缓存
什么是缓存?
在高并发下,为了提高访问的性能,需要将数据库中 一些经常展现和不会频繁变更的数据,存放在存取速率更快的内存中。这样可以
- 降低数据的获取时间,带来更好的体验
- 减轻数据库的压力
缓存适用于读多写少的场合,查询时缓存命中率很低、写操作很频繁等场景不适宜用缓存。
MySQL有自己的查询缓存,为什么还要使用 Redis 等缓存应用?
- 当只有一台 MySQL服务器时,可以将缓存放置在本地。这样当有相同的 SQL 查询到达时,可以直接从缓存中取到查询结果,不需要进行 SQL 的解析和执行。MySQL 提供了服务器层面的缓存支持。
- 如果有多台 MySQL 服务器,请求会随机分发给多台中的一台,我们无法保证相同的请求会到达同一台服务器,本地缓存命中率较低。所以基于本机的缓存就没有什么意义,此时采用的策略应该是将查询结果缓存在 Redis 或者 Memcache 中。
而Redis是一个高性能的 key-value 内存数据库,恰恰可以作为缓存使用。
GitHub 地址:https://github.com/antirez/redis 。Github 是这么描述的: Redis is an in-memory database that persists on disk. The data model is key-value, but many different kind of values are supported: Strings, Lists, Sets, Sorted Sets, Hashes, HyperLogLogs, Bitmaps.
但是mysql自己本身有查询缓存,memcached也是一个优秀的内存数据库,为什么一定要选择redis
缓存更新
查看缓存更新的套路,缓存更新的模式有四种:
- Cache aside
- Read through
- Write through
- Write behind cachin。
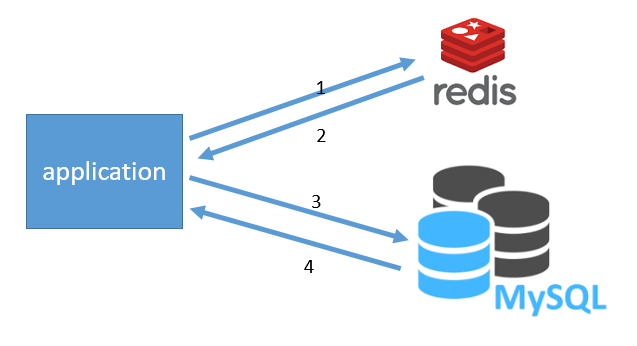
这里我们使用的是 Cache Aside 策略,从三个维度:
- 命中:应用程序从cache中取数据,取到后返回。执行图中1,2步
- 失效:应用程序先从cache取数据,没有得到,则从数据库中取数据,成功后,放到缓存中。执行图中1,2,3,4,1,2步
- 更新:先把数据存到数据库中,成功后,再让缓存失效。执行图中1,2步
spring配置redis缓存
接下来讲解一下spring的配置。
依赖配置
pom.xml中添加
<!-- redis cache-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.7.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
RedisConfig
现在我们使用的是java config 配置,因此需要将本RedisConfig放在可以被
<context:component-scan base-package=""/>
扫描的包下。
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 李文浩
* @version 2017/11/5.
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory();
// Defaults
redisConnectionFactory.setHostName("127.0.0.1");
redisConnectionFactory.setPort(6379);
return redisConnectionFactory;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<String, String>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
setSerializer(redisTemplate);
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager rcm = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
// 设置缓存过期时间,秒
rcm.setDefaultExpiration(600);
return rcm;
}
private void setSerializer(RedisTemplate<String, String> template) {
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
}
@Override
@Bean
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
sb.append(":" + method.getName());
for (Object obj : params) {
sb.append(":" + null == obj ? "null" : obj.toString());
}
return sb.toString();
}
};
}
}
如果我们不配置重写keyGenerator()方法的话,默认的key生成策略是
Cacheable.java
/**
* Spring Expression Language (SpEL) expression for computing the key dynamically.
* <p>Default is {@code ""}, meaning all method parameters are considered as a key,
* unless a custom {@link #keyGenerator} has been configured.
* <p>The SpEL expression evaluates against a dedicated context that provides the
* following meta-data:
* <ul>
* <li>{@code #root.method}, {@code #root.target}, and {@code #root.caches} for
* references to the {@link java.lang.reflect.Method method}, target object, and
* affected cache(s) respectively.</li>
* <li>Shortcuts for the method name ({@code #root.methodName}) and target class
* ({@code #root.targetClass}) are also available.
