. 最近工作上有一个需求,需要将图片打包成图集,以便于让资源更紧凑,利用率更高,提升性能,游戏行内的同志应该很熟练这个操作.通常我们需要用一个app来完成这项工作,最出名的莫过于Texture Packer。
Texture Packer官方示意图

. 最早接触到这一概念的时候,我还是一个学生,当时玩的《暗黑魔破坏神2》,它有一个背包系统,这个背包系统跟现在大多数游戏都不一样,它的道具存放并非等大小,比如长剑比匕首长,斧头比长剑宽,因此在摆放道具时,不能乱放,不然背包就不够用。
暗黑破坏神2背包截图

. 这是一个很有意思的设计,但现在基本上绝迹了,以至于我想到游戏中的背包就会不禁想起暗黑破坏神2的背包系统,我在《天龙八部》游戏中,第一次发现了背包自动整理这一项功能,但是它的背包道具都是等大小的,所以平平无奇,但却不由让我想到《暗黑破坏神2》的背包自动整理,它必然会涉及到一个最优排列组合算法。这个疑惑一直困扰了我很多年,它到底是怎么实现的?直到上周,我重新打开了《暗黑破坏神2》这款游戏,发现它根本没有这个功能,童年幻想破灭~
. 虽然童年幻想破灭了,但成年梦想得跟上,正好工作有这么一个让我去实现的机会,于是我尝试去思考算法,起初想到经典的《背包算法》,仔细研究后发现不太适用,于是放弃。不得不说,厕所是一个很适合思考的地方,因为后来的实现方案是我在蹲厕所的时候突然就想出来了。有没有科学上的解释?
收纳箱算法?
. 这个算法跟我们日常使用收纳箱的思路很相似,起初收纳箱是空的,它只有一个存放空间,但是很大.之后我们逐个物品往里面放,每次放进去一个物品,原来的空间都会被拆分成两个,最后空间越来越小,直到不能装下剩下的物品,或者物品放完了,这一过程就结束了.
收纳箱示意图
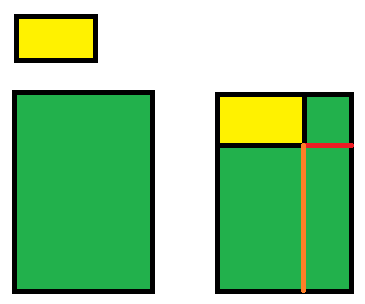
. 上图清晰描述了收纳箱的存放过程,绿色是收纳箱,黄色是物品,起初收纳箱是空的,只有一个空间,放进物品后,空间被拆分了,这一步是关键,因为放进一个物品会有两种拆分策略,红色线和棕色线分表分表显示了两种拆分策略,如果按红色线拆分,则会产生一个很小的空间和一个很大的空间,如果按棕色线拆分,则产生两个大小均匀的空间。这两种策略对应不同的物品有奇效。每次放进去一个物品,收纳箱的一处空间就会被占用,而算法只考虑没有被占用的空间即可。
. 接下来就是逐个物品往收纳箱里放,这一步也是关键,因为每次放进一个物品,空间都会被划分,这个划分依据是物品的大小,如果先放进去一个很小的物品,比如1x1大小的物品,那么空间无论怎么分,都会产生一个很狭窄的空间,这个狭窄的空间很可能存不下后续的任何物品,那么这个空间就浪费了,因此在此之前,先对所有物品进行一个排序,这个排序可以按物品的面积,物品的宽度,物品的高度,物品的最长的边,等等。这些排列策略也会影响最终的排列组合。
改进
空间被浪费
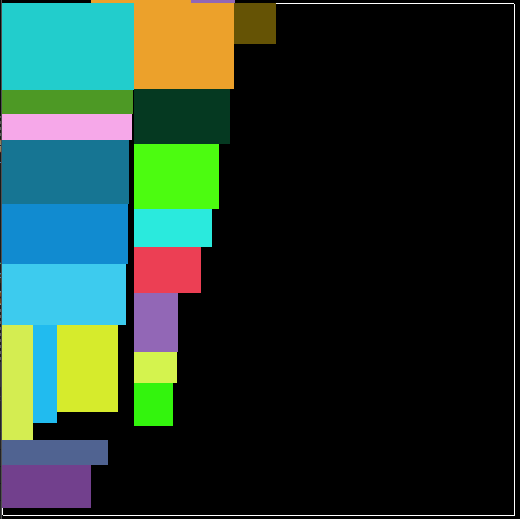
. 上图是一个空间被浪费的例子,因为上文描述的算法需要已知收纳箱大小,比如已知收纳箱512x512大小,如果物品总面积超出这个大小,则装不下,如果物品远小于这个大小,则浪费空间,所以算法能动态计算大小,那就再好不过了。不过谢天谢地,很容易就可以搞定这个问题,我们只需要提前计算出单个物品最大需要的大小,用这个大小作为收纳箱的大小就可以了。
自动适应

