Load Balance负载均衡是用于解决一台机器(一个进程)无法解决所有请求而产生的一种算法。
像nginx可以使用负载均衡分配流量,ribbon为客户端提供负载均衡,dubbo服务调用里的负载均衡等等,很多地方都使用到了负载均衡。
使用负载均衡带来的好处很明显:
- 当集群里的1台或者多台服务器down的时候,剩余的没有down的服务器可以保证服务的继续使用
- 使用了更多的机器保证了机器的良性使用,不会由于某一高峰时刻导致系统cpu急剧上升
负载均衡有好几种实现策略,常见的有:
- 随机 (Random)
- 轮询 (RoundRobin)
- 一致性哈希 (ConsistentHash)
- 哈希 (Hash)
- 加权(Weighted)
我们以ribbon的实现为基础,看看其中的一些算法是如何实现的。
ribbon是一个为客户端提供负载均衡功能的服务,它内部提供了一个叫做ILoadBalance的接口代表负载均衡器的操作,比如有添加服务器操作、选择服务器操作、获取所有的服务器列表、获取可用的服务器列表等等。
还提供了一个叫做IRule的接口代表负载均衡策略:
package com.netflix.loadbalancer; public interface IRule{ /* * choose one alive server from lb.allServers or * lb.upServers according to key * * @return choosen Server object. NULL is returned if none * server is available */ public Server choose(Object key); public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb); public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(); }
IRule接口的实现类有以下几种:
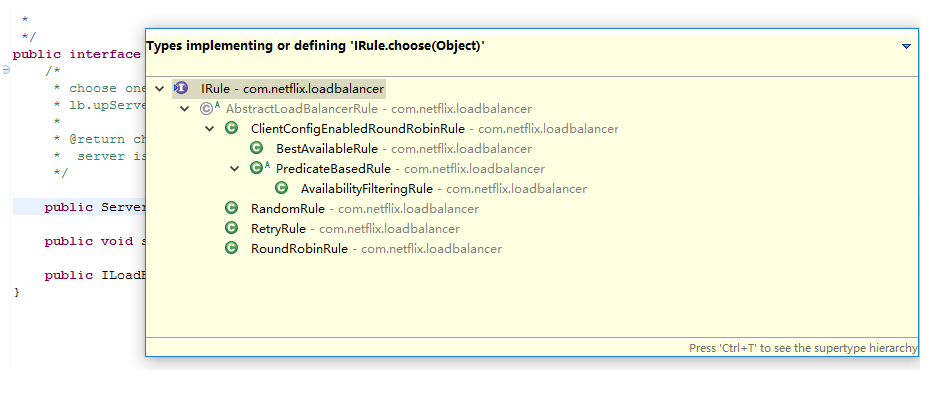
其中RandomRule表示随机策略、RoundRobin表示轮询策略、WeightedResponseTimeRule表示加权策略、BestAvailableRule表示请求数最少策略等等。
随机策略很简单,就是从服务器中随机选择一个服务器,RandomRule的实现代码如下:
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { if (lb == null) { return null; } Server server = null; while (server == null) { if (Thread.interrupted()) { return null; } List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers(); List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers(); int serverCount = allList.size(); if (serverCount == 0) { return null; } int index = rand.nextInt(serverCount); // 使用jdk内部的Random类随机获取索引值index server = upList.get(index); // 得到服务器实例 if (server == null) { Thread.yield(); continue; } if (server.isAlive()) { return (server); } server = null; Thread.yield(); } return server; }
RoundRobin轮询策略表示每次都取下一个服务器,比如一共有5台服务器,第1次取第1台,第2次取第2台,第3次取第3台,以此类推:
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { if (lb == null) { log.warn("no load balancer"); return null; } Server server = null; int count = 0; while (server == null && count++ < 10) { // retry 10 次 List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers(); List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers(); int upCount = reachableServers.size(); int serverCount = allServers.size(); if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) { log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb); return null; } int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount); // incrementAndGetModulo方法内部使用nextServerCyclicCounter这个AtomicInteger属性原子递增对serverCount取模得到索引值 server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex); // 得到服务器实例 if (server == null) { Thread.yield(); continue; } if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) { return (server); } server = null; } if (count >= 10) { log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb); } return server; }
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) { for (;;) { int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get(); int next = (current + 1) % modulo; if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) return next; } }
BestAvailableRule策略用来选取最少并发量请求的服务器:
public Server choose(Object key) { if (loadBalancerStats == null) { return super.choose(key); } List<Server> serverList = getLoadBalancer().getAllServers(); // 获取所有的服务器列表 int minimalConcurrentConnections = Integer.MAX_VALUE; long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Server chosen = null; for (Server server: serverList) { // 遍历每个服务器 ServerStats serverStats = loadBalancerStats.getSingleServerStat(server); // 获取各个服务器的状态 if (!serverStats.isCircuitBreakerTripped(currentTime)) { // 没有触发断路器的话继续执行 int concurrentConnections = serverStats.getActiveRequestsCount(currentTime); // 获取当前服务器的请求个数 if (concurrentConnections < minimalConcurrentConnections) { // 比较各个服务器之间的请求数,然后选取请求数最少的服务器并放到chosen变量中 minimalConcurrentConnections = concurrentConnections; chosen = server; } } } if (chosen == null) { // 如果没有选上,调用父类ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule的choose方法,也就是使用RoundRobinRule轮询的方式进行负载均衡 return super.choose(key); } else { return chosen; } }
加权响应时间负载均衡 (WeightedResponseTime)
区域感知轮询负载均衡(ZoneAware):
区域感知负载均衡内置电路跳闸逻辑,可被配置基于区域同源关系(Zone Affinity,也就是更倾向于选择发出调用的服务所在的托管区域内,这样可以降低延迟,节省成本)选择目标服务实例。它监控每个区域中运行实例的行为,而且能够实时的快速丢弃一整个区域。这样在面对整个区域故障时,帮我们提升了弹性。
实例验证Ribbon中的LoadBalance功能
ServerList中提供了3个instance,分别是:
compute-service:2222 compute-service:2223 compute-service:2224
然后使用不同的IRule策略查看负载均衡的实现。
加权响应时间负载均衡 (WeightedResponseTime) 区域感知轮询负载均衡(ZoneAware): 区域感知负载均衡内置电路跳闸逻辑,可被配置基于区域同源关系(Zone Affinity,也就是更倾向于选择发出调用的服务所在的托管区域内,这样可以降低延迟,节省成本)选择目标服务实例。它监控每个区域中运行实例的行为,而且能够实时的快速丢弃一整个区域。这样在面对整个区域故障时,帮我们提升了弹性。 实例验证Ribbon中的LoadBalance功能 ServerList中提供了3个instance,分别是: compute-service:2222 compute-service:2223 compute-service:2224 然后使用不同的IRule策略查看负载均衡的实现。
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.java为实现客户端负载均衡器的自动化配置类。
package org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer; /** * Auto configuration for Ribbon (client side load balancing). * * @author Spencer Gibb * @author Dave Syer * @author Will Tran */ @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class) @ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class) public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration { @LoadBalanced @Autowired(required = false) private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList(); @Bean public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializer( final List<RestTemplateCustomizer> customizers) { return new SmartInitializingSingleton() { @Override public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() { for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) { for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) { customizer.customize(restTemplate); } } } }; }
Ribbon要实现负载均衡自动化配置需要满足如下两个条件:
- @ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class):RestTemplate类必须存在于当前工程的环境中。
- @ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class):在spring的Bean工程中必须有LoadBalancerClient.class的实现Bean。
在自动化配置中主要做三件事:
- 创建一个LoadBalancerInterceptor的Bean,用于实现对客户端发起请求时进行拦截,以实现客户端负载均衡。
- 创建一个RestTemplateCustomizer的Bean,用于给RestTemplate增加LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器。
- 维护了一个被@LoadBalanced注解修饰的RestTemplate对象列表,并在这里进行初始化,通过调用RestTemplateCustomizer的实例来给需要客户端负载均衡的RestTemplate增加LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器。
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.java里面有2个内部类,如下:
@Configuration @ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate") static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig { @Bean public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor( LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer( final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) { return new RestTemplateCustomizer() { @Override public void customize(RestTemplate restTemplate) { List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>( restTemplate.getInterceptors()); list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor); restTemplate.setInterceptors(list); } }; } } @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(RetryTemplate.class) static class RetryAutoConfiguration { @Bean public RetryTemplate retryTemplate() { RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate(); template.setThrowLastExceptionOnExhausted(true); return template; } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory() { return new LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory.NeverRetryFactory(); } @Bean public RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor( LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerRetryProperties properties, LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory lbRetryPolicyFactory, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { return new RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, retryTemplate(), properties, lbRetryPolicyFactory, requestFactory); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer( final RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) { return new RestTemplateCustomizer() { @Override public void customize(RestTemplate restTemplate) { List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>( restTemplate.getInterceptors()); list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor); restTemplate.setInterceptors(list); } }; } }
接下来,我们看看LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器是如何将一个普通的RestTemplate变成客户度负载均衡的:
/* * Copyright 2013-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; import org.springframework.http.HttpRequest; import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestExecution; import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestInterceptor; import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpResponse; /** * @author Spencer Gibb * @author Dave Syer * @author Ryan Baxter * @author William Tran */ public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor { private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer; private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory; public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer; this.requestFactory = requestFactory; } public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) { // for backwards compatibility this(loadBalancer, new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancer)); } @Override public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException { final URI originalUri = request.getURI(); String serviceName = originalUri.getHost(); return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution)); //看这里 } }
