因为需要在单位用pycharm实在是太卡了,所以换成网页的编辑器
安装操作系统
本文使用的镜像:Ubuntu - Official Image | Docker Hub
docker pull ubuntu:20.04
很小,下载一小会就结束了然后运行这个docker
这里开放的8888端口指的是一会网页的端口
docker run -itd -p 8888:8888 --name jupyterhub --restart always ubuntu:20.04 bash
安装jupyter
进入容器,用可视化网页进入也可以
docker exec -it jupyterhub bash
先升级一下,如果太慢的话,可以换源后升级,会快一点
apt update
apt upgrade
安装一些基本依赖,等待一段时间
apt install python3 python3-pip wget
进入nodejs的官网,copy一下Linux Binaries (x64)的下载地址(视操作系统而定

输入wget 刚才的链接
wget https://nodejs.org/dist/v16.15.0/node-v16.15.0-linux-x64.tar.xz
可以ls一下,看看下载的文件名
然后解压
tar -xvf node-v16.15.0-linux-x64.tar.xz
使用ln命令建立软链接同步
ln -s /node-v16.15.0-linux-x64/bin/node /usr/local/bin/
ln -s /node-v16.15.0-linux-x64/bin/npm /usr/local/bin/
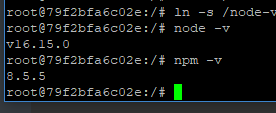
使用node和npm命令确认是否安装成功
node -v
npm -v
有版本号说明安装成功了
改一下pip3的源,这个不改会真的卡
