说明
核酸序列打分算法脚本,基于动态规划进行双序列全局比对,得到两条DNA序列的相似度并打分,但程序还有一些问题,在匹配长序列的时候还不够完善.(20年初写的放在简书上,这次copy到博客园,欢迎访问我的简书:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6bedaa9f6de1)
环境
Linux、Python3.6
实例

command
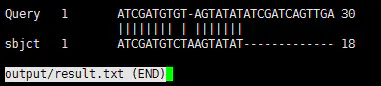
result
以下为代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Feb 19 13:42:52 2020 @author: moDD Email:312198221@qq.com """ import pandas as pd import re,argparse x_seq = 'ATCGATGTGTAGTATATATCGATCAGTTGA' y_seq = 'ATCGATGTCTAAGTATAT' def parameter(): '''设置三个参数''' parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog=" Pairwise Sequence Alignment ", usage='python3.6 ./Pairwise_Sequence_Alignment.py -seq_a ATCGATGTGTAGTATATATCGATCAGTTGA -seq_b ATCGATGTCTAAGTATAT -o ./output/result.txt', description="description:此脚本基于动态规划进行双序列全局比对,输入数据为a序列和b序列,输出为文本文件,得到两条DNA序列的相似度", epilog="Tip:此脚本使用python3.6编写完成, 请尽量使用python3.6版本执行") parser.add_argument("-seq_a", dest='seq_a',type=str, help="first sequence. for example:ATCGATGTGTAGTATATATCGATCAGTTGA") parser.add_argument("-seq_b", dest='seq_b',type=str, help="second sequence. for example:ATCGATGTCTAAGTATAT") parser.add_argument("-o", dest='outfilename',type=str, help="The name of result. for example:result.txt") (para, args) = parser.parse_known_args() try: x_seq= para.seq_a y_seq= para.seq_b if len(y_seq) > len(x_seq): #确保x为长序列 y为短序列 x_seq= para.seq_b y_seq= para.seq_a out_file_name = para.outfilename except: print('Missing parameters or Parameter error! Please check parameters!') raise ValueError #没有设置这些参数的外部输入 ,如有需要直接添加即可 gap = -5 wrong = -5 right = 2 base_pair = -2 return (x_seq,y_seq,out_file_name,right,base_pair,wrong,gap) def Generating_scoring_matrix(right,base_pair,wrong,gap): '''创建分数数据框''' scoring_matrix = pd.DataFrame({ '-':[0,gap,gap,gap,gap], 'A':[gap,right,base_pair,wrong,wrong], 'T':[gap,base_pair,right,wrong,wrong], 'C':[gap,wrong,wrong,right,base_pair], 'G':[gap,wrong,wrong,base_pair,right] }, index = ['-','A','T','C','G'] ) return scoring_matrix def cutText(text, sec): '''切割字符串为多段 每段长度为sec''' return [text[i:i+sec] for i in range(0,len(text),sec)] def Adjust_output_format_and_output(align_a,Middle_row,align_b,out_file_name): '''切割字符串为固定长度 并保存为指定文件名的文件''' with open(out_file_name , 'w') as f: index = 1 for (row_1,row_2,row_3) in zip(cutText(align_a,50),cutText(Middle_row,50),cutText(align_b,50)): end_len_row_1 = len(re.sub('-',"",row_1)) #去除减号 得到长度 加在字符串末尾 end_len_row_3 = len(re.sub('-',"",row_3)) #同上 element = str('Query' + '\t' + str(index) + '\t' + row_1 + '\t' + str(end_len_row_1) +'\n'+ ' ' + '\t' + ' ' + '\t' + row_2 + '\n'+ 'sbjct' + '\t' + str(index) + '\t' + row_3 + '\t' + str(end_len_row_3) +'\n\n') f.write(element) #写入 index += 1 def compute_result_matrix(x_seq, y_seq, scoring_matrix): '''得到一个高为length_x+1,宽为length_y+1 的数据框. 即(length_x+1) * (length_y+1) ''' length_x = len(x_seq) length_y = len(y_seq) result_matrix = [[0 for i in range(length_y + 1)] for j in range(length_x + 1)] result_matrix = pd.DataFrame(result_matrix) #根据动态规划算法 , 首先,生成第0列的数据 依次为 0 -5 -10 -15 for x_index in range(1, length_x+1): result_matrix[0][x_index] = result_matrix[0][x_index-1] + scoring_matrix[x_seq[x_index-1]]['-'] #数据框 列index在前面 行index在后面 #之后,生成第0行的数据 依次为 0 -5 -10 -15 for y_index in range(1, length_y+1): result_matrix[y_index][0] = result_matrix[y_index-1][0] + scoring_matrix[y_seq[y_index-1]]['-'] #最后从数据框的左上角开始,向右下角逐步计算每一个值 for x_index in range(1,length_x+1): for y_index in range(1, length_y+1): #取以下三者的最大值 这三个数分别为: 1,此位置左上角的值 + 得分矩阵中两个字符对应的值 # 2,此位置上面的值 + 得分矩阵中的gap # 2,此位置左边的值 + 得分矩阵中的gap result_matrix.iloc[x_index,y_index]=max(result_matrix.iloc[x_index-1,y_index-1]+ scoring_matrix.loc[y_seq[y_index-1],x_seq[x_index-1]], result_matrix.iloc[x_index,y_index-1] + scoring_matrix.loc['-',x_seq[x_index-1]], #x序列对应y的空值 result_matrix.iloc[x_index-1,y_index] + scoring_matrix.loc[y_seq[y_index-1],'-'] #y序列对应x的空值 ) return (result_matrix) def compute_global_alignment(x_seq, y_seq, scoring_matrix, result_matrix): '''将 矩阵数据逆推回序列数据''' #确定累积得分最大值是在数据框的最后一列还是最后一行,用于确定累积得分最大值所在的索引 如[17,18] length_x = len(x_seq) length_y = len(y_seq) terminal_max = max(max(result_matrix[length_y]), #最后一列最大值 max(result_matrix.loc[length_x,:]) #最后一行最大值 ) if terminal_max in list(result_matrix[length_y]): the_value_x_index = list(result_matrix[length_y]==terminal_max).index(True) the_value_x_y_index = [the_value_x_index , length_y] x_index=the_value_x_y_index[0] y_index=the_value_x_y_index[1] else: the_value_y_index = list(result_matrix.loc[length_x,:]==terminal_max).index(True) the_value_x_y_index = [length_x , the_value_y_index] x_index=the_value_x_y_index[0] y_index=the_value_x_y_index[1] #取此位置以后的两端序列, 开始向前依次添加ATCG或者'-' section_x_seq = x_seq[x_index:] section_y_seq = y_seq[y_index:] #因为从右下角到左上角依次检索,所以先给字符串反转,然后再尾部添加. 这一过程相当与从尾部向头部依次添加 section_x_seq = section_x_seq[::-1] section_y_seq = section_y_seq[::-1] #此过程为从后往前把序列补齐 while x_index and y_index: #如果是1,相同的碱基 # 2,AT GC互补 , # 3,AG TC错配 这三种情况之一则分别添加原序列的原位置的碱基 if result_matrix.iloc[x_index,y_index] == result_matrix.iloc[x_index-1,y_index-1] + scoring_matrix[x_seq[x_index-1]][y_seq[y_index-1]]: section_x_seq += x_seq[x_index-1]#;print(1) section_y_seq += y_seq[y_index-1] x_index -= 1 y_index -= 1 #否则 , 分别添加原序列的原位置的碱基和'-' else: if result_matrix.iloc[x_index,y_index] == result_matrix.iloc[x_index-1,y_index] + scoring_matrix[x_seq[x_index-1]]['-']: section_x_seq += x_seq[x_index-1]#;print(1) section_y_seq += '-' x_index -= 1 else: section_x_seq += '-'#;print(1) section_y_seq += y_seq[y_index-1] y_index -= 1 #如果x_index或者y_index 其中一个未归零,另个为零, 则直接给未归零的序列补'-' while x_index: section_x_seq += x_seq[x_index-1]#;print(1) section_y_seq += '-' x_index -= 1 while y_index: section_x_seq += '-'#;print(1) section_y_seq += y_seq[y_index-1] y_index -= 1 #把倒转的序列再转回来 result_x_seq = section_x_seq[::-1] result_y_seq = section_y_seq[::-1] # 使section_x_seq 和section_y_seq为同一长度 , 短序列补值'-' length_x = len(result_x_seq) length_y = len(result_y_seq) if length_x < length_y: result_x_seq += '-' * (length_y - length_x)#;print(1) else: result_y_seq += '-' * (length_x - length_y)#;print(1) #依据补值完成的两列数据和得分矩阵 , 计算总得分 Total_score = sum([scoring_matrix[result_x_seq[x_index]][result_y_seq[x_index]] for x_index in range(len(result_x_seq))]) ################################################################################### #得到输出结果的中间行 例如 '|||||||||| |||| ||||||' Middle_row='' for (x_element,y_element) in zip(result_x_seq,result_y_seq): if x_element==y_element: Middle_row += '|' else: Middle_row += ' ' return Total_score, result_x_seq, result_y_seq,Middle_row ################################################################################ if __name__ == '__main__': (x_seq,y_seq,out_file_name,right,base_pair,wrong,gap) = parameter() #得到所有参数 scoring_matrix = Generating_scoring_matrix(right,base_pair,wrong,gap) #生成得分矩阵 result_matrix = compute_result_matrix(x_seq=x_seq, y_seq=y_seq, scoring_matrix=scoring_matrix) #生成序列得分矩阵 score, result_x_seq, result_y_seq,Middle_row = compute_global_alignment(x_seq=x_seq, y_seq=y_seq, scoring_matrix=scoring_matrix, result_matrix=result_matrix) #将矩阵转化为结果序列 Adjust_output_format_and_output(result_x_seq,Middle_row,result_y_seq,out_file_name) #整理数据,写入数据