LoadBalancerRequestFactory .java
/* * Copyright 2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance; import org.springframework.http.HttpRequest; import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestExecution; import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpResponse; /** * Creates {@link LoadBalancerRequest}s for {@link LoadBalancerInterceptor} and * {@link RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor}. Applies * {@link LoadBalancerRequestTransformer}s to the intercepted * {@link HttpRequest}. * * @author William Tran * */ public class LoadBalancerRequestFactory { private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer; private List<LoadBalancerRequestTransformer> transformers; public LoadBalancerRequestFactory(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer, List<LoadBalancerRequestTransformer> transformers) { this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer; this.transformers = transformers; } public LoadBalancerRequestFactory(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) { this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer; } public LoadBalancerRequest<ClientHttpResponse> createRequest(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) { return new LoadBalancerRequest<ClientHttpResponse>() { @Override public ClientHttpResponse apply(final ServiceInstance instance) throws Exception { HttpRequest serviceRequest = new ServiceRequestWrapper(request, instance, loadBalancer); if (transformers != null) { for (LoadBalancerRequestTransformer transformer : transformers) { serviceRequest = transformer.transformRequest(serviceRequest, instance); } } return execution.execute(serviceRequest, body); } }; } }
ServiceRequestWrapper.java
package org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer; import java.net.URI; import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance; import org.springframework.http.HttpRequest; import org.springframework.http.client.support.HttpRequestWrapper; /** * @author Ryan Baxter */ public class ServiceRequestWrapper extends HttpRequestWrapper { private final ServiceInstance instance; private final LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer; public ServiceRequestWrapper(HttpRequest request, ServiceInstance instance, LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) { super(request); this.instance = instance; this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer; } @Override public URI getURI() { URI uri = this.loadBalancer.reconstructURI( this.instance, getRequest().getURI()); return uri; } }
spring cloud中对应的实现类:
package org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon; /** * @author Spencer Gibb * @author Dave Syer * @author Ryan Baxter */ public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient { private SpringClientFactory clientFactory; public RibbonLoadBalancerClient(SpringClientFactory clientFactory) { this.clientFactory = clientFactory; } @Override public URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original) { Assert.notNull(instance, "instance can not be null"); String serviceId = instance.getServiceId(); RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory .getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId); Server server = new Server(instance.getHost(), instance.getPort()); IClientConfig clientConfig = clientFactory.getClientConfig(serviceId); ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector = serverIntrospector(serviceId); URI uri = RibbonUtils.updateToHttpsIfNeeded(original, clientConfig, serverIntrospector, server); return context.reconstructURIWithServer(server, uri); } @Override public ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId) { Server server = getServer(serviceId); if (server == null) { return null; } return new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server)); } @Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId); Server server = getServer(loadBalancer); if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server)); return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request); } @Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { Server server = null; if(serviceInstance instanceof RibbonServer) { server = ((RibbonServer)serviceInstance).getServer(); } if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory .getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId); RibbonStatsRecorder statsRecorder = new RibbonStatsRecorder(context, server); try { T returnVal = request.apply(serviceInstance); statsRecorder.recordStats(returnVal); return returnVal; } // catch IOException and rethrow so RestTemplate behaves correctly catch (IOException ex) { statsRecorder.recordStats(ex); throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { statsRecorder.recordStats(ex); ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex); } return null; } private ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector(String serviceId) { ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector = this.clientFactory.getInstance(serviceId, ServerIntrospector.class); if (serverIntrospector == null) { serverIntrospector = new DefaultServerIntrospector(); } return serverIntrospector; } private boolean isSecure(Server server, String serviceId) { IClientConfig config = this.clientFactory.getClientConfig(serviceId); ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector = serverIntrospector(serviceId); return RibbonUtils.isSecure(config, serverIntrospector, server); } protected Server getServer(String serviceId) { return getServer(getLoadBalancer(serviceId)); } protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer) { if (loadBalancer == null) { return null; } return loadBalancer.chooseServer("default"); // TODO: better handling of key } protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) { return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId); }
getServer方法中并没有使用LoadBalancerClient中的choose方法,而是使用Netflix Rion自身的ILoadBalancer接口中定义的chooseServer方法。再看ILoadBalancer 接口:
package com.netflix.loadbalancer; public interface ILoadBalancer { //向负载均衡器的实例列表中增加实例 public void addServers(List<Server> newServers); //通过某种策略,从负载均衡器中选择一个具体的实例 public Server chooseServer(Object key); //用来通知和标识负载均衡器中某个具体实例已经停止服务,不然负载均衡器在下一次获取服务实例清单前都会认为服务实例均是正常服务的。 public void markServerDown(Server server); //获取正常服务列表 public List<Server> getReachableServers(); //所有已知实例列表 public List<Server> getAllServers();
再看实现类,BaseLoadBalancer类是实现了基础的负载均衡,而DynamicServerListLoadBalancer和ZoneAwareLoadBalancer在负载均衡基础上做了一些功能的扩展。

那么Spring cloud在整合Ribbon的时候采用的哪个具体实现,可以看RibbonClientConfiguration配置类中的代码片段如下,采用的是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer来实现负载均衡器。
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter, IRule rule, IPing ping) { if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) { return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name); } ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<Server> balancer = LoadBalancerBuilder.newBuilder() .withClientConfig(config).withRule(rule).withPing(ping) .withServerListFilter(serverListFilter).withDynamicServerList(serverList) .buildDynamicServerListLoadBalancer(); return balancer; }
在回到主方法RibbonLoadBalancerClient.execute()
LoadBalancerClient的execute()
-->1、ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.chooseServer()获取了负载均衡策略分配到的服务实例对象Server
-->2、将Server对象封装成RibbonService实例
-->3、调用LoadBalancerRequest的apply()
-->4-1、在apply()中,先将request包装成ServiceRequestWrapper,在Wrapper中拼接URI
-->4-2、拼接URI中,调用RibbonLoadBalancerClient.reconstructURI()
-->4-3、拼接URI中,调用RibbonLoadBalancerContext.reconstructURIWithServer()
-->4-4、拼接URI中,调用RibbonLoadBalancerContext.reconstructURIWithServer()
-->5、拦截器调用
-->6、执行完成后,Ribbon还通过RibbonStatsRecorder对象对服务的请求进行了记录
@Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId); //在springcloud中是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer实例 Server server = getServer(loadBalancer); //1、ZoneAwareLoadBalancer获取了负载均衡策略分配到的服务实例对象Server if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } //2、将Server实例封装成RibbonService实例 RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server)); return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request); }
@Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { Server server = null; if(serviceInstance instanceof RibbonServer) { server = ((RibbonServer)serviceInstance).getServer(); } if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory .getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId); RibbonStatsRecorder statsRecorder = new RibbonStatsRecorder(context, server); try { T returnVal = request.apply(serviceInstance); //3、request看LoadBalancerRequestFactory中的createRequest()方法返回的匿名类 statsRecorder.recordStats(returnVal); return returnVal; } // catch IOException and rethrow so RestTemplate behaves correctly catch (IOException ex) { statsRecorder.recordStats(ex); throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { statsRecorder.recordStats(ex); ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex); } return null; }
