描述符的使用
python是弱类型语言,及参数的赋值没有类型限制,下面通过描述符机制来实现类型限制功能
描述符应用1.py
class Typed:
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
print('get方法')
print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
print('owner是[%s]'%owner)
def __set__(self, instance, value):
print('set方法')
#instance就是实例化出来的对象本身
print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
print('value是[%s]'%value)
def __delete__(self, instance):
print('delete方法')
print('instance是[%s]' % instance)
class People:
name = Typed()
def __init__(self,name,age,salary):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.salary = salary
#实例化触发了以下三个赋值操作
#p1.__dict__['name'] = 'zhangsan'
#p1.__dict__['age'] = 18
#p1.__dict__['salary'] = 999999
#但是数据属性被描述符描述了进行赋值操作调用的是描述类的set方法
#因为set方法没有进行实际赋值操作所以字典的name属性为None
p1 = People('zhangsan',18,999999)
# set方法
# instance是[<__main__.People object at 0x000001E527F67390>]
# value是[zhangsan]
print(p1)
#<__main__.People object at 0x000001BF1B047390>
print(p1.__dict__)
#调用数据属性触发__get__方法输出
p1.name
# get方法
# instance是[<__main__.People object at 0x000001F7F3ED8080>]
# owner是[<class '__main__.People'>]
#调用del删除数据属性,触发__delete__方法输出
del p1.name
# delete方法
# instance是[<__main__.People object at 0x0000018239F274E0>]
以上只是测试是否调用了描述符,但是对应的__get__,__set__,__delete__只是执行了打印操作没有进行返回值,设置值,删除值的操作所以只有打印输出
PS:根据优先级数据描述符大于实例所以优先调用数据描述符,假如进行了p1.name = ‘lisi’会执行set方法但是不会赋值,name依旧为空
下面在__get__,__set__,__delete__执行对应的返回值,设置值,删除值操作
描述符应用2.py
class Typed:
def __init__(self,key):
self.key=key
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
print('get方法')
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('owner是[%s]'%owner)
#使用对应的key返回值
return instance.__dict__[self.key]
def __set__(self, instance, value):
print('set方法')
#instance就是实例化出来的对象本身
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('value是[%s]'%value)
#对对应的key进行赋值设置操作
instance.__dict__[self.key] = value
def __delete__(self, instance):
print('delete方法')
# print('instance是[%s]' % instance)
#使用对应的key删除操作
instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)
class People:
name = Typed('name')
def __init__(self,name,age,salary):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.salary = salary
#实例化触发了以下三个赋值操作
#p1.name = 'zhangsan'
#p1.age = 18
#p1.salary = 999999
#其中p1.name = 'zhangsan'调用了描述符类Typed进行实例化
#name = Typed('name')运行初始化函数__init__
#self.name = 'name'
p1 = People('zhangsan',18,999999)
#set方法
#打印字典name也赋值成功
print(p1.__dict__)
#{'age': 18, 'name': 'zhangsan', 'salary': 999999}
p1.name
#get方法
del p1.name
#delete方法
#打印字典上一步的删除操作也成功删除了属性name
print(p1.__dict__)
#{'age': 18, 'salary': 999999}
通过定义描述符类的初始化__init__函数获取字典需要修改对应的key值然后执行相应的返回值,设置值,删除值的操作
下面对用户实例化输入的信息进行判断,比如输入姓名只能是字符串格式不能是数字或者其他格式
描述符应用3.py
class Typed:
def __init__(self,key):
self.key=key
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
print('get方法')
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('owner是[%s]'%owner)
#使用对应的key返回值
return instance.__dict__[self.key]
def __set__(self, instance, value):
print('set方法')
#instance就是实例化出来的对象本身
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('value是[%s]'%value)
#对应的key进行赋值设置操作
if not isinstance(value,str):
print('你输入是不是字符串类型,错误')
return
instance.__dict__[self.key] = value
def __delete__(self, instance):
print('delete方法')
# print('instance是[%s]' % instance)
#使用对应的key删除操作
instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)
class People:
name = Typed('name')
def __init__(self,name,age,salary):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.salary = salary
p1=People(18,18,999999)
#因为调用__set__方法的时候检测到输入的名字不是字符串,然后直接return了所以name没有赋值
print(p1.__dict__)
#set方法
#你输入是不是字符串类型,错误
#{'salary': 999999, 'age': 18}
可以把错误返回改的高端一点
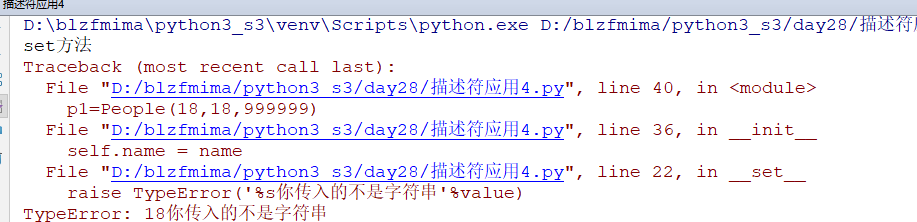
描述符应用4.py
class Typed:
def __init__(self,key):
self.key=key
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
print('get方法')
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('owner是[%s]'%owner)
#使用对应的key返回值
return instance.__dict__[self.key]
def __set__(self, instance, value):
print('set方法')
#instance就是实例化出来的对象本身
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('value是[%s]'%value)
#对应的key进行赋值设置操作
if not isinstance(value,str):
# print('你输入是不是字符串类型,错误')
# return
raise TypeError('%s你传入的不是字符串'%value)
instance.__dict__[self.key] = value
def __delete__(self, instance):
print('delete方法')
# print('instance是[%s]' % instance)
#使用对应的key删除操作
instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)
class People:
name = Typed('name')
def __init__(self,name,age,salary):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.salary = salary
p1=People(18,18,999999)
运行直接报错
以上只是实现了输入的name必须是字符串,并没有对输入的age限制必须是整型
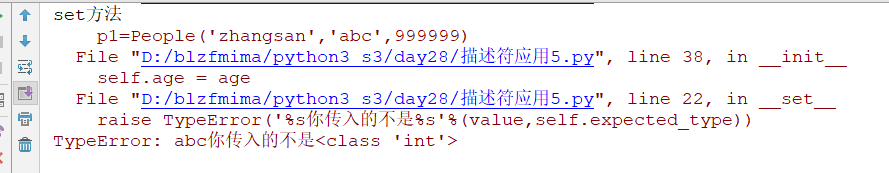
描述符应用5.py
class Typed:
def __init__(self,key,expected_type):
self.key=key
self.expected_type=expected_type
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
print('get方法')
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('owner是[%s]'%owner)
#使用对应的key返回值
return instance.__dict__[self.key]
def __set__(self, instance, value):
print('set方法')
#instance就是实例化出来的对象本身
# print('instance是[%s]'%instance)
# print('value是[%s]'%value)
#对应的key进行赋值设置操作
if not isinstance(value,self.expected_type):
# print('你输入是不是字符串类型,错误')
# return
raise TypeError('%s你传入的不是%s'%(value,self.expected_type))
instance.__dict__[self.key] = value
def __delete__(self, instance):
print('delete方法')
# print('instance是[%s]' % instance)
#使用对应的key删除操作
instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)
class People:
name = Typed('name',str)
age = Typed('age',int)
def __init__(self,name,age,salary):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.salary = salary
p1=People('zhangsan','abc',999999)
print(p1.__dict__)
因为age输入的是字符串所以报错