高级编程技巧只是相对的,其实主要是讲物理模拟和着色器程序的使用。
本章主要讲解利用Box2D并用它来实现萝卜雨,然后是使用单色着色器shader让画面呈现单色状态:http://files.cnblogs.com/mignet/shaders.zip
如果你不知道Box2D,那你肯定玩过用它做的游戏:Angry Birds, Limbo, Tiny Wings, Crayon Physics Deluxe
Libgdx集成了Box2D,类似于其他框架,用了很薄的一层java API进行了封装,等效利用Box2D的所有功能。如果你以前学过Box2D的任何知识,Libgdx这里都可以直接使用。
一些教程:
• C++: http://www.iforce2d.net/b2dtut/
• Objective-C: http://www.raywenderlich.com/28602/intro-to-box2dwith-cocos2d-2-x-tutorial-bouncing-balls
• Flash: http://www.emanueleferonato.com/category/box2d/
• JavaScript: http://blog.sethladd.com/2011/09/box2d-collisiondamage-for-javascript.html
了解Box2D的基本概念:
首先,我们来理解一个看起来很神秘的术语:刚体。
物体,从物理上讲,只是一个物质和一些属性(比如它的位置和方向)的集合,刚体就是不会在外力的作用下变形的理想化的物体。
为简便起见,刚体(rigid body)简写为body。Box2D里提到body其实就是刚体,因为它只支持一种体。
其实Libgdx还集成了另一种物理引擎:Bullet,与Box2D相比,Box2D局限于二维空间和刚体的支持,Bullet支持全面的三维物理模拟以及同时支持刚体和软体。
我们这里专注Box2D,3D物理是个更高端的话题。哈哈
除了位置和方向,刚体还有:质量(kg)速度(m/s)旋转速度(rad/s).
刚体类型:
Static:静态的就是固定的,通常用于地板啊墙啊不动的平台啊等等。不和Static的和Kinematic的物体发生碰撞
Kinematic:可移动的就是位置会变动,可以是手动的或者根据速度变化(首选),通常用于可移动的平台比如电梯,动态物体的镜像等。不和Static的和Kinematic的物体发生碰撞
Dynamic:动态的就是位置会变动,可以是手动或者是在力的作用下(首选),Dynamic可以和所有其他类型的物体碰撞。通常用于玩家,敌人,道具等等
注意到Kinematic的物体是不受力的作用的,它只会根据自己设定的速度来移动。
使用形状:
形状描述的是几何属性,比如圆的半径,矩形的宽和高,或者是一系列的点来描述更复杂的形状的多边形,所以,这些形状定义区域,可以与其他形状进行碰撞检测。
使用夹具:
夹具是为形状增加的材质属性,比如密度,摩擦力,反弹力。夹具附加到形状然后附加到body上,所以夹具在body之间的交互上扮演了十分重要的角色。
物理世界:
world是整个物理模型模拟的一个虚拟的沙盒。每个body都需要放在world里。
Box2D是一个非常丰富的引擎,它还包括很多特性,像约束,关节,传感器,接触监听器等等,这里用不到,就不介绍了。
有个物理body编辑器可以试试:https://code.google.com/p/box2d-editor/
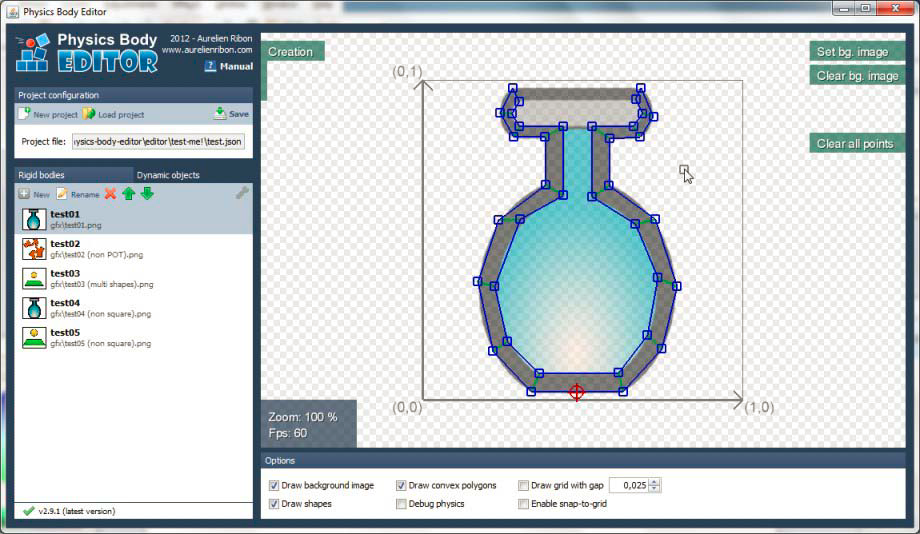
它有些很有用的特性:比如可以把凹边形变成凸多边形,跟踪图像的轮廓,还有个内置的碰撞测试器。
接下来,我们要开始下萝卜雨了。要添加两个新的对象到Canyon Bunny。
一个就是关卡结束的点,通关点。另一个就是一个普通胡萝卜。
当玩家到达通关点,就开始下萝卜雨。在金色的萝卜雕像旁,胡萝卜从天而降,摔倒地上,然后互相堆积。
首先把图片carrot.png,goal.png添加到images。然后打包到pack。
在Assets修改内部类:
public final AtlasRegion carrot; public final AtlasRegion goal; public AssetLevelDecoration(TextureAtlas atlas) { cloud01 = atlas.findRegion("cloud01"); cloud02 = atlas.findRegion("cloud02"); cloud03 = atlas.findRegion("cloud03"); mountainLeft = atlas.findRegion("mountain_left"); mountainRight = atlas.findRegion("mountain_right"); waterOverlay = atlas.findRegion("water_overlay"); carrot = atlas.findRegion("carrot"); goal = atlas.findRegion("goal"); }
增加Carrot类:
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.Assets; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.AbstractGameObject; public class Carrot extends AbstractGameObject { private TextureRegion regCarrot; public Carrot() { init(); } private void init() { dimension.set(0.25f, 0.5f); regCarrot = Assets.instance.levelDecoration.carrot; // Set bounding box for collision detection bounds.set(0, 0, dimension.x, dimension.y); origin.set(dimension.x / 2, dimension.y / 2); } public void render(SpriteBatch batch) { TextureRegion reg = null; reg = regCarrot; batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x - origin.x, position.y - origin.y, origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y, scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(), reg.getRegionY(), reg.getRegionWidth(), reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false); } }