pip3 config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
安装一些依赖
apt install libffi-dev
npm install -g configurable-http-proxy
pip3 install notebook
pip3 install jupyterhub
pip3 install --upgrade cython
配置
cd /etc/
mkdir jupyterhub
cd jupyterhub
jupyterhub --generate-config
增加用户,和输入密码,后面回车就行
adduser 用户名
增加授权
chmod -R 700 /home/用户名/
安装文本编辑器nano或者vim,我习惯nano
apt install nano
nano /etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub_config.py
使用Ctrl+w进行查找,找到proxy_cmd
取消注释,在其中加入单引号,然后加入路径
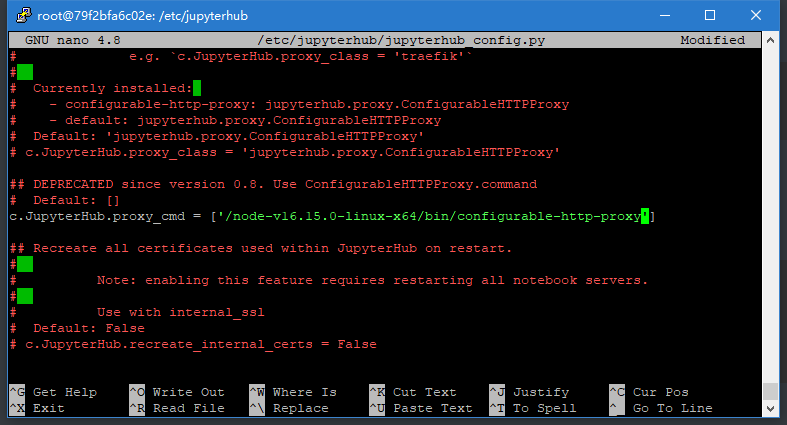
/node-v16.15.0-linux-x64/bin/configurable-http-proxy
根据你实际情况来
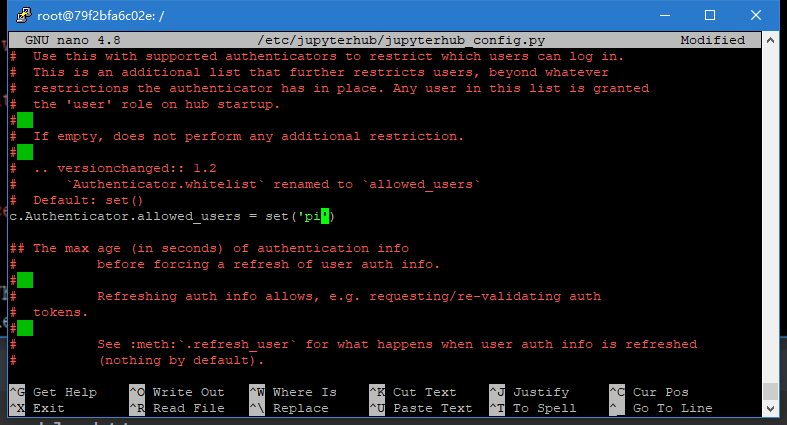
找到c.Authenticator.allowed,和上面操作相似,在单引号内加入自己用户名,如果之后登陆失败可以按照后一种图片来修改
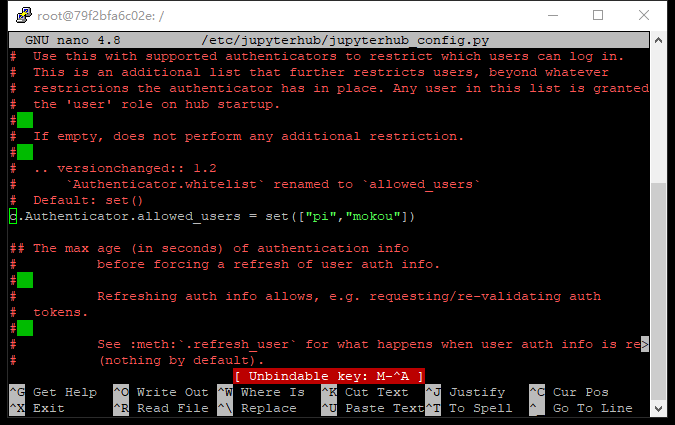
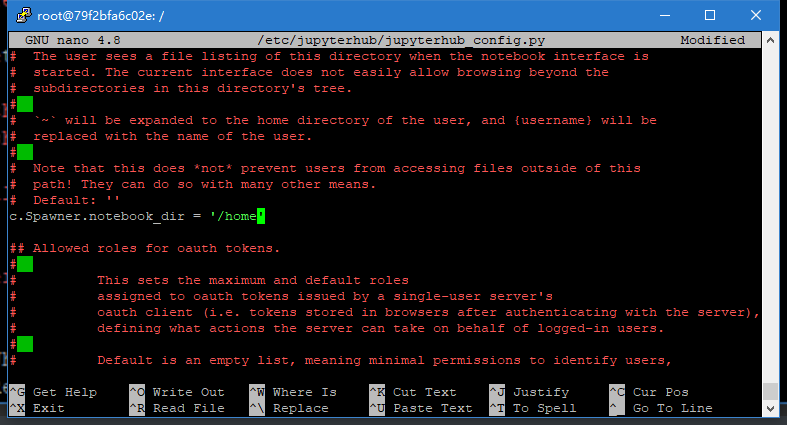
找到c.Spawner.notebook
在这其中加入'/home'
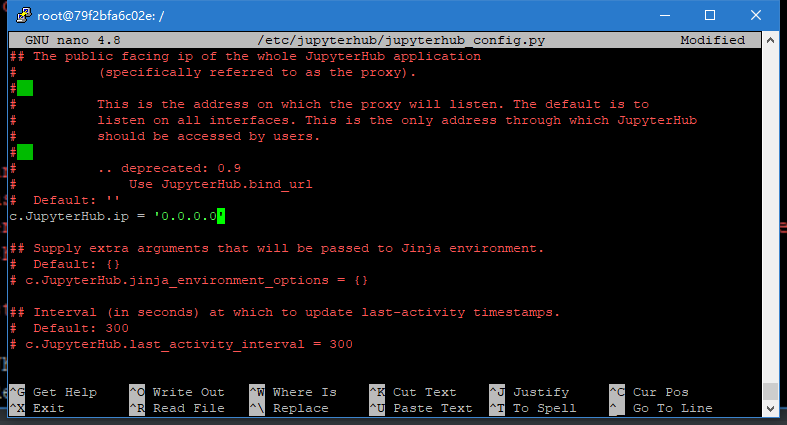
找到c.JupyterHub.ip
改为0.0.0.0
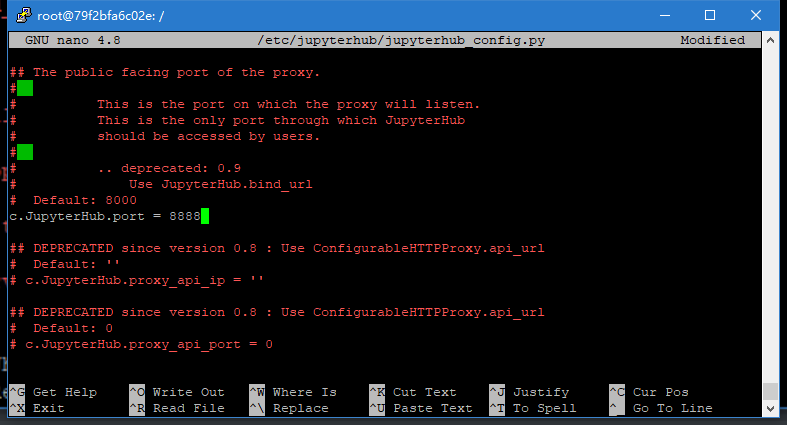
找到c.JupyterHub.port
改为8888
Ctrl+x 回车退出
然后在文件中加入
nano /etc/init.d/jupyterhub
输入
#! /bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: jupyterhub
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Start jupyterhub
# Description: This file should be used to construct scripts to be
# placed in /etc/init.d.
### END INIT INFO
# Author: Alisue <lambdalisue@hashnote.net>
#
# Please remove the "Author" lines above and replace them
# with your own name if you copy and modify this script.
# Do NOT "set -e"
# PATH should only include /usr/* if it runs after the mountnfs.sh script
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin
DESC="Multi-user server for Jupyter notebooks"
NAME=jupyterhub
DAEMON=/usr/local/bin/jupyterhub
DAEMON_ARGS="--config=/etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub_config.py"
PIDFILE=/var/run/$NAME.pid
SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/$NAME
# Exit if the package is not installed
[ -x "$DAEMON" ] || exit 0
# Read configuration variable file if it is present
[ -r /etc/default/$NAME ] && . /etc/default/$NAME
# Load the VERBOSE setting and other rcS variables
. /lib/init/vars.sh
# Define LSB log_* functions.
# Depend on lsb-base (>= 3.2-14) to ensure that this file is present
# and status_of_proc is working.
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
#
# Function that starts the daemon/service
#
do_start()
{
# Return
# 0 if daemon has been started
# 1 if daemon was already running
# 2 if daemon could not be started
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --pidfile $PIDFILE --exec $DAEMON --test > /dev/null \
|| return 1
start-stop-daemon --start --background --make-pidfile --quiet --pidfile $PIDFILE --exec $DAEMON -- \
$DAEMON_ARGS \
|| return 2
# Add code here, if necessary, that waits for the process to be ready
# to handle requests from services started subsequently which depend
# on this one. As a last resort, sleep for some time.
}
#
# Function that stops the daemon/service
#
do_stop()
{
# Return
# 0 if daemon has been stopped
# 1 if daemon was already stopped
# 2 if daemon could not be stopped
# other if a failure occurred
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --retry=TERM/30/KILL/5 --pidfile $PIDFILE --name $NAME
RETVAL="$?"
[ "$RETVAL" = 2 ] && return 2
# Wait for children to finish too if this is a daemon that forks
# and if the daemon is only ever run from this initscript.
# If the above conditions are not satisfied then add some other code
# that waits for the process to drop all resources that could be
# needed by services started subsequently. A last resort is to
# sleep for some time.
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --oknodo --retry=0/30/KILL/5 --exec $DAEMON
[ "$?" = 2 ] && return 2
# Many daemons don't delete their pidfiles when they exit.
rm -f $PIDFILE
return "$RETVAL"
}
#
# Function that sends a SIGHUP to the daemon/service
#
do_reload() {
#
# If the daemon can reload its configuration without
# restarting (for example, when it is sent a SIGHUP),
# then implement that here.
#
start-stop-daemon --stop --signal 1 --quiet --pidfile $PIDFILE --name $NAME
return 0
}
case "$1" in
start)
[ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && log_daemon_msg "Starting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_start
case "$?" in
0|1) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && log_end_msg 0 ;;
2) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && log_end_msg 1 ;;
esac
;;
stop)
[ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && log_daemon_msg "Stopping $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case "$?" in
0|1) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && log_end_msg 0 ;;
2) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && log_end_msg 1 ;;
esac
;;
status)
status_of_proc "$DAEMON" "$NAME" && exit 0 || exit $?
;;
#reload|force-reload)
#
# If do_reload() is not implemented then leave this commented out
# and leave 'force-reload' as an alias for 'restart'.
#
#log_daemon_msg "Reloading $DESC" "$NAME"
#do_reload
#log_end_msg $?