public LoadBalancerRequest<ClientHttpResponse> createRequest(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) { return new LoadBalancerRequest<ClientHttpResponse>() { @Override public ClientHttpResponse apply(final ServiceInstance instance) throws Exception { HttpRequest serviceRequest = new ServiceRequestWrapper(request, instance, loadBalancer); //4-1、中拼接URI,见下面的ServiceRequestWrapper中的getURI() if (transformers != null) { for (LoadBalancerRequestTransformer transformer : transformers) { serviceRequest = transformer.transformRequest(serviceRequest, instance); } } return execution.execute(serviceRequest, body); //5、拦截器调用见InterceptingClientHttpRequest的内部类InterceptingRequestExecution.execute() } }; }
@Override public URI getURI() { URI uri = this.loadBalancer.reconstructURI( this.instance, getRequest().getURI()); //4-2、reconstructURI被RibbonLoadBalancerClient重载,看RibbonLoadBalancerClient.reconstructURI() return uri; }
@Override public URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original) { Assert.notNull(instance, "instance can not be null"); String serviceId = instance.getServiceId(); RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory .getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId); Server server = new Server(instance.getHost(), instance.getPort()); IClientConfig clientConfig = clientFactory.getClientConfig(serviceId); ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector = serverIntrospector(serviceId); URI uri = RibbonUtils.updateToHttpsIfNeeded(original, clientConfig, serverIntrospector, server); return context.reconstructURIWithServer(server, uri);//4-3、构建服务实例的URI,RibbonLoadBalancerContext.reconstructURIWithServer()见下面的LoadBalancerContext.reconstructURIWithServer() }
public URI reconstructURIWithServer(Server server, URI original) {//4-4、LoadBalancerContext的reconstructURIWithServer() String host = server.getHost(); int port = server .getPort(); if (host.equals(original.getHost()) && port == original.getPort()) { return original; } String scheme = original.getScheme(); if (scheme == null) { scheme = deriveSchemeAndPortFromPartialUri(original).first(); } try { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(scheme).append("://"); if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(original.getRawUserInfo())) { sb.append(original.getRawUserInfo()).append("@"); } sb.append(host); if (port >= 0) { sb.append(":").append(port); } sb.append(original.getRawPath()); if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(original.getRawQuery())) { sb.append("?").append(original.getRawQuery()); } if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(original.getRawFragment())) { sb.append("#").append(original.getRawFragment()); } URI newURI = new URI(sb.toString()); return newURI; } catch (URISyntaxException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }
@Override public ClientHttpResponse execute(HttpRequest request, byte[] body) throws IOException {//5、拦截器调用,InterceptingClientHttpRequest的内部类InterceptingRequestExecution.execute() if (this.iterator.hasNext()) { ClientHttpRequestInterceptor nextInterceptor = this.iterator.next(); return nextInterceptor.intercept(request, body, this); } else { ClientHttpRequest delegate = requestFactory.createRequest(request.getURI(), request.getMethod()); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : request.getHeaders().entrySet()) { List<String> values = entry.getValue(); for (String value : values) { delegate.getHeaders().add(entry.getKey(), value); } } if (body.length > 0) { StreamUtils.copy(body, delegate.getBody()); } return delegate.execute(); } }
public class RibbonStatsRecorder { private RibbonLoadBalancerContext context; private ServerStats serverStats; private Stopwatch tracer; public RibbonStatsRecorder(RibbonLoadBalancerContext context, Server server) { this.context = context; if (server != null) { serverStats = context.getServerStats(server); context.noteOpenConnection(serverStats); tracer = context.getExecuteTracer().start(); } } public void recordStats(Object entity) { this.recordStats(entity, null); } public void recordStats(Throwable t) { this.recordStats(null, t); } protected void recordStats(Object entity, Throwable exception) { if (this.tracer != null && this.serverStats != null) { this.tracer.stop(); long duration = this.tracer.getDuration(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); this.context.noteRequestCompletion(serverStats, entity, exception, duration, null/* errorHandler */); } } }
LoadBalancerRequestFactory .java