一个Android视图有很多控件,那么怎么来控制它们的位置排列呢?我们需要容器来存放这些控件并控制它们的位置排列,就像HTML中div, table一样,Android布局也起到同样的作用。
Android布局主要有以下几种: LinearLayout, RelativeLayout,TableLayout,AbsoluteLayout. 最后一种AbsoluteLayout是通过指定控件的x/y坐标来定位的,不太灵活所以已经不推荐使用了。
(1) LinearLayout
LinearLayout线性布局,包含在LinearLayout里面的控件按顺序排列成一行或者一列,类似于Swing里的FlowLayout和Silverlight里的StackPanel,它的常用的属性主要包括:
Orientation方向,即指定LinearLayout是代表一行还是一列,可以为horizontal或vertical,如android:orientation="vertical",当然也在可以在代码里通过setOrientation()方法来设置。
Fill Mode填充方式,所有在LinearLayout的控件都必须指定它的填充方式, 即设置android:layout_width和android:layout_height,可以为三种值(1)具体的像素值,如20px (2) wrap_content, 表示按控件文本实际长度显示 (3) fill_parent, 表示填充剩下的所有可用空间。
Weight权重,如果你想让一行或一列的控件按比例显示,这时候权重就起到作用了,如想让一行里面两控件其中一控件占两倍于另一控件的空间,可以把其中一控件的android:layout_weight设置为1, 另一个为2 即可。
在前面一篇Android消息提示框和对话框也有个LinearLayout的例子, 现在来看一下Android官方的一个Demo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView android:text="red" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#aa0000" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:text="green" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#00aa00" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:text="blue" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#0000aa" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:text="yellow" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#aaaa00" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView android:text="row one" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:text="row two" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:text="row three" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:text="row four" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
可以看到父类LinearLayout包含了一个水平布局的LinearLayout和一个垂直布局的LinearLayout,它们分别包含了四个平分宽度和高度的TextView,运行效果如下:
(2) RelativeLayout
相对布局,它是依靠与父容器,同一容器中其它控件的相对位置来排列显示的。主要常用的属性如下:
相对父容器的属性:
android:layout_alignParentTop: 控件的顶部与父容器的顶部对齐,类似的几个属性从名字可以看出它们的作用:android:layout_alignParentBottom, android:layout_alignParentLeft, android:layout_alignParentRight.
相对同一容器中其它控件的属性:
android:layout_above: 表示此控件在另一控件的上面,类似的还有android:layout_below, android:layout_toLeftOf, android:layout_toRightOf.
android:layout_alignTop: 表示此控件与另一控件顶部对齐,类似的还有android:layout_alignBottom, android:layout_alignLeft, android:layout_alignRight.
既然是相对于另一个控件,就必须在定义这控件时候指定是哪个控件,如控件A的ID为@+id/widget_a, 控件B若要在控件A下面可以这样设置android:layout_below="@id/widget_a"。
来看一下官方的一个Demo:
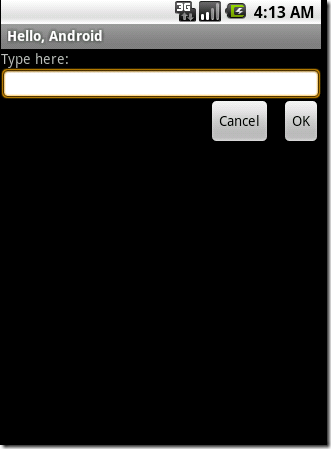
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/label" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Type here:" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/entry" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@android:drawable/editbox_background" android:layout_below="@id/label" /> <Button android:id="@+id/ok" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/entry" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_marginLeft="10dip" android:text="OK" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/ok" android:layout_alignTop="@id/ok" android:text="Cancel" /> </RelativeLayout>
运行效果如下:
(3) TableLayout
表格布局,类似于HTML的Table和Silverlight的Grid。通过TableRow来定义一行,如果一个控件占用多列可以设置android:layout_span, 类似于HTML的colspan。默认情况下一个控件是按顺序放置在每一列的(column 0, column 1….), 也可以通过android:layout_column指定放在哪一列。如果一列内容过长或者过短,可以通过android:stretchColumns和android:shrinkColumns来增加或者减少此列的宽度。
来看一下官方的一个Demo:
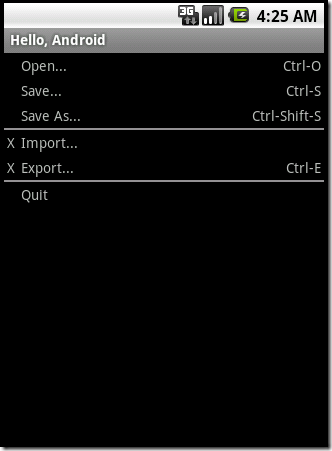
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:stretchColumns="1"> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Open..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-O" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Save..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-S" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Save As..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-Shift-S" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <View android:layout_height="2dip" android:background="#FF909090" /> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="X" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Import..." android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="X" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Export..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-E" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <View android:layout_height="2dip" android:background="#FF909090" /> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Quit" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
这个表格有三列,通过设置android:stretchColumns="1"来增加了第二列的宽度。运行效果如下:
希望本文对您有所帮助,其它与Android相关文章如下:
Android Project Structure(项目结构)
欢迎关注我的微信公众号

参考书籍:Beginning Android 2 和Android官方文档