. 优化过后,已经提高了不少空间利用率,第一个收纳箱装进了最大的物品,后面的收纳箱采用较小的尺寸继续装剩下的物品,直到全部装完为止。但是这里产生了一个新问题,会生成多个收纳箱,如果多个收纳箱都很小,那资源复用率就下降了,所以还需要进一步优化,尽可能提高资源复用率。比如两个128x128可以合并成一个256x256,两个256x256可以合并成一个512x512。
. 思路是这样的,设定一个打包级别,当这个级别的打包数量达到一个值,就将这个级别提升一级,再重新打包,直到所有级别的收纳箱都没有超出限制。比如,128x128 2,256x256 2,512x512 3 分别代表三个不同的级别,他们是递增关系,当128x128的收纳箱达到2个的时候,说明它需要提升一个级别重新打包,于是级别提升到256x256,依次类推。
最终版本
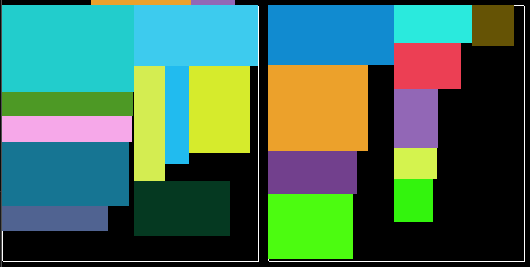
以上结果是采用按棕色线拆分空间,按物品最长边排序,及以下打包级别:
{ 128, 128, 1 },
{ 256, 256, 2 },
{ 512, 512, 3 },
{ 1024, 1024, 4 },
{ 2048, 2048, 100 },
动态图
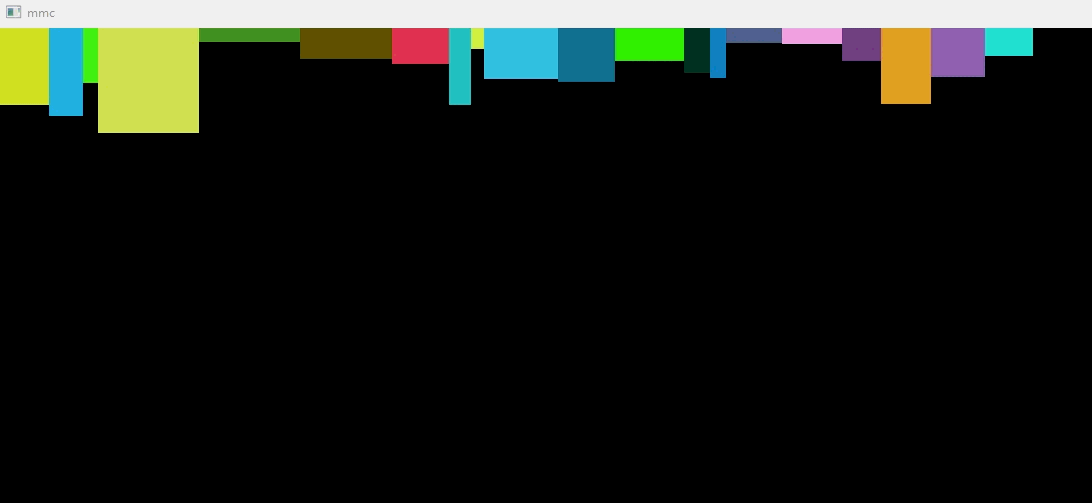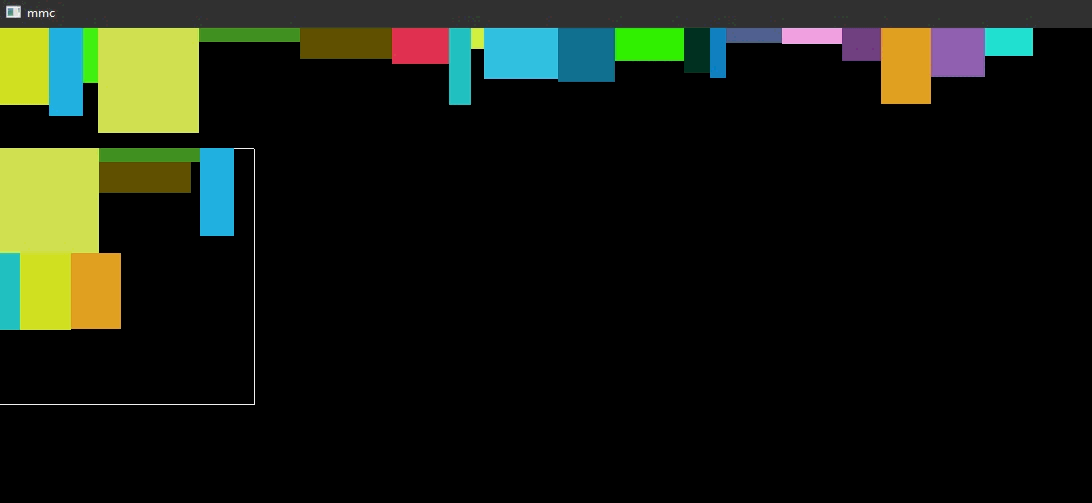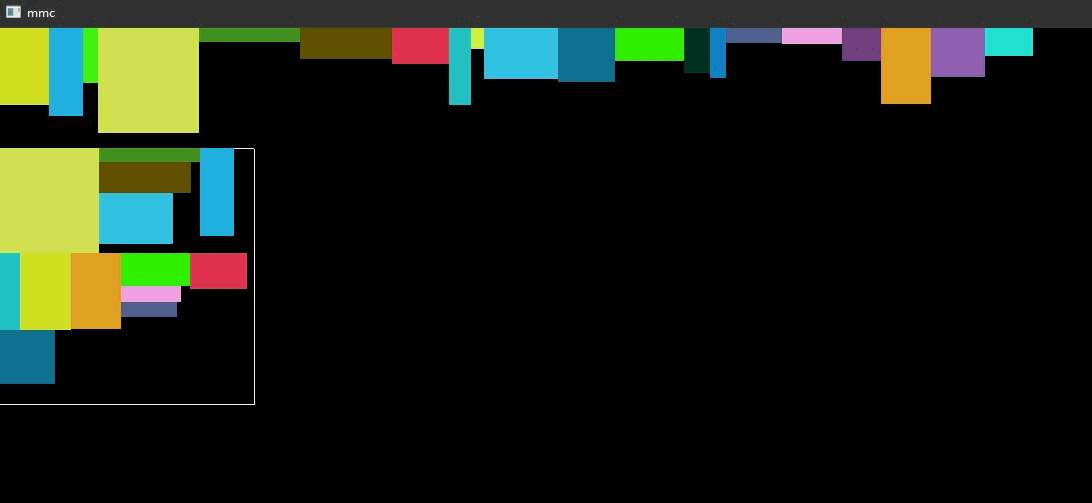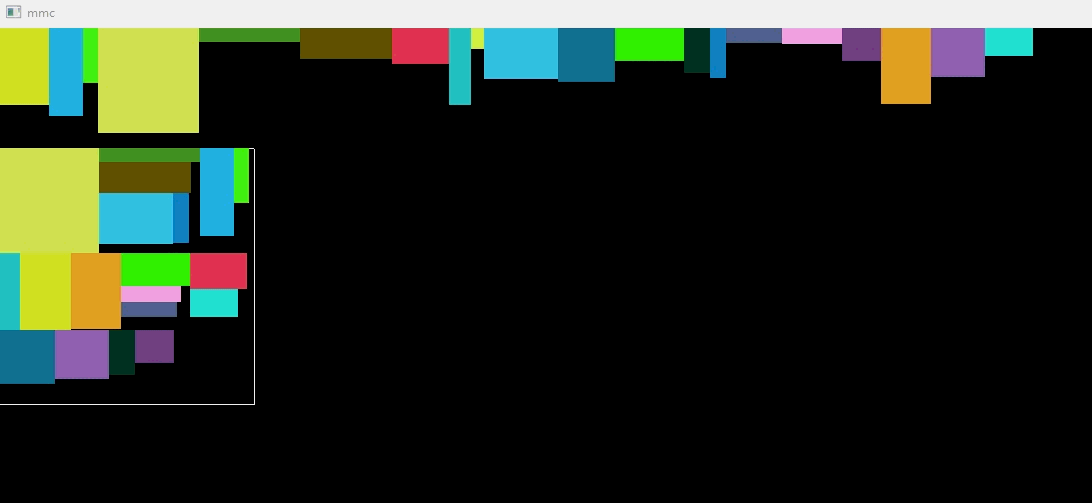
// storage_box.h
#pragma once
#include <list>
#include <tuple>
#include <array>
#include <vector>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm>
using iint = int;
using uint = unsigned int;
class StorageBox {
public:
struct Item {
uint i;
uint w;
uint h;
uint GetV() const
{
return std::max(w, h);
}
};
struct ResultItem {
uint i;
uint x;
uint y;
uint w;
uint h;
ResultItem(): i((uint)~0)
{ }
uint GetV() const
{
return w * h;
}
bool IsReady() const
{
return i != (uint)~0;
}
bool IsContains(const Item & item) const
{
return w >= item.w && h >= item.h;
}
bool AddItem(const Item & item, ResultItem * out0, ResultItem * out1)
{
if (!IsContains(item))
{
return false;
}
auto nx = x + item.w;
auto ny = y + item.h;
auto s0 = (w - item.w) * item.h;
auto s1 = (h - item.h) * w;
auto s2 = (w - item.w) * h;
auto s3 = (h - item.h) * item.w;
// 两种切分策略:
// 按最大面积切分
// 按均匀面积切分
//if (std::max(s0, s1) > std::max(s2, s3))
