sersync+rsync原理及部署
转载于http://blog.51cto.com/liubao0312/1677586
一、为什么要用rsync+sersync架构?
1、sersync是基于inotify开发的,类似于inotify-tools的工具
2、sersync可以记录下被监听目录中发生变化的(包括增加、删除、修改)具体某一个文件或者某一个目录的名字,然后使用rsync同步的时候,只同步发生变化的文件或者目录
二、rsync+inotify-tools与rsync+sersync架构的区别?
1、rsync+inotify-tools
a、inotify只能记录下被监听的目录发生了变化(增,删,改)并没有把具体是哪个文件或者哪个目录发生了变化记录下来;
b、rsync在同步的时候,并不知道具体是哪个文件或目录发生了变化,每次都是对整个目录进行同步,当数据量很大时,整个目录同步非常耗时(rsync要对整个目录遍历查找对比文件),因此效率很低
2、rsync+sersync
a、sersync可以记录被监听目录中发生变化的(增,删,改)具体某个文件或目录的名字;
b、rsync在同步时,只同步发生变化的文件或目录(每次发生变化的数据相对整个同步目录数据来说很小,rsync在遍历查找对比文件时,速度很快),因此效率很高。
总结:
当同步的目录数据量不大时,建议使用rsync+inotify
当同步的目录数据量很大时(几百G甚至1T以上)文件很多时,建议使用rsync+sersync
二、sersync安装配置
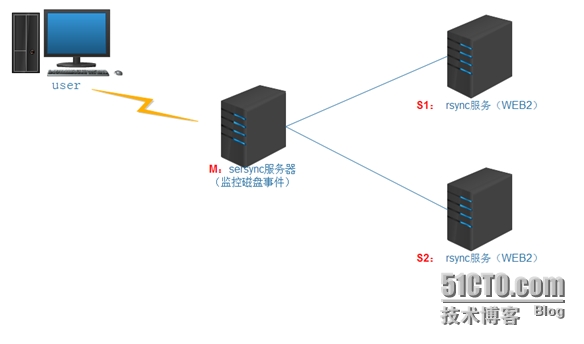
2.1sersync同步逻辑图
当前版本的sersync依赖于rsync进行数据同步;
原理步骤:
-
1. 在同步服务器(Master)上开启sersync服务,sersync负载监控配置路径中的文件系统事件变化;
-
2. 调用rsync命令把更新的文件同步到目标服务器(S1 和 S2);
-
3. 需要在主服务器配置sersync,在同步目标服务器配置rsync server(注意:是rsync服务)
同步原理:
1. 用户实时的往sersync服务器(M)上写入更新文件数据;
2. 此时需要在同步主服务器(M)上配置sersync服务;
3. 在S1 和S2上开启rsync守护进程服务,以同步拉取来自sersync服务器(M)上的数据;
通过rsync的守护进程服务后可以发现,实际上sersync就是监控本地的数据写入或更新事件;然后,在调用rsync客户端的命令,将写入或更新事件对应的文件通过rsync推送到目标服务器(S1 和S2),如此简单;
2.2 安装环境准备
1.系统资源列表
|
角色 |
服务器配置 |
操作系统版本 |
IP |
机器名 |
|
sersync服务(M) |
VM |
CentOS6.6 |
172.16.1.28 |
sersync |
|
rsync服务(S1) |
VM |
CentOS6.6 |
172.16.1.25 |
WEB1 |
|
rsync服务(S2) |
VM |
CentOS6.6 |
172.16.1.26 |
WEB2 |
2.检查系统环境
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@web ~]# cat/etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.6 (Final)[root@web ~]# uname -r2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64[root@web ~]# uname -mx86_64 |
2.3 配置同步服务器
1.slave上部署rsync服务
2. 升级rsync到3.0版本
|
1
2
3
|
[root@web1 ~]# rsync --version|head -2rsync version 3.0.6 protocol version 30Copyright (C) 1996-2009 byAndrew Tridgell, Wayne Davison, and others. |
3.部署rsync服务
确定S1和S2服务器版本是最新的,这看下多台目标服务器(S1,S2)上配置如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
[root@web1 ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf#Rsync serveruid = rootgid = rootuse chroot = no # 安全相关max connections = 2000 # 并发连接数timeout = 600 # 超时时间(秒)pid file =/var/run/rsyncd.pid # 指定rsync的pid目录lock file =/var/run/rsync.lock # 指定rsync的锁文件【重要】log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log # 指定rsync的日志目录ignore errors read only = falselist = falsehosts allow = 172.16.1.0/24hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32auth users = rsync_backupsecrets file =/etc/rsync.password#################################################[www] # 模块 comment = www path = /data/www/#################################################[bbs]comment = bbspath = /data/bbs/#################################################[blog]comment = blogpath = /data/blog/#rsync_config____________end |
特别提示: S1,S2的机器 同时部署上述服务;
上面rsync服务的配置文件,表面允许sersync主服务器(ip:172.16.1.28)访问rsync同步模块名为[www][bbs][blog] 将同步过来的文件分别放入对应的path指定的目录/data/{www,bbs,blog}下面; 如果有多台目标服务器,则每一台都需要进行类似的rsync服务配置,上面的uid、gid要换成您服务器的相应的同步用户;注意,rsync服务账户(本文用的是root)要有对被同步目录(/data/)的写入更新权限;
4.创建rsync同步密码文件,并设置权限为600
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@web1 ~]# echo"rsync_backup:liubl">/etc/rsync.password[root@web1 ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password [root@web1 ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw-------. 1 root root 19Jun 3 18:19 /etc/rsync.password [root@web1 ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password rsync_backup:liubl |
5.启动守护进程,并写入开机自启动
