一、Masonry介绍
之前我们在屏幕适配的章节中学习过AutoLayout的使用,但那都是在可视化界面上进行添加约束完成的,我们很多时候都需要在代码中使用AutoLayout约束,苹果也为我们提供了实现,使用NSLayoutConstraint类表示约束,但使用起来比较复杂,代码量比较大,例如创建一个约束的方法:
+ (id)constraintWithItem:(id)view1 /* 一个UIView */
attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attribute1 /* 属性 */
relatedBy:(NSLayoutRelation)relation /* 关系 */
toItem:(id)view2 /* 另一个UIView */
attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attribute2 /* 属性 */
multiplier:(CGFloat)multiplier /* 倍数 */
constant:(CGFloat)constant; /* 偏移 */如果约束一多,这个方法调用次数就会越多,代码就会变得很长。
实际上我们可以使用第三方框架Masonry,该框架是一个轻量级的布局框架,封装了AutoLayout,拥有自己的描述语法,采用更优雅的链式语法,简洁明了,并具有高可读性。
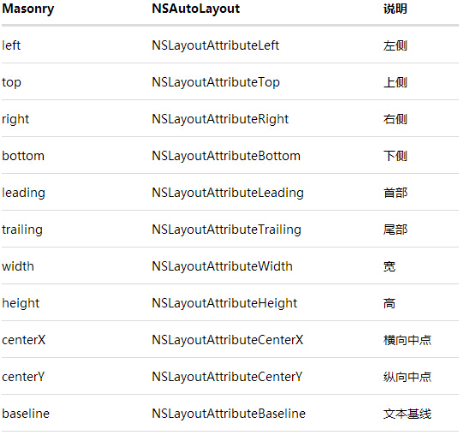
Masonry基本支持AutoLayout的所有属性:
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *left;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *top;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *right;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *bottom;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *leading;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *trailing;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *width;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *height;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerX;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerY;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *baseline;这些属性与NSLayoutAttrubute的对照表如下:
二、Masonry使用
Masonry的大部分方法都为UIView实现了分类,使我们可以十分简单的使用
下面是Masonry添加约束的方法:
/* 添加新约束,只负责新增约束,不能同时存在两条针对于同一对象的约束,否则会报错 */
- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
/* 更新原有的约束,针对上面的情况,会更新在block中出现的约束,不会导致出现两个相同约束的情况 */
- (NSArray *)mas_updateConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
/* 删除之前约束,重新添加约束,会清除之前的所有约束,仅保留最新的约束 */
- (NSArray *)mas_remakeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
- 上面三个方法不仅只有
UIView可以调用,存有UIView的NSArray数组也可以调用,表示遍历数组中所有UIView进行调用
下面是Block中使用的常见约束语法,[attribute]表示属性,[value]表示值:
/*
属性attribute可以连用,比如top.right.bottom.left
加mas_前缀和没有mas_前缀效果差不多,只是加mas_前缀会对参数装箱,
参数有结构体的时候,需要使用mas_前缀,没有mas_前缀的参数必须为对象
*/
/* 数值约束,top对应NSInteger,center对应NSPoint,size对应NSSize */
make.[attribute].mas_equalTo([value]);
/* 等于约束,两个view之间比较,注意:没有other.edges的属性,edges对应otherView */
make.[attribute].equalTo(otherView.[attribute]);
/* 大于等于约束,两个view之间比较 */
make.[attribute].greaterThanOrEqualTo(otherView.[attribute]);
/* 小于等于约束,两个view之间比较 */
make.[attribute].lessThanOrEqualTo(otherView.[attribute]);
/* 偏移约束 */
make.[attribute].equalTo(otherView.[attribute]).offset([value]);
/* 边界约束,有上、下、左、右边界 */
make.edges.equalTo(otherView).insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake([topValue],[leftValue],[bottomValue],[rightValue]));
/* Margin约束 */
make.[attribute].equalTo(otherView.[attribute]Margin);注意:
添加约束前,必须先把
UIView添加到父视图中,否则会闪退
下面我们通过几个实例来理解:
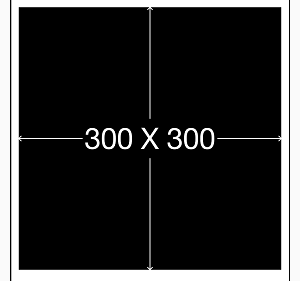
1. 实例一[基础]:居中显示一个view
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
}
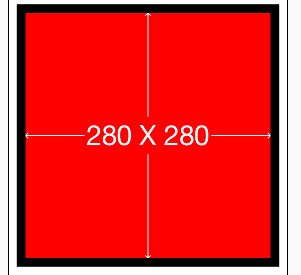
2. 实例二[初级]:让一个view略小于其superView(边距为10)
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
UIView *sv1 = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv1.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[sv addSubview:sv1];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
[sv1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10));
/* 等价于
make.top.equalTo(sv).with.offset(10);
make.left.equalTo(sv).with.offset(10);
make.bottom.equalTo(sv).with.offset(-10);
make.right.equalTo(sv).with.offset(-10);
*/
/* 也等价于
make.top.left.bottom.and.right.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10));
*/
}];
实际上and和with这两个方法什么事情都没做:
- (MASConstraint *)with {
return self;
}
- (MASConstraint *)and {
return self;
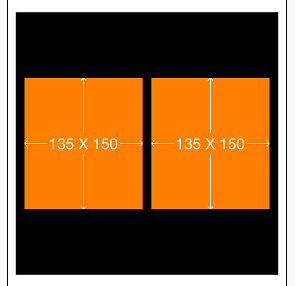
}3. 实例三[初级]:让两个高度为150的view垂直居中且等宽且等间隔排列,间隔为10(自动计算其宽度)
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
int padding1 = 10;
UIView *leftView = [[UIView alloc] init];
leftView.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
[sv addSubview:leftView];
UIView *rightView = [[UIView alloc] init];
rightView.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
[sv addSubview:rightView];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
[leftView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.mas_equalTo(sv.mas_centerY);//中心Y轴和sv中心Y轴相等
make.left.equalTo(sv.mas_left).with.offset(padding1);//左边距离sv的左边界10
make.right.equalTo(rightView.mas_left).with.offset(-padding1);//右边距离rightView的左边界-10
make.height.mas_equalTo(@150);//高度150
make.width.equalTo(rightView);//宽度等于rightView
}];
[rightView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.mas_equalTo(sv.mas_centerY);//中心Y轴和sv中心Y轴相等
make.left.equalTo(leftView.mas_right).with.offset(padding1);//左边距离leftView的右边界10
make.right.equalTo(sv.mas_right).with.offset(-padding1);//右边距离sv的右边界-10
make.height.mas_equalTo(@150);//高度150
make.width.equalTo(leftView);//宽度等于leftView
}];
4. 实例四[中级]:在UIScrollView顺序排列一些view并自动计算contentSize
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
/* 创建ScrollView */
UIScrollView *scrollView = [[UIScrollView alloc] init];
scrollView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[sv addSubView:scrollView];
[scrollView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
//设置边界约束
make.edges.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(5,5,5,5));
}];
//创建ScrollView子视图容器视图
UIView *container = [[UIView alloc] init];
[scrollView addSubView:container];
//添加container约束
[container mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(scrollView);//边界紧贴ScrollView边界
make.width.equalTo(scrollView);//宽度和ScrollView相等
}];
//向container添加多个View
int count = 10;
UIView *lastView = nil;
for(int i = 1;i <= count;++i ){
//创建一个View
UIView *subView = [[UIView alloc] init];
[container addSubView:subView];
//颜色随机
subView.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
green:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
blue:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
alpha:1];
//向subView添加约束
[subView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.and.right.equalTo(container);//左右边界和container紧贴
make.height.mas_equalTo(@(20*i));//高度随i递增
//判断是否有前一个子View
if ( lastView ) {
//如果有前一个View,上边界和前一个View的下边界紧贴
make.top.mas_equalTo(lastView.mas_bottom);
} else {
//如果没有前一个View,上边界和container的下边界紧贴
make.top.mas_equalTo(container.mas_top);
}
}];
//保存前一个View
lastView = subView;
}
//添加container的最后一个约束
[container mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
//container的下边界和最后一个View的下边界紧贴
make.bottom.equalTo(lastView.mas_bottom);
}];
三、Masonry进阶
Masonry为NSArray实现了2个特殊的分类方法:
/*
该方法只有存有UIView的NSArray数组可以调用,NSArray里面的UIView必须有共同的spuerView
该方法作用是UIView之间的水平等宽定距约束,或者垂直等高定距约束。
先确定间距,宽度或高度不确定,但相等
axisType只有MASAxisTypeHorizontal(水平间距类型)和MASAxisTypeVertical(垂直间距类型)
fixedSpacing是UIView两两之间的间距大小
leadSpacing是第一个UIView距离superView左(或上)边界的间距大小
tailSpacing是最后一个UIView距离superView右(或下)边界的间距大小
数组里的所有UIView水平宽度相等,或者垂直高度相等
*/
- (void)mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:(MASAxisType)axisType
withFixedSpacing:(CGFloat)fixedSpacing
leadSpacing:(CGFloat)leadSpacing
tailSpacing:(CGFloat)tailSpacing;
/*
该方法只有存有UIView的NSArray数组可以调用,NSArray里面的UIView必须有共同的spuerView
该方法作用是UIView之间的水平定宽等距约束,或者垂直定高等距约束。
先确定宽度或高度,间距不确定,但相等
axisType只有MASAxisTypeHorizontal(水平间距类型)和MASAxisTypeVertical(垂直间距类型)
fixedSpacing是UIView两两之间的间距大小
leadSpacing是第一个UIView距离superView左(或上)边界的间距大小
tailSpacing是最后一个UIView距离superView右(或下)边界的间距大小
数组里的所有UIView间距相等
*/
- (void)mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:(MASAxisType)axisType
withFixedItemLength:(CGFloat)fixedItemLength
leadSpacing:(CGFloat)leadSpacing
tailSpacing:(CGFloat)tailSpacing;下面是等间距方法的使用实例:
/*
设置水平等宽定距
UIView之间水平间距为20,第一个UIView距离superView左边6,
最后一个UIView距离superView右边7,UIView高度为60,距离顶部40
*/
[array mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:MASAxisTypeHorizontal
withFixedSpacing:20
leadSpacing:6
tailSpacing:7];
[array mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(@40);
make.height.equalTo(@60);
}];/*
设置水平定宽等距
所有UIView的宽度为20,第一个UIView距离superView左边6,
最后一个UIView距离superView右边7,UIView高度为60,距离顶部40
*/
[array mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:MASAxisTypeHorizontal
withFixedItemLength:20
leadSpacing:6
tailSpacing:7];
[array mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(@40);
make.height.equalTo(@60);
}];