if (std::max(s0, s1) - std::min(s0, s1) < std::max(s2, s3) - std::min(s2, s3))
{
out0->x = nx;
out0->y = y;
out0->w = w - item.w;
out0->h = item.h;
out1->x = x;
out1->y = ny;
out1->w = w;
out1->h = h - item.h;
}
else
{
out0->x = nx;
out0->y = y;
out0->w = w - item.w;
out0->h = h;
out1->x = x;
out1->y = ny;
out1->w = item.w;
out1->h = h - item.h;
}
w = item.w;
h = item.h;
i = item.i;
return true;
}
};
struct ResultBox {
uint level;
std::vector<ResultItem> items;
};
// 打包级别
static constexpr iint PACK_LEVEL[][3] = {
{ 128, 128, 1 },
{ 256, 256, 2 },
{ 512, 512, 3 },
{ 1024, 1024, 4 },
{ 2048, 2048, 100 },
};
std::vector<ResultBox> Pack(std::vector<Item> items);
private:
// 确定使用哪个级别打包图集
uint CheckLevel(const Item & item);
uint CheckLevel(const std::vector<Item> & items);
// 根据图片的V值进行排序
void SortItems(std::vector<Item> & items);
void SortItems(std::vector<ResultItem> & items);
uint CheckLimit(
std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator cur,
std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator end);
// 打包
ResultBox PackBox(
std::vector<Item> & items, uint level);
void PackBox(
std::vector<Item> & items, uint level, std::vector<ResultBox> & retBoxs);
// 解包
void UnpackBox(std::vector<Item> & items,
std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator cur,
std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator end);
};
// storage_box.cpp
#include "storage_box.h"
std::vector<StorageBox::ResultBox> StorageBox::Pack(std::vector<Item> items)
{