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@web1 ~]# rsync --daemon[root@web1 ~]# lsof -i:873COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAMErsync 1070 root 4u IPv4 17190189 0t0 TCP *:rsync (LISTEN)[root@web1 ~]# [root@web1 ~]# netstat -nulpt| grep rsynctcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1070/rsync设置开机自启动【写入到/etc/rc.local里面】[root@web1 ~]# vim /etc/rc.local# rsync server progress/usr/bin/rsync --daemon |
6. 创建相关待同步的目录
|
1
2
3
|
mkdir -p /data/{www,bbs,blog}tree /data提示: 此步骤在S1,S2都要执行,否则rsync服务会因为没有PATH路径而无法启动 |
2.4Master上配置rsync客户端
在master上配置rsync客户端相关权限认证:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@web ~]# echo"liubl">/etc/rsync.password[root@web ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password [root@web ~]# ll/etc/rsync.password -rw-------. 1 root root 19Jun 5 05:57 /etc/rsync.password[root@web ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password liubl |
2.4.1master上手工测试rsync同步情况
特别提示:此步非常关键,如果测试不成功,后面的sersync配好了也不会同步数据;
1)分别创建待同步数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
[root@web ~]# mkdir -p /data/{www,bbs,blog}[root@web ~]# touch /data/www/www.log /data/bbs/bbs.log/data/blog/blog.log[root@web ~]# tree /data//data/├── bbs│ └── bbs.log├── blog│ └── blog.log└── www └── www.log 3 directories, 3 files |
2)执行同步命令
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
# rsync-avzP /data/www/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www/--password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordsending incremental file list sent 38 bytes received 8 bytes 92.00 bytes/sectotal size is 0 speedup is 0.00rsync-avzP /data/www/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www/--password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordrsync-avzP /data/www/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.26::www/--password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordrsync-avzP /data/bbs/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.26::bbs/--password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordrsync-avzP /data/bbs/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::bbs/--password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordrsync-avzP /data/blog/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::blog/--password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordrsync-avzP /data/blog/ rsync_backup@172.16.1.26::blog/--password-file=/etc/rsync.password提示: 在后面进行部署sersync之前,sersync主服务器上必须要确保手工可以把文件推送到S1,S2上,这样后续sersync才能调用这些命令来自动推送在推送前关闭iptables |
3)推送的命令是在 master端(也就是 sersync服务器上)操作的,同步后查看S1,S2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
[root@web1 ~]# tree /data//data/├── bbs│ └── bbs.log├── blog│ └── blog.log└── www └── www.log 3 directories, 3 files |
2.5Mster上开始部署sersync服务
1、下载sersync
在google code下载sersync的可执行文件版本,里面有配置文件与可执行文件,这用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
mkdir -p /applition/toolscd /applition/toolswgethttps://sersync.googlecode.com/files/sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz【有时下载失败,所有要本地留存才行】[root@web ~]# tar fxzsersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz -C /usr/local/[root@web ~]# cd /usr/local/[root@cache local]# mv GNU-Linux-x86 sersync[root@cache local]# treesersync/sersync/├── confxml.xml # 配置文件└── sersync2 # 二进制文件【启动sersync使用】 0 directories, 2 files |
2、配置sersync