增加Goal类:
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.Assets; public class Goal extends AbstractGameObject { private TextureRegion regGoal; public Goal() { init(); } private void init() { dimension.set(3.0f, 3.0f); regGoal = Assets.instance.levelDecoration.goal; // Set bounding box for collision detection bounds.set(1, Float.MIN_VALUE, 10, Float.MAX_VALUE); origin.set(dimension.x / 2.0f, 0.0f); } public void render(SpriteBatch batch) { TextureRegion reg = null; reg = regGoal; batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x - origin.x, position.y - origin.y, origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y, scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(), reg.getRegionY(), reg.getRegionWidth(), reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false); } }
编辑Level图片,增加一个红色的色块表示目的点。然后修改Level类:
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game; import com.badlogic.gdx.Gdx; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Pixmap; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch; import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Array; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.AbstractGameObject; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.BunnyHead; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Carrot; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Clouds; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Feather; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Goal; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.GoldCoin; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Mountains; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Rock; import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.WaterOverlay; public class Level { public static final String TAG = Level.class.getName(); public Array<Carrot> carrots; public Goal goal; public enum BLOCK_TYPE { GOAL(255, 0, 0), // red EMPTY(0, 0, 0), // black ROCK(0, 255, 0), // green PLAYER_SPAWNPOINT(255, 255, 255), // white ITEM_FEATHER(255, 0, 255), // purple ITEM_GOLD_COIN(255, 255, 0); // yellow private int color; private BLOCK_TYPE(int r, int g, int b) { color = r << 24 | g << 16 | b << 8 | 0xff; } public boolean sameColor(int color) { return this.color == color; } public int getColor() { return color; } } public BunnyHead bunnyHead; public Array<GoldCoin> goldcoins; public Array<Feather> feathers; // objects public Array<Rock> rocks; // decoration public Clouds clouds; public Mountains mountains; public WaterOverlay waterOverlay; public Level(String filename) { init(filename); } private void init(String filename) { // player character bunnyHead = null; // objects rocks = new Array<Rock>(); goldcoins = new Array<GoldCoin>(); feathers = new Array<Feather>(); carrots = new Array<Carrot>(); // load image file that represents the level data Pixmap pixmap = new Pixmap(Gdx.files.internal(filename)); // scan pixels from top-left to bottom-right int lastPixel = -1; for (int pixelY = 0; pixelY < pixmap.getHeight(); pixelY++) { for (int pixelX = 0; pixelX < pixmap.getWidth(); pixelX++) { AbstractGameObject obj = null; float offsetHeight = 0; // height grows from bottom to top float baseHeight = pixmap.getHeight() - pixelY; // get color of current pixel as 32-bit RGBA value int currentPixel = pixmap.getPixel(pixelX, pixelY); // find matching color value to identify block type at (x,y) // point and create the corresponding game object if there is // a match // empty space if (BLOCK_TYPE.EMPTY.sameColor(currentPixel)) { // do nothing } // rock else if (BLOCK_TYPE.ROCK.sameColor(currentPixel)) { if (lastPixel != currentPixel) { obj = new Rock(); float heightIncreaseFactor = 0.25f; offsetHeight = -2.5f; obj.position.set(pixelX, baseHeight * obj.dimension.y * heightIncreaseFactor + offsetHeight); rocks.add((Rock) obj); } else { rocks.get(rocks.size - 1).increaseLength(1); } } // player spawn point else if (BLOCK_TYPE.PLAYER_SPAWNPOINT.sameColor(currentPixel)) { obj = new BunnyHead(); offsetHeight = -3.0f; obj.position.set(pixelX, baseHeight * obj.dimension.y + offsetHeight); bunnyHead = (BunnyHead) obj; } // feather else if (BLOCK_TYPE.ITEM_FEATHER.sameColor(currentPixel)) { obj = new Feather(); offsetHeight = -1.5f; obj.position.set(pixelX, baseHeight * obj.dimension.y + offsetHeight); feathers.add((Feather) obj); } // gold coin else if (BLOCK_TYPE.ITEM_GOLD_COIN.sameColor(currentPixel)) { obj = new GoldCoin(); offsetHeight = -1.5f; obj.position.set(pixelX, baseHeight * obj.dimension.y + offsetHeight); goldcoins.add((GoldCoin) obj); } // goal else if (BLOCK_TYPE.GOAL.sameColor(currentPixel)) { obj = new Goal(); offsetHeight = -7.0f; obj.position.set(pixelX, baseHeight + offsetHeight); goal = (Goal) obj; } // unknown object/pixel color else { int r = 0xff & (currentPixel >>> 24); // red color channel int g = 0xff & (currentPixel >>> 16); // green color channel int b = 0xff & (currentPixel >>> 8); // blue color channel int a = 0xff & currentPixel; // alpha channel Gdx.app.error(TAG, "Unknown object at x<" + pixelX + "> y<" + pixelY + ">: r<" + r + "> g<" + g + "> b<" + b + "> a<" + a + ">"); } lastPixel = currentPixel; } } // decoration clouds = new Clouds(pixmap.getWidth()); clouds.position.set(0, 2); mountains = new Mountains(pixmap.getWidth()); mountains.position.set(-1, -1); waterOverlay = new WaterOverlay(pixmap.getWidth()); waterOverlay.position.set(0, -3.75f); // free memory pixmap.dispose(); Gdx.app.debug(TAG, "level '" + filename + "' loaded"); } public void update(float deltaTime) { bunnyHead.update(deltaTime); for (Rock rock : rocks) rock.update(deltaTime); for (GoldCoin goldCoin : goldcoins) goldCoin.update(deltaTime); for (Feather feather : feathers) feather.update(deltaTime); for (Carrot carrot : carrots) carrot.update(deltaTime); clouds.update(deltaTime); } public void render(SpriteBatch batch) { // Draw Mountains mountains.render(batch); // Draw Goal goal.render(batch); // Draw Rocks for (Rock rock : rocks) rock.render(batch); // Draw Gold Coins for (GoldCoin goldCoin : goldcoins) goldCoin.render(batch); // Draw Feathers for (Feather feather : feathers) feather.render(batch); // Draw Carrots for (Carrot carrot : carrots) carrot.render(batch); // Draw Player Character bunnyHead.render(batch); // Draw Water Overlay waterOverlay.render(batch); // Draw Clouds clouds.render(batch); } }
现在,我们修改AbstractGameObject让它下萝卜雨:
public Body body; public void update(float deltaTime) { if (body == null) { updateMotionX(deltaTime); updateMotionY(deltaTime); // Move to new position position.x += velocity.x * deltaTime; position.y += velocity.y * deltaTime; } else { position.set(body.getPosition()); rotation = body.getAngle() * MathUtils.radiansToDegrees; } }
这里的意思就是说如果我们的物体对象不是body的话,那就按照我们自己的简易物理模拟来移动,如果是的话,就通过Box2D计算反馈的值来移动。
接下来在WorldController添加:
private boolean goalReached; public World b2world; private void initPhysics() { if (b2world != null) b2world.dispose(); b2world = new World(new Vector2(0, -9.81f), true); // Rocks Vector2 origin = new Vector2(); for (Rock rock : level.rocks) { BodyDef bodyDef = new BodyDef(); bodyDef.type = BodyType.KinematicBody; bodyDef.position.set(rock.position); Body body = b2world.createBody(bodyDef); rock.body = body; PolygonShape polygonShape = new PolygonShape(); origin.x = rock.bounds.width / 2.0f; origin.y = rock.bounds.height / 2.0f; polygonShape.setAsBox(rock.bounds.width / 2.0f, rock.bounds.height / 2.0f, origin, 0); FixtureDef fixtureDef = new FixtureDef(); fixtureDef.shape = polygonShape; body.createFixture(fixtureDef); polygonShape.dispose(); } }
一直记得在world不用的时候释放掉,当然也包括PolygonShape, CircleShape这些Box2D的shape类
body物体都会有蓝色的边框,这是Box2D的类Box2DDebugRenderer的效果。我们在WorldRenderer里加上它:
private static final boolean DEBUG_DRAW_BOX2D_WORLD = false; private Box2DDebugRenderer b2debugRenderer; private void init () { batch = new SpriteBatch(); camera = new OrthographicCamera(Constants.VIEWPORT_WIDTH, Constants.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT); camera.position.set(0, 0, 0); camera.update(); cameraGUI = new OrthographicCamera(Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_WIDTH, Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_HEIGHT); cameraGUI.position.set(0, 0, 0); cameraGUI.setToOrtho(true); // flip y-axis cameraGUI.update(); b2debugRenderer = new Box2DDebugRenderer(); } private void renderWorld (SpriteBatch batch) { worldController.cameraHelper.applyTo(camera); batch.setProjectionMatrix(camera.combined); batch.begin(); worldController.level.render(batch); batch.end(); if (DEBUG_DRAW_BOX2D_WORLD) { b2debugRenderer.render(worldController.b2world, camera.combined); } }
增加一些常量准备:
// Number of carrots to spawn public static final int CARROTS_SPAWN_MAX = 100; // Spawn radius for carrots public static final float CARROTS_SPAWN_RADIUS = 3.5f; // Delay after game finished public static final float TIME_DELAY_GAME_FINISHED = 6;
在WorldController添加产生萝卜的代码:
private void spawnCarrots(Vector2 pos, int numCarrots, float radius) { float carrotShapeScale = 0.5f; // create carrots with box2d body and fixture for (int i = 0; i < numCarrots; i++) { Carrot carrot = new Carrot(); // calculate random spawn position, rotation, and scale float x = MathUtils.random(-radius, radius); float y = MathUtils.random(5.0f, 15.0f); float rotation = MathUtils.random(0.0f, 360.0f) * MathUtils.degreesToRadians; float carrotScale = MathUtils.random(0.5f, 1.5f); carrot.scale.set(carrotScale, carrotScale); // create box2d body for carrot with start position // and angle of rotation BodyDef bodyDef = new BodyDef(); bodyDef.position.set(pos); bodyDef.position.add(x, y); bodyDef.angle = rotation; Body body = b2world.createBody(bodyDef); body.setType(BodyType.DynamicBody); carrot.body = body; // create rectangular shape for carrot to allow // interactions (collisions) with other objects PolygonShape polygonShape = new PolygonShape(); float halfWidth = carrot.bounds.width / 2.0f * carrotScale; float halfHeight = carrot.bounds.height / 2.0f * carrotScale; polygonShape.setAsBox(halfWidth * carrotShapeScale, halfHeight * carrotShapeScale); // set physics attributes FixtureDef fixtureDef = new FixtureDef(); fixtureDef.shape = polygonShape; fixtureDef.density = 50; fixtureDef.restitution = 0.5f; fixtureDef.friction = 0.5f; body.createFixture(fixtureDef); polygonShape.dispose(); // finally, add new carrot to list for updating/rendering level.carrots.add(carrot); } }
private void onCollisionBunnyWithGoal() { goalReached = true; timeLeftGameOverDelay = Constants.TIME_DELAY_GAME_FINISHED; Vector2 centerPosBunnyHead = new Vector2(level.bunnyHead.position); centerPosBunnyHead.x += level.bunnyHead.bounds.width; spawnCarrots(centerPosBunnyHead, Constants.CARROTS_SPAWN_MAX, Constants.CARROTS_SPAWN_RADIUS); } private void initLevel() { score = 0; scoreVisual = score; goalReached = false; level = new Level(Constants.LEVEL_01); cameraHelper.setTarget(level.bunnyHead); initPhysics(); } private void testCollisions (float deltaTIme) { r1.set(level.bunnyHead.position.x, level.bunnyHead.position.y, level.bunnyHead.bounds.width, level.bunnyHead.bounds.height); // Test collision: Bunny Head <-> Rocks ... // Test collision: Bunny Head <-> Gold Coins ... // Test collision: Bunny Head <-> Feathers ... // Test collision: Bunny Head <-> Goal if (!goalReached) { r2.set(level.goal.bounds); r2.x += level.goal.position.x; r2.y += level.goal.position.y; if (r1.overlaps(r2)) onCollisionBunnyWithGoal(); } } public void update (float deltaTime) { handleDebugInput(deltaTime); if (isGameOver() || goalReached) { timeLeftGameOverDelay -= deltaTime; if (timeLeftGameOverDelay < 0) backToMenu(); } else { handleInputGame(deltaTime); } level.update(deltaTime); testCollisions(); b2world.step(deltaTime, 8, 3); cameraHelper.update(deltaTime); }
