相关包导入
import torch
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
%matplotlib inline
数据集加载
transformation = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(), ## 转化为一个tensor, 转换到0-1之间, 将channnel放在第一维
])
这里是定义了数据变换的方式,用的transforms.ToTensor()。
这个方法的作用是将数据类型转化为一个tensor类型、将数据归一化,并且将channel放在第一维上
train_ds = datasets.MNIST(
'E:/datasets2/1-18/dataset/daatset',
train = True,
transform =transformation,
download = True
)
test_ds = datasets.MNIST(
'E:/datasets2/1-18/dataset/daatset',
train = False,
transform = transformation,
download = True
)
datasets和transforms都在torchvision包里面,用的时候需要引用一下。
这里面四个属性分别表示的是:数据集下载后存放的位置,是否是训练数据,变换方式,是否需要下载
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size = 64, shuffle = True)
test_dl = DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size = 256)
模型定义与训练(套用模板)
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(28 * 28, 120)
self.linear_2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.linear_3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, input):
x = input.view(-1, 28 * 28)
x = F.relu(self.linear_1(x))
x = F.relu(self.linear_2(x))
x = self.linear_3(x)
return x
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def fit(epoch, model, trainloader, testloader):
correct = 0
total = 0
running_loss = 0
for x, y in trainloader:
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim = 1)
correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc = correct / total
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(trainloader.dataset)
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
test_running_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in testloader:
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y)
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim = 1)
test_correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
test_total += y.size(0)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_test_acc = test_correct / test_total
epoch_test_loss = test_running_loss / len(testloader.dataset)
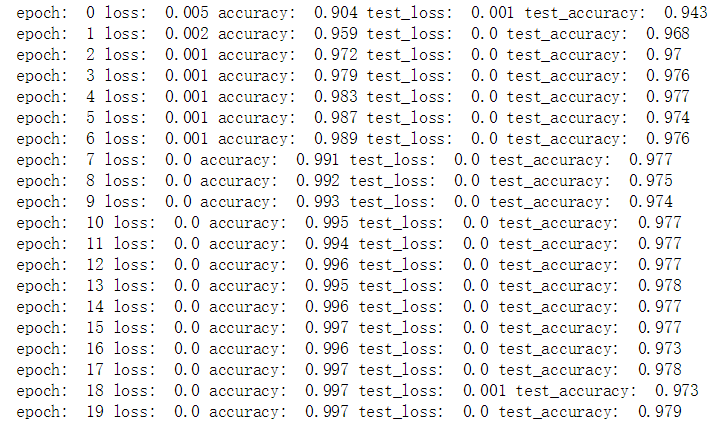
print('epoch: ', epoch,
'loss: ', round(epoch_loss, 3),
'accuracy: ', round(epoch_acc, 3),
'test_loss: ', round(epoch_test_loss, 3),
'test_accuracy: ', round(epoch_test_acc, 3))
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
model = Model()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = 0.001)
epochs = 20
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc = fit(epoch, model, train_dl, test_dl)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
训练结果