std::vector<ResultBox> retBoxs;
PackBox(items, 0, retBoxs);
for (auto it = retBoxs.begin(); it != retBoxs.end();)
{
auto level = it->level;
auto limit = StorageBox::PACK_LEVEL[level][2];
auto count = CheckLimit(it, retBoxs.end());
if (count > limit)
{
UnpackBox(items, it, retBoxs.end());
retBoxs.erase(it, retBoxs.end());
PackBox(items, level+1, retBoxs);
it = retBoxs.begin();
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
return retBoxs;
}
uint StorageBox::CheckLevel(const Item & item)
{
for (auto i = 0; i != sizeof(PACK_LEVEL) / sizeof(PACK_LEVEL[0]); ++i)
{
if ((uint)PACK_LEVEL[i][0] >= item.w &&
(uint)PACK_LEVEL[i][1] >= item.h)
{
return i;
}
}
return (uint)~0;
}
uint StorageBox::CheckLevel(const std::vector<Item>& items)
{
uint level = 0;
for (auto & item : items)
{
auto i = CheckLevel(item);
assert((uint)~0 != i);
if (i > level) { level = i; }
}
return level;
}
void StorageBox::SortItems(std::vector<Item>& items)
{
std::sort(items.begin(), items.end(), [](const Item & item0, const Item & item1)
{
return item0.GetV() > item1.GetV();
});
}
void StorageBox::SortItems(std::vector<ResultItem> & items)
{
std::sort(items.begin(), items.end(), [](const ResultItem & item0, const ResultItem & item1)
{
return item0.GetV() < item1.GetV();
});
}
uint StorageBox::CheckLimit(std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator cur, std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator end)
{
uint count = 0;
uint level = cur->level;
cur = std::next(cur);
while (cur != end && cur->level == level)