最后修改Rock:
@Override public void update(float deltaTime) { super.update(deltaTime); floatCycleTimeLeft -= deltaTime; if (floatTargetPosition == null) floatTargetPosition = new Vector2(position); if (floatCycleTimeLeft <= 0) { floatCycleTimeLeft = FLOAT_CYCLE_TIME; floatingDownwards = !floatingDownwards; body.setLinearVelocity(0, FLOAT_AMPLITUDE* (floatingDownwards ? -1 : 1)); } else { body.setLinearVelocity(body.getLinearVelocity().scl(0.98f)); } /*floatTargetPosition.y += FLOAT_AMPLITUDE * (floatingDownwards ? -1 : 1); } position.lerp(floatTargetPosition, deltaTime);*/ }
有人发现了上面提到的问题没?上面明明说world要dispose,但是又没释放,这不是自相矛盾吗?下面我们来释放它,首先要让worldcontroller实现dispose接口:implements Disposable
@Override public void dispose () { if (b2world != null) b2world.dispose(); }
然后修改GameScreen的hide方法:
worldController.dispose();
Ok,大功告成,跑起。。
现在,让我们把注意力放到着色器shader上来。
这也是只有OpenGL (ES) 2.0支持的功能。它就是利用叫做可编程管线的东东。着色器通常是小程序,它允许我们接管控制图形处理器渲染场景的某些阶段。因此,着色器在今天的计算机图形学领域是一个重要的组成部分,也是一个用来创建各种各样的(特殊)的其他方式很难实现的效果的极其强大的工具。为了简单起见,我们在这里将只讨论顶点和片段着色器(vertex and fragment)。
(片段着色器也称为像素着色器,不幸的是,这个名字有点误导,这种类型的着色器实际上操作的是片段而不是像素)
以下原因将告诉你为什么着色器通常是有用的以及为什么强烈建议每个(图形)的程序员把它作为必备列入工具箱
•可编程GPU的渲染管道通过着色器来创建任意复杂的效果。这意味着通过数学公式表述特效的高度灵活性。
•着色器是运行在GPU上的,这会节省CPU时间,让它可以把时间花在其他的任务上,比如做物理和一般游戏逻辑。
•重度的数学计算在gpu上通常比cpu更快的完成。
•GPU可以并行处理顶点和片段。
每个顶点的顶点着色器的操作给了GPU,一个顶点是一个在3d空间带属性(如位置,颜色和纹理坐标)的点.着色器就可以操纵这些值来达到效果,比如一个对象的变形。
通过顶点着色器计算的每个顶点的输出传输到渲染管道作为下一个阶段渲染的输入。
片段着色器计算每个片段像素的颜色,这样,很多因素都可以控制来渲染不同的材质,这些因素包含光照lighting, 透明translucency, 阴影shadows等等。
一个顶点和片段着色器的组合被称为一个着色器程序。
着色器通常是写在一个特定api的高级语言里,比如OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) for OpenGL。语法类似于C。更多信息请google。
创建一个单色过滤着色器程序
我们先从vertex shader开始
在CanyonBunnyandroid/assets下创建一个子文件夹shaders。然后在里面新建一个文件monochrome.vs。
在里面添加代码:
attribute vec4 a_position; attribute vec4 a_color; attribute vec2 a_texCoord0; varying vec4 v_color; varying vec2 v_texCoords; uniform mat4 u_projTrans; void main() { v_color = a_color; v_texCoords = a_texCoord0; gl_Position = u_projTrans * a_position; }
前6行声明的不同的变量用GLSL的术语叫做存储限定符。
接下来创建文件monochrome.fs,添加代码:
#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif varying vec4 v_color; varying vec2 v_texCoords; uniform sampler2D u_texture; uniform float u_amount; void main() { vec4 color = v_color * texture2D(u_texture, v_texCoords); float grayscale = dot(color.rgb, vec3(0.222, 0.707, 0.071)); color.rgb = mix(color.rgb, vec3(grayscale), u_amount); gl_FragColor = color; }
接下来,在我们的游戏中使用单色过滤着色器程序。
先在常量里添加
// Shader public static final String shaderMonochromeVertex = "shaders/monochrome.vs"; public static final String shaderMonochromeFragment = "shaders/monochrome.fs";
修改GamePreferences的load和save:
