1、asio综述
asio的核心类是io_service,它相当于前摄器模式的Proactor角色,在异步模式下发起的I/O操作,需要定义一个用于回调的完成处理函数,当I/O完成时io_service会调用注册的完成处理函数。通过调用io_service的成员函数run()来启动前摄器的事件处理循环,阻塞等待所有的操作完成并分派事件。在异步模式下,如果不调用run()就没有了等待异步操作完成的机制,回调函数将得不到执行。
asio不直接使用线程,而是定义了一个自己的线程概念:strand,它保证在多线程环境中不使用互斥量代码可以正确执行,io_service::strand::wrap()可以封装一个函数在strand中执行。
asio中的两个类mutable_buffer和const_buffer用来封装缓冲区,可以被安全的用在异步读写中。asio通常不能直接使用数组、string、vector等来作为收发数据的缓冲区,函数buffer()能够包装常用的数据类型(数组、string、vector等)用于asio的数据收发。
asio的函数有两种重载形式:一种是有一个error_code(boost::system库中)的输出参数,调用函数后可以检查这个参数以判断是否发生了错误;一种是没有error_code参数,但发生了错误会抛出system_error(boost::system库中)异常,调用函数的时候应该使用try-catch块来捕获错误。
使用asio需要包含头文件"boostasio.hpp",在VC下还要添加以下定义避免编译警告:
#ifdef _MSC_VER #define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501 #endif #include "boostasio.hpp"
2、定时器
deadline_timer是asio中的定时器类,它有两种形式的构造函数,第一个参数都是一个io_service对象,第二个参数可以是posix_time的绝对时间或者是自当前时间开始的一个时间段。创建定时器并指定终止时间后它就会立即开始计时,如果创建定时器时不指定终止时间,那么定时器不会开始工作,可以使用成员函数expires_at()或expires_from_now()设置终止时间,调用wait()同步等待或async_wai()设置异步等待,并注册完成时的回调handler。
deadline_timer的成员函数expires_at()可以获得计时器终止的绝对时间,成员函数cancel()用来取消异步操作。
deadline_timer的一些功能需要包含头文件"boostdate_timeposix_timeposix_time.hpp"。
下面为一个同步定时器的使用:

#ifdef _MSC_VER #define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501 #endif #include "boostasio.hpp" #include "boostdate_timeposix_timeposix_time.hpp" int main() { boost::asio::io_service ios; boost::asio::deadline_timer dt(ios, boost::posix_time::seconds(3)); cout << dt.expires_at() << endl; //输出终止时间 dt.wait(); //一直等待定时器终止 cout << "here" << endl; return 0; }
以下是一个异步定时器的使用:

#ifdef _MSC_VER #define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501 #endif #include "boostasio.hpp" #include "boostdate_timeposix_timeposix_time.hpp" void Printf(const boost::system::error_code& e, int n) { cout << "Printf func, thread id: " << n << endl; cout << boost::this_thread::get_id() << endl; } int main() { cout << "main thread id: " << boost::this_thread::get_id() << endl; boost::asio::io_service ios; boost::asio::deadline_timer dt(ios, boost::posix_time::seconds(3)); int num = 999; dt.async_wait(bind(Printf, _1, num)); //通知io_service异步的执行I/O操作,并注册回调函数后立即返回 ios.run(); //启动Proactor的事件处理循环 cout << "here" << endl; return 0; }
3、同步socket通信
asio主要支持TCP、UDP、ICMP协议,在名字空间boost::asio::ip里提供了大量的网络通信的功能类和函数。ip::address是IP地址类,在ip::tcp类里包含了网络通信主要的类,如:端点类endpoint、套接字类socket、流类iostream、接受器acceptor、解析器resolver等。
同步socket处理客户端:

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
using namespace std;
void main()
try
{
cout << "client start." << endl;
boost::asio::io_service ios; //asio程序必需的io_service对象
boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket sock(ios); //创建socket对象
boost::asio::ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint(boost::asio::ip::address::from_string("127.0.0.1"), 6688); //创建连接点
sock.connect(endpoint); //连接到端点
vector<char> str(100, 0);
sock.read_some(boost::asio::buffer(str)); //接收数据,使用buffer()包装缓冲区
cout << "recive from " << sock.remote_endpoint().address().to_string() << ": " << &str[0] << endl; //输出对方地址及发送内容
//sock.close(); //sock析构的时候会自动调用close()
getchar();
}
catch (exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
同步socket处理服务端:

#include <iostream>
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
using namespace std;
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_boost;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::acceptor acceptor_boost;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint_boost;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket socket_boost;
void main()
try
{
cout << "server start, bind ";
io_service_boost ios; //asio程序必需的io_service对象
acceptor_boost acceptor(ios, endpoint_boost(boost::asio::ip::tcp::v4(), 6688)); //创建acceptor对象,绑定本机IP及6688端口
cout << acceptor.local_endpoint().address() << ": " << acceptor.local_endpoint().port() << endl; //输出绑定的地址信息
while (true)
{
socket_boost sock(ios); //创建socket对象
acceptor.accept(sock); //等待客户连接
cout << sock.remote_endpoint().address() << ": " << sock.remote_endpoint().port() << " now connect." << endl; //输出对方信息
sock.write_some(boost::asio::buffer("hello!")); //发送数据,使用buffer()包装缓冲区
//sock.close(); //sock析构的时候会自动调用close()
}
}
catch(exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
4、异步socket通信
异步socket通信的函数名称比同步的函数多了async_,且应该设置异步操作完成后的回调函数,以下为使用异步socket通信的服务端示例:

#include <iostream>
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostsmart_ptr.hpp"
#include "boost/bind.hpp"
#include "boostasio.hpp"
using namespace std;
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::acceptor acceptor_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket socket_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp tcp_t;
typedef boost::shared_ptr<socket_t> spSock_t;
class CServer
{
public:
CServer(io_service_t& io)
: ios(io) //使用传入的io_service
, acceptor(ios, endpoint_t(tcp_t::v4(), 6688)) //绑定本机IP及6688端口
{
accept_async();
}
virtual ~CServer(){}
public:
void accept_async() //发起一个异步接受连接
{
spSock_t spSock(new socket_t(ios));
acceptor.async_accept(*spSock, boost::bind(&CServer::accept_handler, this, _1, spSock));
}
void accept_handler(const boost::system::error_code& ec, spSock_t spSock) //accept完成后的回调
{
if (ec) //检测错误码
return;
cout << "a client connect, form ";
cout << spSock->remote_endpoint().address() << ": " << spSock->remote_endpoint().port() << endl; //输出客户地址和端口号
spSock->async_write_some(boost::asio::buffer("hello"), boost::bind(&CServer::send_handler, this, _1, spSock)); //发送数据
accept_async(); //再次发起一个异步接受连接
}
void send_handler(const boost::system::error_code& ec, spSock_t spSock) //发送数据完成的回调
{
cout << "send msg complete" << endl;
}
private:
io_service_t& ios;
acceptor_t acceptor;
};
void main()
{
cout << "server start." << endl;
io_service_t ios;
CServer srv(ios);
ios.run(); //开启事件处理循环
}
5、解析器resolver
resolver的主要功能是通过主机名获得主机地址等信息,相当于getaddrinfo()。以下封装了一个使用域名来连接服务器的函数resolv_connect():

