作业题目:教材49页第7题a到d,并基于Junit及Eclemma实现一个主路径覆盖的测试
一、Use the following method printPrimes() for questions a-f below
1./** ***************************************************** 2. * Finds and prints n prime integers 3. * Jeff Offutt, Spring 2003 4. ********************************************************* */ 5. private static void printPrimes (int n) 6. { 7. int curPrime; // Value currently considered for primeness 8. int numPrimes; // Number of primes found so far. 9. boolean isPrime; // Is curPrime prime? 10. int [] primes = new int [MAXPRIMES]; // The list of prime numbers. 11. 12. // Initialize 2 into the list of primes. 13. primes [0] = 2; 14. numPrimes = 1; 15. curPrime = 2; 16. while (numPrimes < n) 17. { 18. curPrime++; // next number to consider ... 19. isPrime = true; 20. for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) 21. { // for each previous prime. 22. if (isDivisible (primes[i], curPrime)) 23. { // Found a divisor, curPrime is not prime. 24. isPrime = false; 25. break; // out of loop through primes. 26. } 27. } 28. if (isPrime) 29. { // save it! 30. primes[numPrimes] = curPrime; 31. numPrimes++; 32. } 33. } // End while 34. 35. // Print all the primes out. 36. for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) 37. { 38. System.out.println ("Prime: " + primes[i]); 39. } 40. } // end printPrimes
(a) Draw the control flow graph for the printPrimes() method.
(b) Consider test cases t1 = (n = 3) and t2 = (n = 5). Although these tour the
same prime paths in printPrimes(), they do not necessarily find the same faults.
Design a simple fault that t2 would be more likely to discover than t1 would.
数组越界
(c) For printPrimes(), find a test case such that the corresponding test path visits
the edge that connects the beginning of the while statement to the for statement
without going through the body of the while loop.
t3=(n=1)
(d) Enumerate the test requirements for Node Coverage, Edge Coverage, and Prime
Path Coverage for the graph for printPrimes().
Node Coverage:{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}
Edge Coverage:{(0,1),(1,2),(1,9),(2,3),(3,4),(3,7),(4,5),(4,6),(5,7),(6,3),(7,1),(7,8),(8,1),(9,10),(10,11),(10,12),(11,10)}
Prime Path Coverage:
{(0,1,2,3,4,6),
(0,1,2,3,4,6,7,8),
(0,1,2,3,7,8),
(0,1,9,10,11),
(0,1,9,10,12),
(3,4,6,3),
(4,6,3,4),
(6,3,4,6),
(6,3,4,5,7,8,1,2),
(6,3,4,5,7,8,1,9,10,11),
(6,3,4,5,7,8,1,9,10,12),
(6,3,7,8,1,2),
(6,3,7,8,1,9,10,11),
(6,3,7,8,1,9,10,12),
(10,11,10),
(11,10,11)}
二、主路径覆盖测试
以第一次上机判断三角形程序为例
Calculator.java
1 package moody; 2 public class Calculator { 3 private static int result = 0; 4 public void triangle(int a,int b,int c) 5 { 6 if((a+b)>c && (a+c)>b && (b+c)>a && a>0 && b>0 && c>0)//判断是否构成三角形 7 { 8 if((a==b)||(a==c)||(b==c)) 9 { 10 if((a == b)&&(a == c)) 11 { 12 result = 3;//等边 13 } 14 else 15 { 16 result = 2;//等腰 17 } 18 19 } 20 else 21 { 22 result = 1;//普通 23 } 24 } 25 26 else 27 { 28 result = 0;//不是三角形 29 } 30 31 } 32 public int getReuslt(){ 33 return result; 34 } 35 }
TestCalculator.java
1 package moody; 2 import static org.junit.Assert.*; 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 public class TestCalculator { 5 private static Calculator cal = new Calculator(); 6 @Test 7 public void testTriangle(){ 8 9 cal.triangle(2, 2, 2); 10 assertEquals(3, cal.getReuslt());//等边三角形 11 cal.triangle(3, 3, 5); 12 assertEquals(2, cal.getReuslt());//等腰三角形 13 cal.triangle(2, 3, 4); 14 assertEquals(1, cal.getReuslt());//普通三角形 15 cal.triangle(1, 2, 3); 16 assertEquals(0, cal.getReuslt());//不能构成三角形 17 cal.triangle(-1, 5, 3); 18 assertEquals(0, cal.getReuslt());//不能构成三角形 19 } 20 21 }
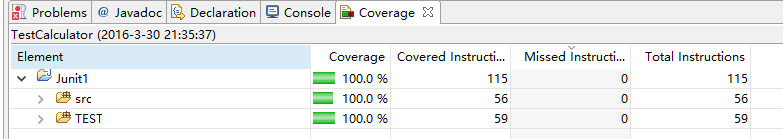
覆盖率截图