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@cache local]# cp sersync/confxml.xmlsersync/confxml.xml.$(date +%F)[root@cache local]# ll sersync/confxml.xml-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 2214Oct 26 2011 sersync/confxml.xml[root@cache local]# llsersync/confxml.xml*-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 2214Oct 26 2011 sersync/confxml.xml-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 2214Jun 5 06:38sersync/confxml.xml.2015-06-05 |
更改优化sersync配置文件:
a) 修改24--28行
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
24 <localpathwatch="/opt/tongbu"> # 定义本地要同步的目录 25 <remote ip="127.0.0.1"name="tongbu1"/> 26 <!--<remoteip="192.168.8.39" name="tongbu"/>--> # 同步到哪台机器上 tongbu模块rsync端模块名字 27 <!--<remoteip="192.168.8.40" name="tongbu"/>--> # 同步到哪台机器上 tongbu模块 28 </localpath> |
修改后的内容为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<localpathwatch="/data/www"> <remoteip="172.16.1.25" name="www"/> <remoteip="172.16.1.26" name="www"/> </localpath> <!--################################################## --> <localpathwatch="/data/bbs"> <remoteip="172.16.1.25" name="bbs"/> <remoteip="172.16.1.26" name="bbs"/> </localpath> <!--################################################## --> <localpathwatch="/data/blog"> <remote ip="172.16.1.25"name="blog"/> <remoteip="172.16.1.26" name="blog"/> </localpath> <!--################################################## -->提示: 此步watch="/data/blog"就是定义服务端待同步的目录,和目标服务器的模块name="blog" |
b)修改31--34行,认证部分【rsync密码认证】
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<rsync> <commonParamsparams="-artuz"/> <auth start="false"users="root" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.pas"/> <userDefinedPortstart="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 --> <timeoutstart="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 --> <sshstart="false"/> </rsync> |
修改后的内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<rsync> <commonParamsparams="-artuz"/> <auth start="true"users="rsync_backup" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.password"/> <userDefinedPortstart="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 --> <timeout start="true" time="100"/><!--timeout=100 --> <sshstart="false"/> </rsync># ***修改内容为 rsync的密码文件以及 同步所使用的账号类似:rsync -avzP /data/www/rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www/ --password-file=/etc/rsync.password |
c)修改37行
|
1
|
<failLogpath="/tmp/rsync_fail_log.sh"timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once--> |
修改后如下:
|
1
2
|
<failLog path="/usr/local/sersync/logs/rsync_fail_log.sh"timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once--># 当同步失败后,日志记录到/usr/local/sersync/logs/rsync_fail_log.sh文件中,并且每60分钟对失败的log进行重新同步 |
修改后的完整配置文件为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
[root@cache local]# cat sersync/confxml.xml<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?><headversion="2.5"> <host hostip="localhost"port="8008"></host> <debug start="false"/> <fileSystem xfs="false"/> <filter start="false"> <excludeexpression="(.*).svn"></exclude> <excludeexpression="(.*).gz"></exclude> <excludeexpression="^info/*"></exclude> <excludeexpression="^static/*"></exclude> </filter> <inotify> <delete start="true"/> <createFolderstart="true"/> <createFilestart="false"/> <closeWritestart="true"/> <moveFromstart="true"/> <moveTo start="true"/> <attrib start="false"/> <modify start="false"/> </inotify> <sersync> <localpathwatch="/data/www"> <remoteip="172.16.1.25" name="www"/> <remoteip="172.16.1.26" name="www"/> </localpath> <!--################################################## --> <localpathwatch="/data/bbs"> <remoteip="172.16.1.25" name="bbs"/> <remoteip="172.16.1.26" name="bbs"/> </localpath> <!--################################################## --> <localpathwatch="/data/blog"> <remoteip="172.16.1.25" name="blog"/> <remoteip="172.16.1.26" name="blog"/> </localpath> <!-- ##################################################--> <rsync> <commonParamsparams="-artuz"/> <auth start="true"users="rsync_backup"passwordfile="/etc/rsync.password"/> <userDefinedPortstart="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 --> <timeout start="true"time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 --> <sshstart="false"/> </rsync> <failLogpath="/usr/local/sersync/logs/rsync_fail_log.sh"timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once--> <crontab start="false"schedule="600"><!--600mins--> <crontabfilterstart="false"> <excludeexpression="*.php"></exclude> <excludeexpression="info/*"></exclude> </crontabfilter> </crontab> <plugin start="false"name="command"/> </sersync> <plugin name="command"> <param prefix="/bin/sh"suffix="" ignoreError="true"/> <!--prefix /opt/tongbu/mmm.sh suffix--> <filter start="false"> <include expression="(.*).php"/> <includeexpression="(.*).sh"/> </filter> </plugin> <plugin name="socket"> <localpathwatch="/opt/tongbu"> <deshostip="192.168.138.20" port="8009"/> </localpath> </plugin> <plugin name="refreshCDN"> <localpathwatch="/data0/htdocs/cms.xoyo.com/site/"> <cdninfodomainname="ccms.chinacache.com" port="80"username="xxxx" passwd="xxxx"/> <sendurlbase="http://pic.xoyo.com/cms"/> <regexurlregex="false"match="cms.xoyo.com/site([/a-zA-Z0-9]*).xoyo.com/images"/> </localpath> </plugin></head> |
3、开启sersync守护进程同步数据
启动命令
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@web ~]# /usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -r -o /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xml配置sersync环境变量[root@web ~]# echo"PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/sersync/">>/etc/profile[root@web ~]# source /etc/profile[root@web ~]# sersync2 |
启动命令后返回结果如下为正常:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
set the system paramexecute:echo50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watchesexecute:echo 327679> /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_eventsparse the command paramoption: -d run as a daemonoption: -r rsync all the local files to the remoteservers before the sersync workoption: -o config xml name: /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xmldaemon thread num: 10parse xml config filehost ip : localhost host port: 8008daemon start,sersync runbehind the console use rsync password-file :user is rsync_backuppasswordfile is /etc/rsync.passwordconfig xml parse successplease set /etc/rsyncd.confmax connections=0 Manuallysersync working thread 12 = 1(primary thread) + 1(fail retry thread) + 10(daemon sub threads)Max threads numbers is: 32 = 12(Thread pool nums) +20(Sub threads)please according your cpu ,use -n paramto adjust the cpu ratechmod: cannot access`/usr/local/sersync/logs/rsync_fail_log.sh': No such file or directory------------------------------------------rsync the directory recursivlyto the remote servers onceworking please wait...execute command: cd /data/www&& rsync -artuz -R --delete ./ --timeout=100 rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www--password-file=/etc/rsync.password >/dev/null 2>&1 run the sersync: watch path is: /data/www |
补充: 多实例情况
1、配置多个confxml.xml文件(比如:www、bbs、blog....等等)