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
#include "boostlexical_cast.hpp"
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket socket_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver resolver_t;
typedef boost::system::error_code error_code_t;
void resolv_connect(socket_t& sock, const char*name, int port)
{
resolver_t rlv(sock.get_io_service());
resolver_t::query qry(name, boost::lexical_cast<string>(port));
resolver_t::iterator iter = rlv.resolve(qry);
resolver_t::iterator end; //逾尾迭代器
error_code_t ec = boost::asio::error::host_not_found;
for (; ec && iter != end; ++iter) //开始迭代端点
{
sock.close();
sock.connect(*iter, ec);
}
if (ec)
{
cout << "can not connect." << endl;
throw boost::system::system_error(ec);
}
else
{
cout << "connect sucess." << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
io_service_t ios;
socket_t sock(ios);
resolv_connect(sock, "www.baidu.com", 80);
sock.close();
return 0;
}
resolver不仅能够解析域名,也支持使用IP地址和服务名,如:
boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver::query qry("127.0.0.1", "http");
6、超时处理
如果要实现超时处理,应该在异步调用后声明一个deadline_timer对象,然后设置deadline_timer的等待时间和回调函数就可以了。如下代码示例了异步连接服务器,如果超过5秒还没有完成则关闭socket:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
#include "boostlexical_cast.hpp"
#include "boostind.hpp"
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket socket_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver resolver_t;
typedef boost::system::error_code error_code_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::address address_t;
void connect_timeout(const error_code_t&, socket_t* sock)
{
sock->close();
}
int main()
{
io_service_t ios;
socket_t sock(ios);
endpoint_t ep(address_t::from_string("127.0.0.1"), 6688);
sock.async_connect(ep, connect_handler);
boost::asio::deadline_timer t(ios, boost::posix_time::seconds(5)); //5秒等待时间
t.async_wait(boost::bind(connect_timeout, _1, &sock)); //超时回调
... //其它操作
ios.run();
return 0;
}
7、流操作
对于TCP连接,可以使用asio::ip::tcp::iostream来代替socket,它也是std::basic_iostream的子类,可以像标准流一样来操作socket,它内部集成了connect和resolver域名解析功能,使用示例:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket socket_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver resolver_t;
typedef boost::system::error_code error_code_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::address address_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp::acceptor acceptor_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::tcp tcp_t;
//客户端
{
...
boost::asio::ip::tcp::iostream tcp_stream("127.0.0.1", 6688); //连接到本机6688端口
string str;
getline(tcp_stream, str); //从数据流中读取一行数据
cout << str << endl;
...
}
//服务端
{
...
io_service_t ios;
endpoint_t ep(tcp_t::v4(), 6688);
acceptor_t acceptor(ios, ep);
boost::asio::ip::tcp::iostream tcp_stream;
acceptor.accept(*tcp_stream.rdbuf());
tcp_stream << "hello
" << endl;
...
}
return 0;
8、UDP通信
UDP是无连接的,所以通信前不需要建立连接,使用send_to()和receive_from()来收发数据。
UDP服务端示例:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::udp::socket socket_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::udp::endpoint endpoint_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::udp udp_t;
typedef boost::system::error_code error_code_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::address address_t;
int main()
{
cout << "udp server start." << endl;
io_service_t ios;
socket_t sock(ios, endpoint_t(udp_t::v4(), 6699));
for (;;)
{
char buf[2] = {0};
endpoint_t ep;
error_code_t ec;
sock.receive_from(boost::asio::buffer(buf), ep, 0, ec);
if (ec && ec != boost::asio::error::message_size)
{
throw boost::system::system_error(ec);
}
cout << "recv from " << ep.address() << ": " << buf << endl;
}
return 0;
}
UDP客户端示例:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0X0501
#endif
#include "boostasio.hpp"
#include "boostlexical_cast.hpp"
#include "boostind.hpp"
typedef boost::asio::io_service io_service_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::udp::socket socket_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::udp::endpoint endpoint_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::udp udp_t;
typedef boost::system::error_code error_code_t;
typedef boost::asio::ip::address address_t;
int main()
{
cout << "udp client start." << endl;
io_service_t ios;
socket_t sock(ios);
sock.open(udp_t::v4());
char buf[1];
buf[0] = 'a';
endpoint_t send_ep(address_t::from_string("127.0.0.1"), 6699);
sock.send_to(boost::asio::buffer(buf), send_ep);
sock.close();
getchar();
return 0;
}
9、串口通信
aiso也支持串口通信,通过使用serial_port类。
10、post()、dispach()
io_service的post()方法可以向任务队列添加一个任务,调用run()方法开始执行任务队列里所有的任务,可以调用post()添加多个任务,然后调用run()来一次执行所有任务。如下所示我们向io_service的任务队列添加了10个任务,然后在另一个线程里执行run()方法,这样就在这个线程里开始执行所有任务,相当于是异步执行了io_service任务队列里的所有任务:

boost::asio::io_service service;
std::mutex mu;
void func(int i) {
mu.lock();
std::cout << "func called, i= " << i << std::endl;
mu.unlock();
}
void worker_thread() {
service.run();
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
service.post(std::bind(func, i));
std::thread first(worker_thread);
getchar();
}

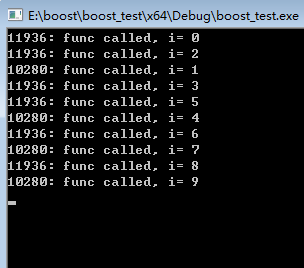
可以在多个线程上执行run函数,这样每个线程都去从io_service的“任务列表”里面获取任务去执行,从而可以充分利用多核的性能。可以看到使用多个线程执行任务队列的话任务的执行顺序是不固定的,而如果只是一个线程去执行任务则任务的执行顺序就是post的顺序:

boost::asio::io_service service;
std::mutex mu;
void func(int i) {
mu.lock();
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << ": func called, i= " << i << std::endl;
mu.unlock();
}
void worker_thread() {
service.run();
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
service.post(std::bind(func, i));
boost::thread_group threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
threads.create_thread(worker_thread);
getchar();
}
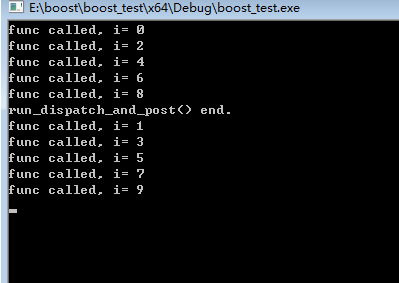
dispatch()也可以向post()那样向io_service添加任务。当只用一个线程来执行任务的时候,我们在任务执行的时候再使用post()添加一个任务的话这个新的任务会排到后面执行,而如果这里使用dispatch()来添加一个任务的话这个任务会立即执行:

using namespace boost::asio;
io_service service;
void func(int i) {
std::cout << "func called, i= " << i << std::endl;
}
void run_dispatch_and_post() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i += 2) {
service.dispatch(std::bind(func, i)); //这里dispatch添加的任务会立即执行
service.post(std::bind(func, i + 1)); //这里post添加的任务会排到run_dispatch_and_post()任务之后来执行
}
std::cout << "run_dispatch_and_post() end." << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
service.post(run_dispatch_and_post);
service.run(); //在主线程里执行任务,前面只使用post添加了一个任务,所以只会执行run_dispatch_and_post()一次
getchar();
}
io_service的wrap()可以包装一个方法,当它被执行的时候相当于调用io_service.dispach(),如下所示跟上面的代码其实是一样的效果:

using namespace boost::asio;
io_service service;
void func(int i) {
std::cout << "func called, i= " << i << std::endl;
}
void run_dispatch_and_post() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i += 2) {
std::function<void()> fun = service.wrap(std::bind(func, i));
fun(); //这里dispatch添加的任务会立即执行
service.post(std::bind(func, i + 1)); //这里post添加的任务会排到run_dispatch_and_post()任务之后来执行
}
std::cout << "run_dispatch_and_post() end." << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
service.post(run_dispatch_and_post);
service.run(); //在主线程里执行任务,前面只使用post添加了一个任务,所以只会执行run_dispatch_and_post()一次
getchar();
}
