file = file;
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(file.getPath());
}
public FileSystemResource(String path) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.file = new File(path);
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
}
// 关键 -> 根据 file 来判断,如果指定路径不存该文件,则返回 false
public boolean exists() {
return this.file.exists();
}
// 是否可读
public boolean isReadable() {
return (this.file.canRead() && !this.file.isDirectory());
}
// 关键 -> 取得 FileInputStream
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileInputStream(this.file);
}
// 关键 -> 创建相相对于当前资源路径下的资源。
// 假设当前的 file 路径为 D:/DEMO/HELLO.TXT,且 relativePath = GOOD.TXT
// 则该方法创建的资源路径为 D:/DEMO/GOOD.TXT
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);
return new FileSystemResource(pathToUse);
}
}接着来看如何使用 FileSystemResource 访问文件对象:
Resource resource = new FileSystemResource("D:/DEMO/HELLO.txt");
// 关键 -> 表示读取 D:/DEMO/HELLO/GOOD.txt 路径下的文件
Resource resource2 = resource.createRelative("HELLO/GOOD.txt");
readResource(resource);
readResource(resource2);4.ClassPathResource
用来访问类加载路径下的资源,相对于其他的 Resource 实现类,其主要优势是方便访问类加载路径里的资源,尤其对于 Web 应用,ClassPathResource 可自动搜索位于 WEB-INF/classes 下的资源文件,无须使用绝对路径访问。
public class ClassPathResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource {
// 路径
private final String path;
// 类加载器
private ClassLoader classLoader;
// 类对象
private Class<?> clazz;
// 关键 ->使用默认的 ClassLoader 加载 path 类路径资源
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, (ClassLoader) null);
}
// 关键-> 使用指定的 ClassLoader 加载 path 类路径资源
public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
this.path = pathToUse;
this.classLoader = ( classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader() );
}
// 关键-> 指定的类进行加载资源,将加载相对于当前类的路径的资源
public ClassPathResource(String path, Class<?> clazz) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.clazz = clazz;
}
protected ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader, Class<?> clazz) {
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.classLoader = classLoader;
this.clazz = clazz;
}
// 获取类加载器
public final ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return ( this.clazz != null ? this.clazz.getClassLoader() : this.classLoader );
}
// 资源是否存在
public boolean exists() {
return ( resolveURL() != null );
}
protected URL resolveURL() {
if (this.clazz != null) {
return this.clazz.getResource(this.path);
} else if (this.classLoader != null) {
return this.classLoader.getResource(this.path);
} else {
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(this.path);
}
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if (this.clazz != null) {
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else if (this.classLoader != null) {
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);
return new ClassPathResource(pathToUse, this.classLoader, this.clazz);
}
}接着来看如何使用 ClassPathResource 访问类加载路径下的资源:
public static void main(String [ ] args) throws IOException {
Test test = new Test;
test.readResource();
}
public void readResource() throws IOException{
// 假设该类的路径是 comdemo,则该资源的路径为 comdemocomdemohello.txt
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("com\demo\hello.txt",this.getClass());
InputStream is = resource.getInputStream();
byte[ ] buf = new byte[1024];
int len =0;
while((len=is.read(buf)) !=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len) );
}
is.close();
}5.UrlResource
该资源代表 URL 资源,用于简化 URL 资源访问,且它可以被多次读取。
一般支持如下资源访问:
-
http:通过标准的http协议访问web资源,如new UrlResource(“http://地址”);
-
ftp:通过ftp协议访问资源,如new UrlResource(“ftp://地址”);
-
file:通过file协议访问本地文件系统资源,如new UrlResource(“file:d:/test.txt”);
6.ServletContextResource
该资源代表 web 应用资源,用于简化 Servlet 容器的 ServletContext 接口的 getResource 操作和 getResourceAsStream 操作。