2、根据不同的需求同步对应的实例文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -o /usr/local/sersync/www_confxml.xml/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -o /usr/local/sersync/bbs_confxml.xml/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -o /usr/local/sersync/blog_confxml.xml# 多实例初始化同步命令:/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -r-d -o /usr/local/sersync/www_confxml.xml/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -r-d -o /usr/local/sersync/bbs_confxml.xml/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -r-d -o /usr/local/sersync/blog_confxml.xml/bin/cp /etc/rc.local/etc/rc.local_$(data +%F)cat>>/etc/rc.local<<EOF#sync data to 25 26/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -o /usr/local/sersync/www_confxml.xml/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -o /usr/local/sersync/bbs_confxml.xml/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -o /usr/local/sersync/blog_confxml.xmlEOF |
压测:写入10K个文件批量同步测试结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
# for n in `seq 10000`;do echodddd>www/$n.txt;done# ps -ef |greprsyncroot 17283 1 0 Jun05 ? 00:00:02 /usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d-r -o /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xmlroot 19363 1 0 Jun05 ? 00:00:01 /usr/local/sersync/bin -d -o/usr/local/sersync/confxml.xmlroot 19394 1 0 Jun05 ? 00:00:01 /usr/local/sersync/bin -r -d-o /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xmlroot 19414 1 0 Jun05 ? 00:00:01 /usr/local/sersync/bin -r -d-o /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xmlroot 29484 17283 0 01:33 ? 00:00:00 sh -c cd /data/www &&rsync -artuz -R --timeout=100"./395.txt" rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www--password-file=/etc/rsync.password >/dev/null 2>&1 root 29487 29484 0 01:33 ? 00:00:00 rsync -artuz -R --timeout=100./395.txt rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www --password-file=/etc/rsync.passwordroot 29490 17283 0 01:33 ? 00:00:00 sh -c cd /data/www &&rsync -artuz -R --timeout=100"./396.txt" rsync_backup@172.16.1.25::www--password-file=/etc/rsync.password >/dev/null 2>&1 提示:我们发现本地已经写完了10000个,但是同步的线程,依然在同步;甚至才同步了1000多个 |
2.6 检查节点是否同步成功
| WEB1 同步查看对比 | WEB2 同步查看对比 |
|
[root@web1 data]# du /data/www/ 26944 /data/www/ [root@web1 data]# du /data/www/ 26964 /data/www/ [root@web1 data]# du /data/www/ 27024 /data/www/ [root@web1 data]# du /data/www/ 27036 /data/www/ |
[root@web2 data]# du /data/www/ 26880 /data/www/ [root@web2 data]# du /data/www/ 26908 /data/www/ [root@web2 data]# du /data/www/ 26940 /data/www/ [root@web2 data]# du /data/www/ 26960 /data/www/ |
| 每秒同步20--30个文件 | 每秒同步20-30个文件 |
三、命令参数说明
| Sersync参数 | 说明 |
| ./sersync -r |
-r参数作用是:开启实时监控的之前对主服务器目录与远程目标机器的目录进行一次整体同步;如果需要将sersync运行前,主服务器目录下已经存在的所有文件或目录全部同步到远端,则要以 -r参数运行sersync,将本地与远程整体同步一次; 提别说明:如果设置了过滤器,即在xml文件中,filter为true,则暂时不能使用-r参数进行整体同步; |
| ./sersync -o xx.xml |
不指定 -o参数: sersync使用sersync可执行文件目录下的默认配置文件confxml.xml 指定 -o 参数:可以指定多个不同的配置文件,从而实现sersync多进程多实例的数据同步 |
| ./sersync -n num |
-n参数为:指定默认的线程池的线程总数; 例如: ./sersync -n 5 则指定线程总数为5,如果不指定,默认启动线程池数量是10,如果cpu使用过高,可以通过该参数调低,如果机器配置较高,可以调高默认的线程总数,提升同步效率; |
| ./sersync -d | -d参数为:后台服务,通常情况下使用 -r参数对本地到远端整体同步一遍后,在后台运行此参数启动守护进程实时同步;在第一次整体同步时,-d 和 -r参数经常会联合使用; |
|
./sersync -m pluginName |
-m参数:不进行同步,只运行插件 ./sersync -m pluginName 例如:./sersync -m command,则在监控到事件后,不对远程目标服务器进行同步,而是直接运行command插件 |
| 组合命令使用说明: | |
| -n 8 -o liubl.xml -r -d | 多个参数可以配合使用,例如:./sersync -n 16 -o config.xml -r -d 表示设置线程池工作线程为16个,指定liubl.xml作为配置文件,在实时监控前 做一次整体同步,以守护进程方式在后台运行; |
| ./sersync --help | 很遗憾,它没有查看帮助(需要的话2条路,要么看源代码,要么自测求验证) |
四、sersync服务配置文件参数详解