#;;
restart|force-reload)
#
# If the "reload" option is implemented then remove the
# 'force-reload' alias
#
log_daemon_msg "Restarting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case "$?" in
0|1)
do_start
case "$?" in
0) log_end_msg 0 ;;
1) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Old process is still running
*) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Failed to start
esac
;;
*)
# Failed to stop
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
;;
*)
#echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload}" >&2
echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|status|restart|force-reload}" >&2
exit 3
;;
esac
:
为其增加权限
chmod +x /etc/init.d/jupyterhub
开启服务
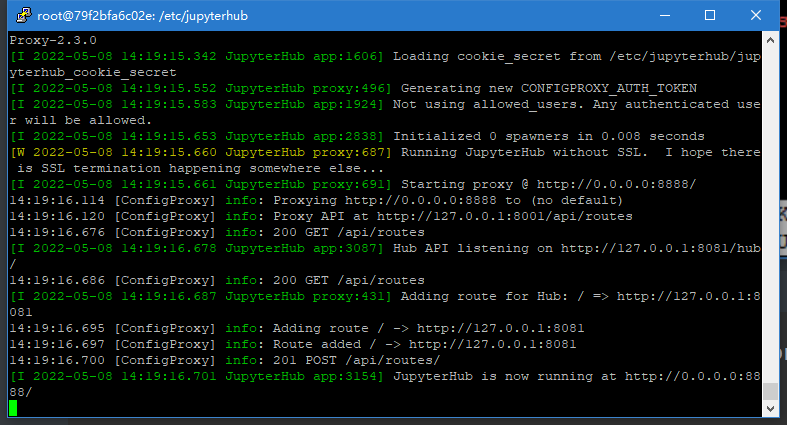
service jupyterhub start
进入网页
开启网页,这里的port是第一步开放的接口
jupyterhub --ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8888 -f /etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub_config.py
可以看到已经运行了
可以进入网页了,输入刚才的账号密码
jupyterlab
因为hub的ui不是很喜欢,对多文件不是很友好,所以改成lab
pip3 install jupyterlab
jupyter labextension install @jupyterlab/hub-extension
jupyter serverextension enable --py jupyterlab --sys-prefix
继续编辑配置文档
nano /etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub_config.py
找到c.Spawner.default,改为/lab
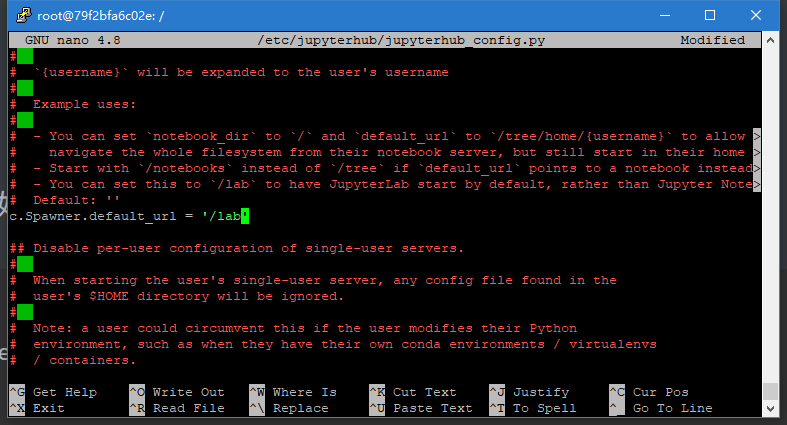
找到c.Spawner.cmd,改为jupyter-labhub
重启网络
service jupyterhub restart
再次进入就是jupyterlab了

修改密码
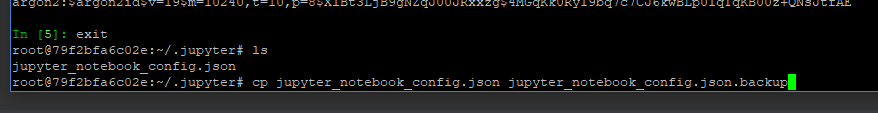
进入交互式python
ipython
输入以下命令,一行一行输
from notebook.auth import passwd
p =passwd()
print(p)
将得到的密码复制,exit退出
cd ~/.jupyter
ls,顺便将那份文件备份下
nano这个文件,替换那个字符串