上篇博客我们讲到,spring在做xml解析的时候,将xml中的各种属性,都封装到一个GenericBeanDefinition对象中,那么在将xml标签进行解析的时候,会出现两种情况,一种是针对传统(默认)标签的解析,而spring也提供了另外一种自定义标签的解析。
首先我们先来看个自定义的例子。
/** * @author monco * @data 2020/9/27 15:28 * @description :自定义需要注入到spring的对象 */ public class CustomUser { private String id; private String username; private String email; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } }
/** * @author monco * @data 2020/9/27 15:37 * @description : 解析自定义标签 custom */ public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { @Override public void init() { registerBeanDefinitionParser("custom", new UserBeanDefinitionParser()); } }
/** * @author monco * @data 2020/9/27 15:32 * @description : 将xml中读取的标签 放入到 BeanDefinition 中 */ public class UserBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser { protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) { return CustomUser.class; } protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) { String username = element.getAttribute("username"); String email = element.getAttribute("email"); if (StringUtils.hasText(username)) { builder.addPropertyValue("username", username); } if (StringUtils.hasText(email)) { builder.addPropertyValue("email", email); } } }
我们在代码层面需要做的事就是三步,第一步,定义一个需要注册的bean,第二步,将xml中解析的元素转化成BeanDefinition,第三步,将BeanDefinition注册到spring容器中,交给spring容器管理。
下面我们需要配置一些其他的东西。请睁大眼睛 仔细观察。

我们需要在resources文件夹下,创建META-INF文件夹,在其中创建3个文件,一个xsd文件,一个handlers文件,一个schemas文件。
xsd 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <!--自定义标签的名字 叫 custom--> <xsd:element name="custom"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:string"></xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="username" type="xsd:string"></xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="email" type="xsd:string"></xsd:attribute> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