* <li>Method arguments can be accessed by index. For instance the second argument
* can be accessed via {@code #root.args[1]}, {@code #p1} or {@code #a1}. Arguments
* can also be accessed by name if that information is available.</li>
* </ul>
*/
String key() default "";
也就是把所有的方法参数作为一个key,但是这可能会重复。
缓存注解
@CacheConfig:主要用于配置该类中会用到的一些共用的缓存配置。在这里@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "companies"),配置了该数据访问对象中返回的内容将存储于名为companies的缓存对象中,我们也可以不使用该注解,直接通过@Cacheable自己配置缓存集的名字来定义。@Cacheable: 声明Spring在调用方法之前,首先应该在缓存中查找方法的返回值。如果这个值能够找到,就会返回存储的值,否则的话,这个方法就会被调用,返回值会放在缓存之中。该注解主要有下面几个参数:value、cacheNames:两个等同的参数(cacheNames为Spring4新增,作为value的别名),用于指定缓存存储的集合名。由于Spring4中新增了@CacheConfig,因此在Spring3中原本必须有的value属性,也成为非必需项了key:缓存对象存储在Map集合中的key值,非必需,缺省按照函数的所有参数组合作为key值,若自己配置需使用SpEL表达式,比如:@Cacheable(key = "#p0"):使用函数第一个参数作为缓存的key值,更多关于SpEL表达式的详细内容可参考官方文档condition:缓存对象的条件,非必需,也需使用SpEL表达式,只有满足表达式条件的内容才会被缓存,比如:@Cacheable(key = "#p0", condition = "#p0.length() < 3"),表示只有当第一个参数的长度小于3的时候才会被缓存,若做此配置上面的AAA用户就不会被缓存,读者可自行实验尝试。unless:另外一个缓存条件参数,非必需,需使用SpEL表达式。它不同于condition参数的地方在于它的判断时机,该条件是在函数被调用之后才做判断的,所以它可以通过对result进行判断。keyGenerator:用于指定key生成器,非必需。若需要指定一个自定义的key生成器,我们需要去实现org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator接口,并使用该参数来指定。需要注意的是:该参数与key是互斥的cacheManager:用于指定使用哪个缓存管理器,非必需。只有当有多个时才需要使用cacheResolver:用于指定使用那个缓存解析器,非必需。需通过org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheResolver接口来实现自己的缓存解析器,并用该参数指定。
除了这里用到的两个注解之外,还有下面几个核心注解:
@CachePut: 表明Spring应该将方法的返回值放到缓存中,在方法的调用前并不会检查缓存,方法始终都会被调用。它的参数与@Cacheable类似,具体功能可参考上面对@Cacheable参数的解析。@CacheEvict:配置于函数上,通常用在删除方法上,用来从缓存中移除相应数据。除了同@Cacheable一样的参数之外,它还有下面两个参数:allEntries:非必需,默认为false。当为true时,会移除所有数据beforeInvocation:非必需,默认为false,会在调用方法之后移除数据。当为true时,会在调用方法之前移除数据。
缓存与数据库一致性
- 数据库处理要求强一致实时性的数据,例如金融数据、交易数据。
- Redis处理不要求强一致实时性的数据,例如网站最热贴排行榜。
也就是说根据你的业务需求,设置你的过期时间,容许redis有一些不一致。
注意:
- 缓存java对象时必须实现Serilaizable接口,因为Spring会将对象先序列化之后再存入到Redis中。
- 缓存方法的
@Cacheable最好使用方法名,避免不同的方法的 @Cacheable 值一致,然后再配以以上缓存策略。 - 在我将这个
@Cacheable放置在SSM的dao层和service层时,redis缓存可以正常运行,但是当我将@Cacheable放在action层上时就会有NPE。 @Cacheable没有配置名字,改为@Cacheable("值"),否则会出现如下错误。java.lang.IllegalStateException: No cache could be resolved for 'Builder[public abstract studio.jikewang.entity.TeacherClass studio.jikewang.dao.TeacherClassDao.getTeacherClass(int)] caches=[] | key='' | keyGenerator='' | cacheManager='' | cacheResolver='' | condition='' | unless='' | sync='false'' using resolver 'org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleCacheResolver@4f8d471b'. At least one cache should be provided per cache operation.
参考文档: