案例:
package cn.dzz;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class Main {
static String shape = "";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建窗体
Frame frame = new Frame();
// 创建所需的组件
// 绘制矩形和椭圆的两个事件按钮
Button rectangleButton = new Button("draw-rectangle");
Button ellipsoidButton = new Button("draw-ellipsoid");
// 逻辑判断
// 判断图形的逻辑
final String RECT = "RECT";
final String OVAL = "OVAL";
// 自定义的Canvas类
class DemoCanvas extends Canvas {
// paint方法在repaint()调用之后触发
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
// super.paint(g);
if (shape.equals(RECT)) {
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.drawRect(100,100,150,100);
} else if (shape.equals(OVAL)){
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g.drawOval(100,100,150,100);
}
}
}
// 初始化画布容器对象
Canvas canvas = new DemoCanvas();
// 按钮的事件监听
rectangleButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
shape = RECT;
canvas.repaint();
}
});
ellipsoidButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
shape = OVAL;
canvas.repaint();
}
});
// 组件组装
Panel panel = new Panel();
panel.add(rectangleButton);
panel.add(ellipsoidButton);
canvas.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300, 300));
frame.add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(canvas);
// 自适应和可见
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
预览效果
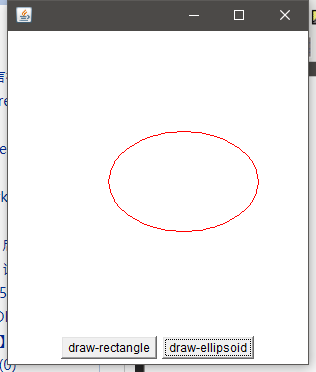
矩形和椭圆

弹球游戏的实现:
借助repaint方法,只要方法执行的频率超过肉眼的速度,
静态的画面就可以实现动画的效果
package cn.dzz;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class SamplePinball {
private Frame frame = new Frame("Pinball-Game");
// 弹跳的活动空间
private final int TABLE_WIDTH = 300;
private final int TABLE_HEIGHT = 400;
// 球拍尺寸
private final int RACKET_WIDTH = 60;
private final int RACKET_HEIGHT = 10;
// 弹球大小
private final int BALL_SIZE = 15;
// 弹球初始出现的坐标位置
private int ball_location_x = 150;
private int ball_location_y = 200;
// 弹球的移动速度
private int speedX = 5;
private int speedY = 10;
// 球拍的坐标
private int racket_location_x = 120;
private final int RACKET_INIT_LOCATION_Y = 340;
private boolean isGameOver = false;
// 计时器?
private Timer flasher;
private Canvas table = new PinballTable();
class PinballTable extends Canvas {
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
// super.paint(g);
// 游戏结束
if(isGameOver) {
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.setFont(new Font("times", Font.BOLD, 30));
g.drawString("游戏结束", 75, 200);
} else {
// 游戏没有结束
// 绘制球拍
g.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
g.fillRect(
racket_location_x,
RACKET_INIT_LOCATION_Y,
RACKET_WIDTH,
RACKET_HEIGHT
);
// 绘制弹球
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g.fillOval(
ball_location_x,
ball_location_y,
BALL_SIZE,
BALL_SIZE
);
}
}
}
public void init() {
// 视图组装与逻辑控制
// 实现球拍变化的控制
KeyListener keyListener = new KeyAdapter(){
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
// super.keyPressed(e);
// 每一个按键都对应了一个按键代码数值
int keyCode = e.getKeyCode();
System.out.println("当前按下的按键是:" + keyCode);
switch (keyCode) {
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT :
if (racket_location_x > 0) {
racket_location_x -= 15;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT :
if (racket_location_x < (TABLE_WIDTH - RACKET_WIDTH)) {
racket_location_x += 15;
}
break;
}
}
};
// 每次刷新需要干的事情:
ActionListener actionListener = new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 弹球碰到墙壁的反弹逻辑
if (ball_location_x <= 0 || ball_location_x >= (TABLE_WIDTH - BALL_SIZE) ) {
speedX = -speedX;
}
if (ball_location_y <= 0 ||
(
ball_location_y > RACKET_INIT_LOCATION_Y - BALL_SIZE &&
ball_location_x > racket_location_x &&
ball_location_x < racket_location_x + RACKET_WIDTH
)
) {
speedY = -speedY;
}
// 弹球越过了球拍的高度,游戏结束了
if (ball_location_y > RACKET_INIT_LOCATION_Y - BALL_SIZE && (ball_location_x < racket_location_x || ball_location_x > racket_location_x + RACKET_WIDTH)
) {
flasher.stop();
isGameOver = true;
}
// 如果没有碰到墙壁则继续移动
ball_location_x += speedX;
ball_location_y += speedY;
// 画布刷新
table.repaint();
}
};
// 弹球的控制 100毫秒(0.1秒)
flasher = new Timer(100, actionListener);
flasher.start();
// 由顶级窗体监听这个事件
frame.addKeyListener(keyListener);
table.addKeyListener(keyListener);
// 设置大小和装填组件
table.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(TABLE_WIDTH, TABLE_HEIGHT));
frame.add(table, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
差点忘了启动类:
package cn.dzz;
public class GUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SamplePinball().init();
}
}