4.1 初始的配置文件
sersync可选功能是通过xml配置文件来实现的,基本配置文件如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
[root@cache sersync]# cat confxml.xml.2015-06-05 1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> 2 <head version="2.5"> 3 <host hostip="localhost" port="8008"></host> 4 <debug start="false"/> 5 <fileSystem xfs="false"/> 6 <filter start="false"> 7 <exclude expression="(.*).svn"></exclude> 8 <exclude expression="(.*).gz"></exclude> 9 <exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude> 10 <exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude> 11 </filter> 12 <inotify> 13 <delete start="true"/> 14 <createFolder start="true"/> 15 <createFile start="false"/> 16 <closeWrite start="true"/> 17 <moveFrom start="true"/> 18 <moveTo start="true"/> 19 <attrib start="false"/> 20 <modify start="false"/> 21 </inotify> 22 23 <sersync> 24 <localpath watch="/opt/tongbu"> 25 <remoteip="127.0.0.1" name="tongbu1"/> 26 <!--<remoteip="192.168.8.39" name="tongbu"/>--> 27 <!--<remoteip="192.168.8.40" name="tongbu"/>--> 28 </localpath> 29 <rsync> 30 <commonParamsparams="-artuz"/> 31 <auth start="false"users="root" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.pas"/> 32 <userDefinedPortstart="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 --> 33 <timeoutstart="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 --> 34 <sshstart="false"/> 35 </rsync> 36 <failLog path="/tmp/rsync_fail_log.sh"timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once--> 37 <crontab start="false"schedule="600"><!--600mins--> 38 <crontabfilterstart="false"> 39 <excludeexpression="*.php"></exclude> 40 <excludeexpression="info/*"></exclude> 41 </crontabfilter> 42 </crontab> 43 <plugin start="false" name="command"/> 44 </sersync> 45 46 <plugin name="command"> 47 <param prefix="/bin/sh" suffix=""ignoreError="true"/> <!--prefix /opt/tongbu/mmm.sh suffix--> 48 <filter start="false"> 49 <includeexpression="(.*).php"/> 50 <includeexpression="(.*).sh"/> 51 </filter> 52 </plugin> 53 54 <plugin name="socket"> 55 <localpath watch="/opt/tongbu"> 56 <deshostip="192.168.138.20" port="8009"/> 57 </localpath> 58 </plugin> 59 <plugin name="refreshCDN"> 60 <localpath watch="/data0/htdocs/cms.xoyo.com/site/"> 61 <cdninfodomainname="ccms.chinacache.com" port="80"username="xxxx" passwd="xxxx"/> 62 <sendurlbase="http://pic.xoyo.com/cms"/> 63 <regexurlregex="false" match="cms.xoyo.com/site([/a-zA-Z0-9]*).xoyo.com/images"/> 64 </localpath> 65 </plugin> 66 </head> |
4.2 xml配置文件说明
说明: xml配置文件的注释不用“#”,而是<!-- 中间是注释内容 -->
|
1
|
3 <host hostip="localhost"port="8008"></host> |
hostip与port是针对插件的保留字段,对于同步功能没有任何作用,保留默认即可;
4.3 Debug开启开关
|
1
|
4 <debug start="false"/> |
设置为true,表示开启debug模式,会在sersync正在运行的控制台打印inotify时间与rsync同步命令;
4.4 XFS文件系统开关
|
1
|
5 <fileSystem xfs="false"/> |
对于xfs文件系统的用户,需要将这个选项开启,才能使用sersync正常工作;
4.5 filter文件过滤功能
说明:一般情况下,不给客户端添加过滤,如有必要才添加;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
6 <filter start="false"> 7 <exclude expression="(.*).svn"></exclude> 8 <exclude expression="(.*).gz"></exclude> 9 <exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude> 10 <exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude> 11 </filter> |
对于大多数应用,可以尝试把createFile(监控文件事件选项)设置为false来提高性能,减少rsync通讯;
因为拷贝文件到监控目录会产生create事件与close_write事件,所以如果关闭create事件,只监控文件拷贝结束时的时间close_write,同样可以实现文件完整同步;
注意:强将creatFolder保持为true,如果将createFolder设为false,则不会对产生的目录进行监控,该目录下的子文件与子目录也不会被监控;所以除非特殊需要,请开启; 默认情况下对创建文件(目录)事件与删除文件(目录)事件都进行监控,如果项目中不需要删除远程目标服务器的文件(目录),则可以将delete参数设置为false,则不对删除事件进行监控;