程序启动入口
@SpringBootApplication public class Chapter001Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Chapter001Application.class, args); } }
调试跟踪

执行初始化方法
/** * Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load * beans from the specified sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level} * documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling * {@link #run(String...)}. * @param sources the bean sources * @see #run(Object, String[]) * @see #SpringApplication(ResourceLoader, Object...) */ public SpringApplication(Object... sources) { initialize(sources); }
初始化方法
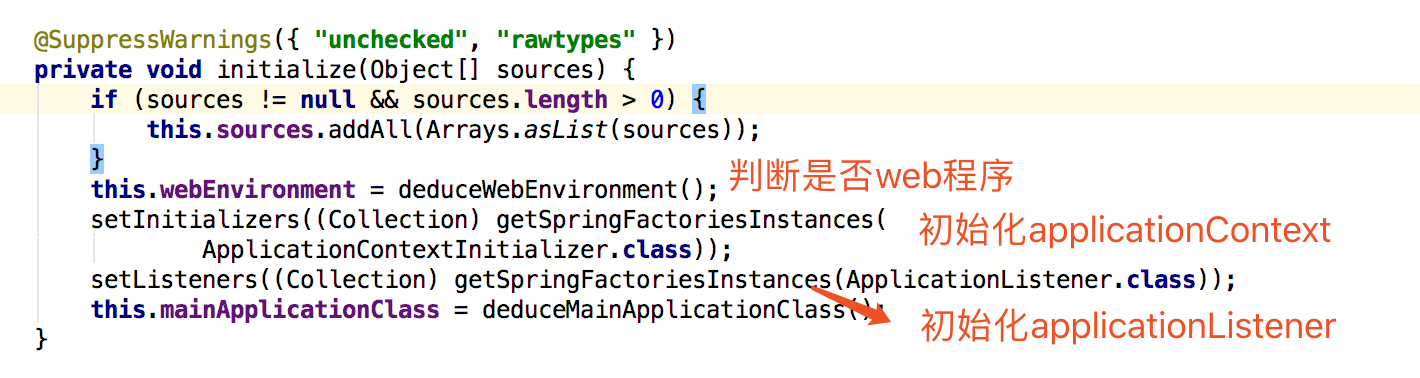
applicationContext和applicationListener方法详情
/** * Sets the {@link ApplicationContextInitializer} that will be applied to the Spring * {@link ApplicationContext}. * @param initializers the initializers to set */ public void setInitializers( Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) { this.initializers = new ArrayList<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>>(); this.initializers.addAll(initializers); }
ApplicationContextInitializer初始化applicationContext
/** * Sets the {@link ApplicationListener}s that will be applied to the SpringApplication * and registered with the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @param listeners the listeners to set */ public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) { this.listeners = new ArrayList<ApplicationListener<?>>(); this.listeners.addAll(listeners); }
注册listener到apllicationContext
applicationContext和applicationlistener初始化都是通过getSpringFactoriesInstances实现的,我们一探究竟
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) { return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {}); } private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>( SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); return instances; }

找到了关键节点spring.factories文件,我们查看spring boot下的这个文件看看情况

通过spring.factories文件拿到一系列的Context和Listener之后 执行run方法
run方法会从spring.factories文件中获取到run listener,然后在spring boot 执行到各个阶段时执行Listener事件和Context事件
最后的run方法如下

了解启动流程,方便优化,下边是网友遇到的问题以及优化方案
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004252885