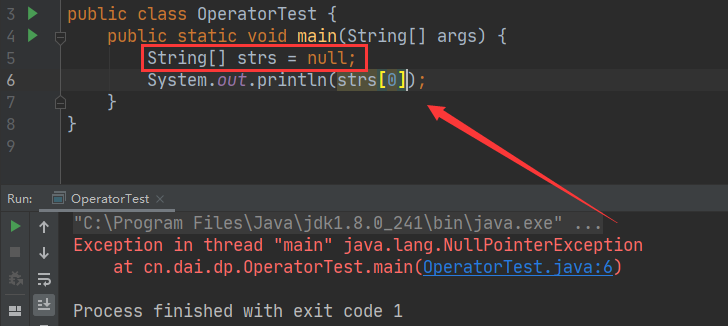
1 JDK JRE JVM 三种之间的关系,以及JDK JRE 包含的主要结构有哪些?
JDK = JRE + 开发工具 javac.exe java.exe javadoc.exe等等
JRE = JVM + 核心类库文件
JDK 包含 JRE 包含 JVM
2 为什么要配置path环境变量?怎么配置?
- 我们希望在任意的文件路径下都可以执行Java的开发工具(执行程序)
- 计算机 右键属性 系统设置 高级系统设置 环境变量 新建JAVA_HOME变量,指向JDK的目录,保存确定
JAVA_HOME是bin的上一级目录,点击path变量,增加 %JAVA_HOME%\bin 变量 保存确定
3 常用的命令行操作
- cd + 要切换的路径
- cd .. 退到上一级目录
- dir 列出当前目录项
- cls 清除屏幕
- javac 源文件名.java
- java 字节码文件名.class
4 标识符的命名规则
- 允许字母、数字、下划线、美元符号、组成【人民币羊角符号也可以,但是不要用】
- 不能使用关键字和保留字,但是可以包含
- 首字符不能是数字开头
- 严格区分大小写
【不遵守命名规则,编译无法通过,硬性要求】
5 标识符的命名规范
- 包名的单词全部小写 cn.dai.pojo cn.dao.controller
- 类名、接口的单词首字母全部大写 【大驼峰规则】class DemoTest
- 变量的单词首字母小写,随后的单词首字母全部大写 【小驼峰规则】 intValue strValue
- 常量的标识符单词全大写,使用下划线分割 FINAL_STRING
- 见名知义,不要使用拼音
【不遵守命名规范,编译可通过,但是可读性差,软性要求】
6 Java的变量按数据类型怎么分类? 基本类型有哪些?
- 分引用类型和基本类型
- 基本类型分为 字符、布尔、数值类型 char、boolean
- 数值类型分为 整型 和浮点型
- 整型 byte short int long
- 浮点型 float double
- 引用类型 类、数组、接口
7 说明基本数据变量的自动类型提升的运算规则
byte、short、char、 -> int -> long -> float -> double
8 说明基本数据类型之间强转的使用规则和可能出现的问题
大精度类型转小精度类型 【小类型 标识名 = (小类型)变量】 强转符 :()
出现精度损失
9 & 和 && 的异同
- & 是 长路且 && 是短路且, 都表示且的意思,两个或多个布尔条件为true 结果才为true
- && 在判断第一个布尔条件是false的情况下,不再执行后面的布尔条件,直接返回false
- & 在判断第一个布尔条件是false的情况下,仍然去判断,执行后面布尔条件,再返回false
10 判断输出结果
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean x = true; boolean y = false; short z = 40; if ((z++ == 40) && (y = true)) z++; // 41、 42 if ((x = false) || (++z == 43)) z++; // 43、 44 System.out.println("z = " + z); // 44 } }
11 定义三个整形变量并赋值,使用三元运算或者if-else 获取这三个数的最大值
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = (int)(Math.random()*100); int b = (int)(Math.random()*100); int c = (int)(Math.random()*100); System.out.println("a = " + a + " b = " + b + " c = " + c); System.out.println("max = " +getMax1(a,b,c)); System.out.println("max = " +getMax2(a,b,c)); System.out.println("max = " +getMax3(a,b,c)); } // 三元 static int getMax1(int a,int b, int c){ int max; max = a > b ? a : b; max = max > c ? max : c; return max; } // if 判断 static int getMax2(int a,int b, int c){ int max = a; if (b > a) max = b; else if (c > max) max = c; return max; } // Math方法 static int getMax3(int a,int b, int c){ int max = Math.max(a,b); max = Math.max(max,c); return max; } }
12 编写程序 声明2个double类型变量并且赋值 判断第一个数大于10.0 且第二个数小于20.0,如果是打印两数之和
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { double d1 = Math.random()*21; double d2 = Math.random()*21; double sum = 0; if (d1 > 10.0 && d2 < 20.0) sum = d1 + d2; else System.out.println("d1 = " + d1 + " d2 = " + d2); System.out.println("sum =" + sum); } }
13 交换变量的实现
参考小学生Vita的交换,太强了 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ef4y1U74X
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 15; System.out.println("a = " + a + " b = " + b); exchange3(a,b); } // 第一种 static void exchange1(int a,int b){ int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; System.out.println("a = " + a + " b = " + b); } // 第二种 static void exchange2(int a,int b){ a = a + b; // a 等于 2数之和 b = a - b; // b 减自己变成了a a = a - b; // a现在是总和 ,减去变成a的b 就是b的值了 System.out.println("a = " + a + " b = " + b); } // 第三种 static void exchange3(int a,int b){ a ^= b; b ^= a; a ^= b; System.out.println("a = " + a + " b = " + b); // c++ 可以写 a ^= b ^= a ^= b; } }
14 Switch可以使用的数据类型
char、byte、short、int、【枚举变量 JDK5】【String JDK7】
15 三元运算 if else 和 swtich case 的适用场景
- 都能使用,优先级考虑 三元 > swtich > if
- 三元适合对变量的处理判断
- if else 适合对范围的一个判断
- swtich - case 适合具体等值的判断
16 控制台获取StrIng 和int 型的变量
import java.util.Scanner; public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("String类型获取"); String str = input.next(); System.out.println("int类型获取"); int i = input.nextInt(); // 整行字符串获取 String line = input.nextLine(); } }
17 for 循环 遍历100 ,计算所有奇数的和 与 输出
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 101; i++) { //sum += i % 2 == 0 ? sum : i; if (i % 2 == 1){ sum += i; System.out.println(i); } } System.out.println("奇合 " + sum); } }
18 循环结构是如何退出循环的?
- 判断循环条件是否为true,如果为false循环条件不成立,中止循环
- 执行循环体内的break关键字,跳出当前循环体
19 求1000内的完数 6 = 1 + 2 + 3 一个数恰好等于因子之和【因子,除去这个数本身的其他数】
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int factor = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i / 2; j++) { if (i % j == 0) factor += j; } if (i == factor) System.out.println(i); // 重置 factor = 0; } } }
20 Break & Continue 使用上的相同点和不同点
- break 可以使用在循环体和switch case分支体
- continue 只能适用循环体
- break 在循环体是结束当前循环体,在switch是跳出分支体
- continue 是结束本次循环
- break & continue 之后都不再执行任何语句
21 实现倒三角【直角三角】
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 10 - i; j++) { System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } } }
22 实现一维数组初始化和二维数组初始化【各两种方法】
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array1 = new int[10]; int[] array2 = {2,3,4,5,6}; int[][] array3 = new int[10][]; int[][] array4 = { {1,2,3,4,5}, {6,7,8,9,10} }; } }
23 遍历二维数组
public class OperatorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][]arr = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}}; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length ; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } } }
24 不同类型数组初始化的默认值是?
char '\u0000'
boolean false
byte short int long 0
float double 0.0
类 接口 数组本身 null
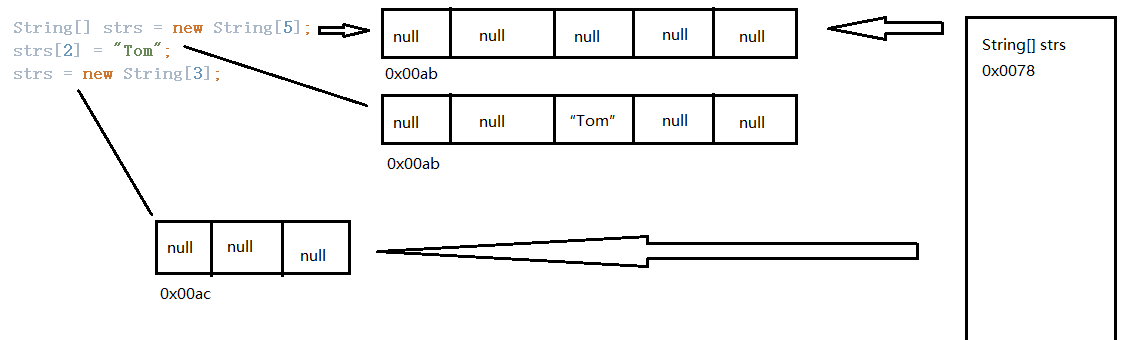
25 画出一维数组的内存解析
String[] strs = new String[5];
strs[2] = "Tom";
strs = new String[3];
26 冒泡排序
public class Arrays { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1,2,5,10,9}; } // 冒泡排序 static int[] bubbleSort(int[] array){ for (int i = 0; i < array.length -1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < array.length -1; j++) { if (array[j] > array[j + i]){ int temp = array[i]; array[j] = array[j + 1]; array[j + 1] = temp; } } } return array; } }
27、反转数组
static int[] reverse1(int[] array){ // 遍历一半长度进行元素交换 for (int i = 0; i < array.length / 2; i++) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[array.length - 1 - i]; array[array.length - 1 - i] = temp; } return array; }
28、复制数组
public class Arrays { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1,3,5,7,9}; // 先复制长度 int[] array2 = new int[array.length]; for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) { // 复制元素 array2[i] = array[i]; } } }
29、线性查找
// 线性查找 static int linearSearch(int[] array,int target){ for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { if (target == array[i]) return i; // 找到直接返回索引 } return -1; // 找不到 返回-1 }
30 数组常见异常