handlers 文件 指定读取的 id namespace
http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags=com.monco.bean.custom.MyNamespaceHandler
schemas 文件 指定读取的xsd 位置
http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags.xsd=META-INF/mytags.xsd
spring.xml 文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags.xsd " xmlns:monco="http://www.monco.com/schema/mytags" default-lazy-init="false"> <!--自定义标签--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.monco"/> <!--传统标签--> <bean class="com.monco.entity.User" id="user"> <constructor-arg name="username" value="monco"/> <constructor-arg name="password" value="123456"/> </bean> <!--replace-method--> <bean id="replaceClass" class="com.monco.bean.ReplaceClass" lazy-init="false"/> <bean id="originClass" class="com.monco.bean.OriginClass"> <replaced-method name="method" replacer="replaceClass"> <!--方法可能出现重载的情况,要根据类型和方法名找方法--> <arg-type match="java.lang.String"/> </replaced-method> </bean> <monco:custom id="customUser" username="monco" email="18552193820@163.com"/> </beans>
测试类
@Test public void testCustomTag() { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); CustomUser customUser = (CustomUser) applicationContext.getBean("customUser"); System.out.println(customUser.getUsername()); }
运行结果
通过上述一个简单的例子,我们可以发现,我们自己定义的Bean竟然奇迹般的被解析到了。现在我们就来分析下,这是why?这些配置文件的作用到底是啥?我们学了这些东西到底有啥用?
上节我们讲到 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 中的 parseBeanDefinitions 的方法
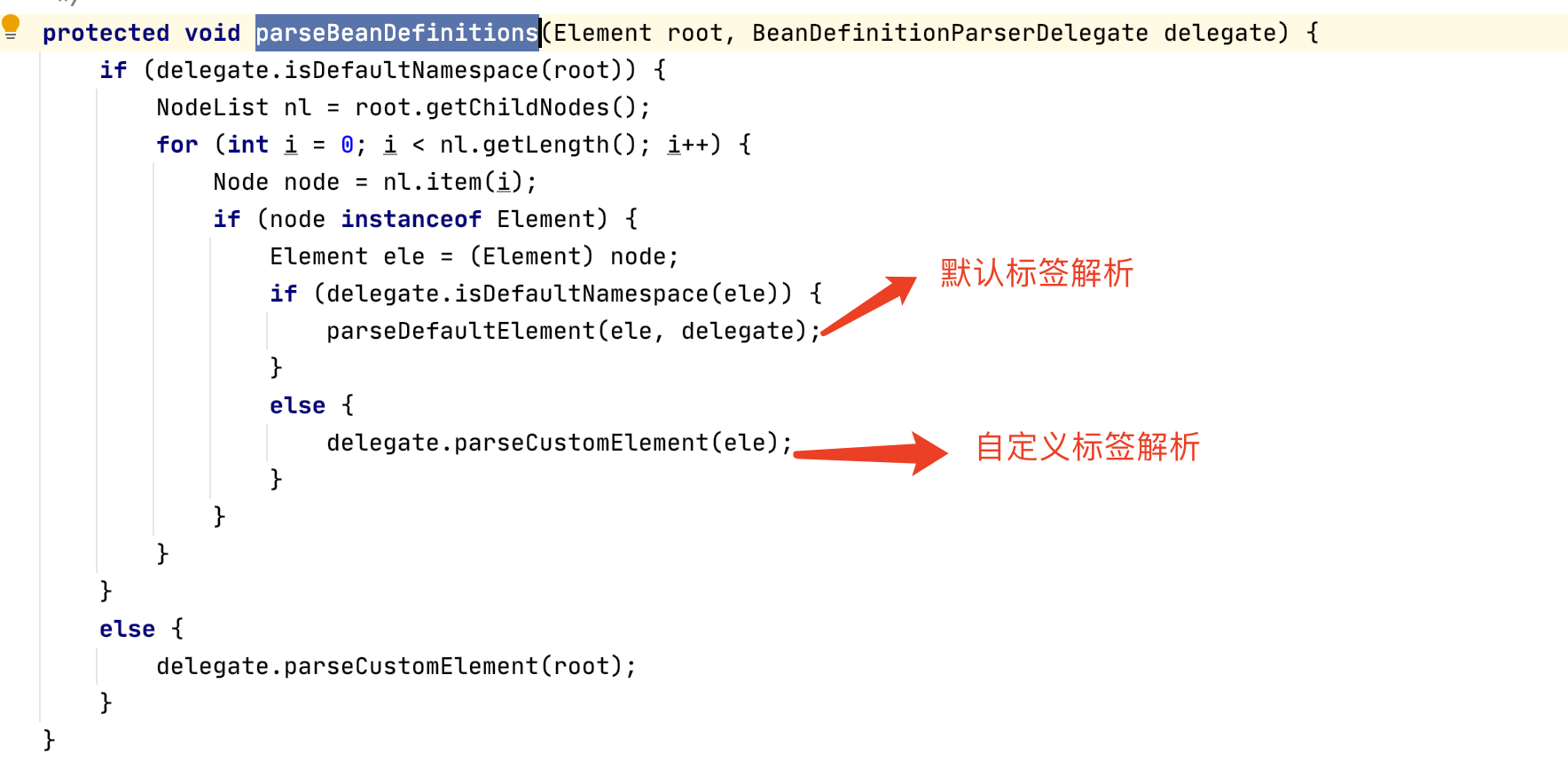
我们发现在实际去解析自定义标签的第一步,就是将元素中的namespaceURI读取出来,读取到 namespaceURI 之后,我们就可以 handlers 文件找到对应的 处理类
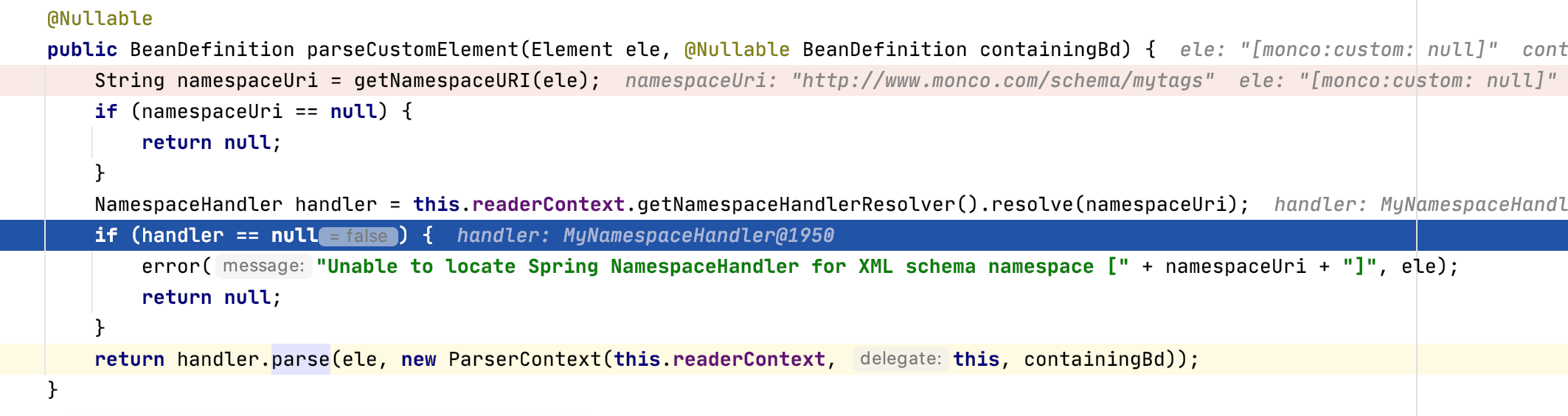
通过 文件 来找到处理类的这个过程 我们暂且称之为 SPI 思想。

我们通过上述步骤可以解决根据namespace 找到对应的处理类,接下来,我们需要执行 parse() 方法,将对应的标签写入BeanDefinition就可以了。主要是SPI的思想。
具体可以参考 这篇博客。
下一节主要介绍,将xml解析到Bean 中,接下来的重点是 怎样加载这个Bean。