Collection子接口 其一:List接口List
接口存储结构:元素有序,且可重复,每个元素都有对应的索引
根据索引获取容器元素
实现类有:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
三个实现类的异同?
- 都实现了List接口,存储数据的特点相同、存储有序的、可重复的数据
- ArrayList 是List接口的主要实现类,线程不安全的,但是效率高,底层Object[] elementData存储
- LinkedList 双向链表结构存储,对于插入和删除频繁操作,效率比ArrayList高
- Vector 初代List接口实现类,线程安全,效率低。底层Object[]存储
List的接口常用方法【索引支持】
在指定索引位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element)
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
从参数的容器对象的索引位置开始到结尾,添加元素到调用此方法的容器对象
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
/** * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this * list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element * currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to * the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear * in the list in the order that they are returned by the * specified collection's iterator. * * @param index index at which to insert the first element from the * specified collection * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }
按索引获取元素
public E get(int index)
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
返回元素的索引位置,如果是重复了多个元素,返回第一个的位置
public int indexOf(Object o)
/** * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, * or -1 if there is no such index. */ public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }
返回元素的索引位置,如果多个重复元素,返回最后一个出现的
public int lastIndexOf(Object o)
/** * Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, * or -1 if there is no such index. */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }
移除参数的索引上的元素,并返回元素
public E remove(int index)
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
修改指定索引位置的元素
public E set(int index, E element)
/** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with * the specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; }
截取一段,返回指定起始位置到结束位置的元素到一个新的容器上 【返回子集合】
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
/** * Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified * {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If * {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is * empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural * changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa. * The returned list supports all of the optional list operations. * * <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of * the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects * a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view * instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom * removes a range of elements from a list: * <pre> * list.subList(from, to).clear(); * </pre> * Similar idioms may be constructed for {@link #indexOf(Object)} and * {@link #lastIndexOf(Object)}, and all of the algorithms in the * {@link Collections} class can be applied to a subList. * * <p>The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if * the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in * any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are * those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such * a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.) * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} */ public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex); } static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) { if (fromIndex < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); if (toIndex > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex); if (fromIndex > toIndex) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")"); }
List支持的三种遍历方式
public class Array { public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("元素1"); list.add("元素2"); list.add("元素3"); list.add("元素4"); list.add("元素5"); list.add("元素6"); // 第一种 迭代器实现遍历 Iterator iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } // 第二种 ForEach for (Object object : list) { System.out.println(object); } // 第三种 For for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); } } }
注意点: remove的重载
如何判断注入的是按元素删除?还是按索引删除?
- 按元素删除,建议使用 new Integer(10) 这样对基本类型数据包装再注入 arrayList.remove(new Integer(5));
- 按索引删除,默认注入数字值即可 arrayList.remove(3);
ArrayList的底层源码查看【未完待续...】
JDK8
底层elementData初始化为0

但是注释依赖没改,仍然称为10初始化容量
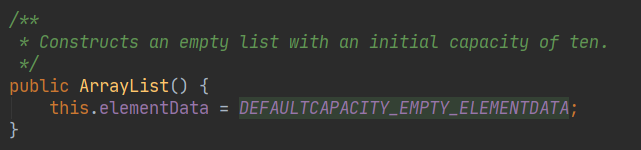
只有在第一次调用add后初始化10的容量,再往后大于10【右移1 除2】增加1.5倍容量
