在优化C#代码或对比某些API的效率时,通常需要测试某个方法的运行时间,可以通过DateTime来统计指定方法的执行时间,也可以使用命名空间System.Diagnostics中封装了高精度计时器QueryPerformanceCounter方法的Stopwatch类来统计指定方法的执行时间:
1.使用DateTime方法:
DateTime dateTime = DateTime.Now;
MyFunc();
Console.WriteLine((DateTime.Now - dateTime).TotalMilliseconds);
2.使用Stopwatch方式:
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch(); stopwatch.Start(); MyFunc();
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds); //本次MyFunc()方法的运行毫秒数
//重置计时器 stopwatch.Restart(); //此处可以使用stopwatch.Reset(); stopwatch.Start();组合代替
MyFunc();
stopwatch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine(stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds); //本次MyFunc()方法的运行毫秒数
以上两种办法都可以达到获取方法执行时间的目的,但是在需要对整个项目中的方法都进行监测用时时,除了使用性能分析工具,我们还可以通过代码注入的方式给程序集中每一个方法加入计时器;
通过命名空间System.Reflection.Emit中的类可以动态的创建程序集、类型和成员,通常类库Mono.Cecil可以动态读取并修改已经生成的IL文件,这种在不修改源代码的情况下给程序集动态添加功能的技术称为面向切面编程(AOP);
这里给出了一个注入使用Stopwatch来检测方法执行时间的代码,这里的Mono.Cecil类库可以通过nuget进行安装:
using System; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Diagnostics; using Mono.Cecil; using Mono.Cecil.Cil; using Mono.Collections.Generic;
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < args.Length; i++) { FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(args[i], FileMode.Open); if (fileStream != null) { AssemblyDefinition aD = AssemblyDefinition.ReadAssembly(fileStream); ModuleDefinition mD = aD.MainModule; Collection<TypeDefinition> typeDefinition = mD.Types; foreach (TypeDefinition type in typeDefinition) { if (type.IsClass) { foreach (MethodDefinition method in type.Methods) { if (method.IsPublic && !method.IsConstructor) { ILProcessor il = method.Body.GetILProcessor(); TypeReference stT = mD.ImportReference(typeof(Stopwatch)); VariableDefinition stV = new VariableDefinition(stT); method.Body.Variables.Add(stV); Instruction first = method.Body.Instructions.First(); il.InsertBefore(first, il.Create(OpCodes.Newobj,
mD.ImportReference(typeof(Stopwatch).GetConstructor(new Type[] { })))); il.InsertBefore(first, il.Create(OpCodes.Stloc_S, stV)); il.InsertBefore(first, il.Create(OpCodes.Ldloc_S, stV)); il.InsertBefore(first, il.Create(OpCodes.Callvirt,