{
++cur; ++count;
}
return count;
}
StorageBox::ResultBox StorageBox::PackBox(std::vector<Item> & items, uint level)
{
ResultBox retBox;
retBox.level = level;
std::vector<ResultItem> retItems;
ResultItem retItem;
retItem.i = (uint)~0;
retItem.x = 0;
retItem.y = 0;
retItem.w = PACK_LEVEL[level][0];
retItem.h = PACK_LEVEL[level][1];
retItems.push_back(retItem);
auto itemIndex = 0u;
ResultItem retItem0;
ResultItem retItem1;
while (itemIndex != items.size())
{
auto isNewItem = false;
for (auto it = retItems.begin(); it != retItems.end(); ++it)
{
if (it->AddItem(items.at(itemIndex), &retItem0, &retItem1))
{
isNewItem = true;
// 添加到收纳箱
retBox.items.push_back(*it);
retItems.erase(it);
// 新增2个新收纳箱
retItems.push_back(retItem0);
retItems.push_back(retItem1);
SortItems(retItems);
// 删除物品
items.erase(items.begin() + itemIndex);
break;
}
}
if (!isNewItem) { ++itemIndex; }
}
return retBox;
}
void StorageBox::PackBox(std::vector<Item>& items, uint level, std::vector<ResultBox>& retBoxs)
{
SortItems(items);
while (!items.empty())
{
retBoxs.push_back(PackBox(items, level == 0? CheckLevel(items): level));
level = 0;
}
}
void StorageBox::UnpackBox(std::vector<Item> & items, std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator cur, std::vector<ResultBox>::iterator end)
{
for (; cur != end; ++cur)
{
for (auto & retItem : cur->items)
{
if (retItem.IsReady())
{
Item item;
item.i = retItem.i;
item.w = retItem.w;
item.h = retItem.h;
items.push_back(item);
}
}
}
}
这个算法并不能得到最优排列组合,但是这个算法简单而且在大多数情况下都够用。