mD.ImportReference(typeof(Stopwatch).GetMethod("Start")))); Instruction @return = method.Body.Instructions.Last(); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Ldloc_S, stV)); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Callvirt,
mD.ImportReference(typeof(Stopwatch).GetMethod("Stop")))); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Ldstr, $"{method.FullName} run time: ")); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Ldloc_S, stV)); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Callvirt,
mD.ImportReference(typeof(Stopwatch).GetMethod("get_ElapsedMilliseconds")))); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Box, mD.ImportReference(typeof(long)))); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Call,
mD.ImportReference(typeof(string).GetMethod("Concat", new Type[] { typeof(object), typeof(object) })))); il.InsertBefore(@return, il.Create(OpCodes.Call,
mD.ImportReference(typeof(Console).GetMethod("WriteLine", new Type[] { typeof(string) })))); } } } } FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(args[i]); string fileName = fileInfo.Name; int pointIndex = fileName.LastIndexOf('.'); string frontName = fileName.Substring(0, pointIndex); string backName = fileName.Substring(pointIndex, fileName.Length - pointIndex); string writeFilePath = Path.Combine(fileInfo.Directory.FullName, frontName + "_inject" + backName); aD.Write(writeFilePath); Console.WriteLine($"Success! Output path: {writeFilePath}"); fileStream.Dispose(); } } Console.Read(); }
完整的项目传到了Github上=>InjectionStopwatchCode,下载项目后,通过dotnet build命令即可编译出可执行程序,将目标程序集文件拖入到该应用程序即可在程序集目录导出注入代码后的程序集文件,经过测试,包括方法拥有返回值和方法的参数列表中包含out和ref参数等情况都不会对运行结果产生影响;
示例:
using System; public class MyClass { public void MyFunc() { int num = 1; for (int i = 0; i < int.MaxValue; i++) { num++; } } } public class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { MyClass myObj = new MyClass(); myObj.MyFunc(); Console.Read(); } }
原始IL代码:

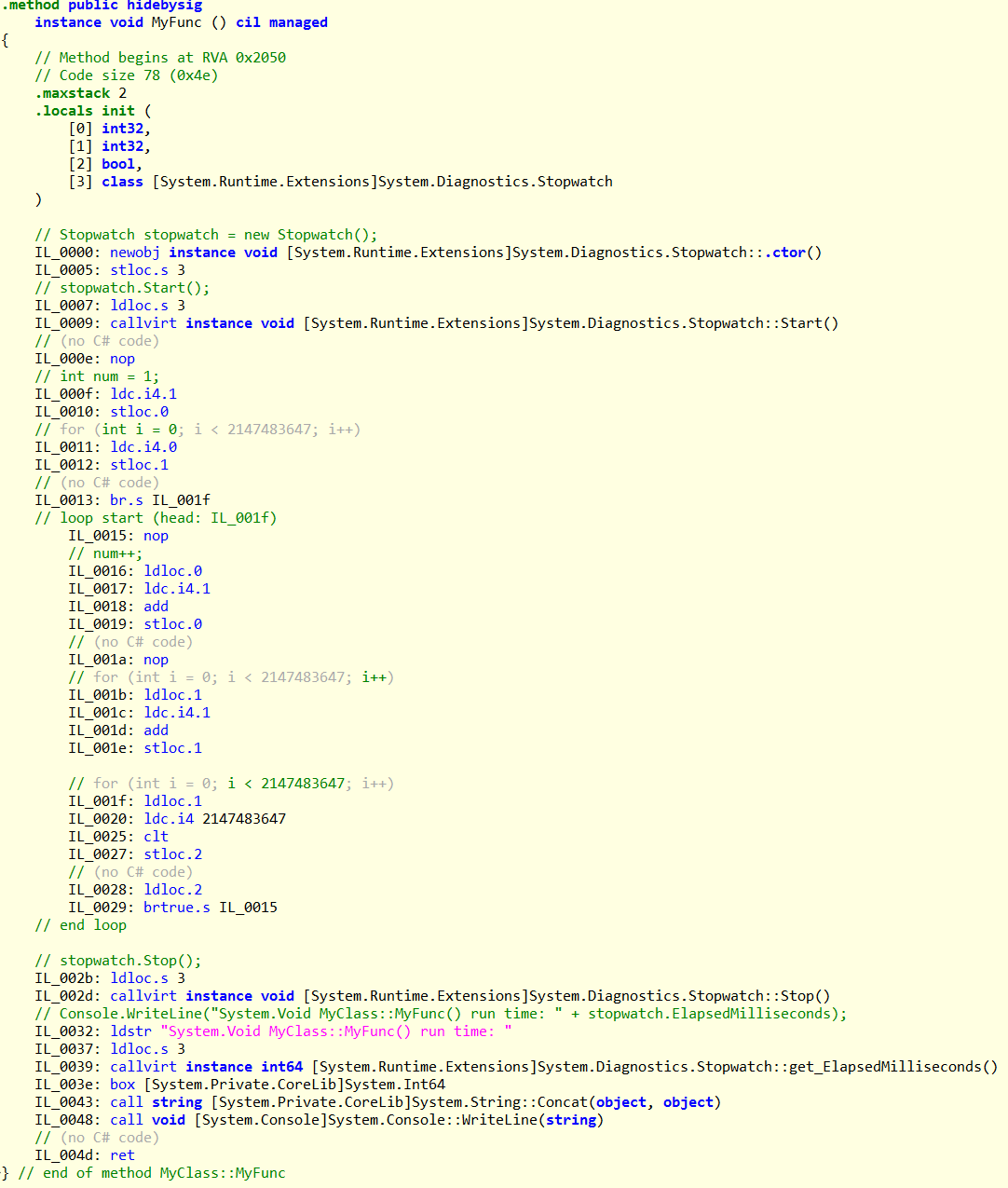
代码注入后IL代码:
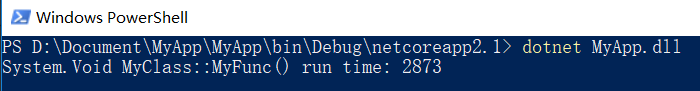
代码注入后运行结果:
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的认可是我写作的最大动力!
作者:Minotauros
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/minotauros/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。