public boolean useMonochromeShader; public void load () { showFpsCounter = prefs.getBoolean("showFpsCounter", false); useMonochromeShader = prefs.getBoolean("useMonochromeShader", false); } public void save () { prefs.putBoolean("showFpsCounter", showFpsCounter); prefs.putBoolean("useMonochromeShader", useMonochromeShader); prefs.flush(); }
修改MenuScreen:
private CheckBox chkUseMonochromeShader; private Table buildOptWinDebug () { Table tbl = new Table(); // + Title: "Debug" // + Checkbox, "Show FPS Counter" label // + Checkbox, "Use Monochrome Shader" label chkUseMonochromeShader = new CheckBox("", skinLibgdx); tbl.add(new Label("Use Monochrome Shader", skinLibgdx)); tbl.add(chkUseMonochromeShader); tbl.row(); return tbl; } private void loadSettings () { chkShowFpsCounter.setChecked(prefs.showFpsCounter); chkUseMonochromeShader.setChecked(prefs.useMonochromeShader); } private void saveSettings () { prefs.showFpsCounter = chkShowFpsCounter.isChecked(); prefs.useMonochromeShader = chkUseMonochromeShader.isChecked(); prefs.save(); }
修改WorldRenderer:
private ShaderProgram shaderMonochrome; private void init () { batch = new SpriteBatch(); camera = new OrthographicCamera(Constants.VIEWPORT_WIDTH, Constants.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT); camera.position.set(0, 0, 0); camera.update(); cameraGUI = new OrthographicCamera(Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_WIDTH, Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_HEIGHT); cameraGUI.position.set(0, 0, 0); cameraGUI.setToOrtho(true); // flip y-axis cameraGUI.update(); b2debugRenderer = new Box2DDebugRenderer(); shaderMonochrome = new ShaderProgram( Gdx.files.internal(Constants.shaderMonochromeVertex), Gdx.files.internal(Constants.shaderMonochromeFragment)); if (!shaderMonochrome.isCompiled()) { String msg = "Could not compile shader program: " + shaderMonochrome.getLog(); throw new GdxRuntimeException(msg); } } private void renderWorld (SpriteBatch batch) { worldController.cameraHelper.applyTo(camera); batch.setProjectionMatrix(camera.combined); batch.begin(); if (GamePreferences.instance.useMonochromeShader) { batch.setShader(shaderMonochrome); shaderMonochrome.setUniformf("u_amount", 1.0f); } worldController.level.render(batch); batch.setShader(null); batch.end(); if (DEBUG_DRAW_BOX2D_WORLD) { b2debugRenderer.render(worldController.b2world, camera.combined); } } @Override public void dispose () { batch.dispose(); shaderMonochrome.dispose(); }
跑起..
速度计的使用:
在Libgdx中,通常的用法float ax = Gdx.input.getAccelerometerX();
一个取自Android SDK开发网站的图像很好地说明了传感器坐标系统:

直接上代码,首先在常量类中增加:
// Angle of rotation for dead zone (no movement) public static final float ACCEL_ANGLE_DEAD_ZONE = 5.0f; // Max angle of rotation needed to gain max movement velocity public static final float ACCEL_MAX_ANGLE_MAX_MOVEMENT = 20.0f;
然后修改WorldController:
private boolean accelerometerAvailable; private void init () { accelerometerAvailable = Gdx.input.isPeripheralAvailable( Peripheral.Accelerometer); cameraHelper = new CameraHelper(); lives = Constants.LIVES_START; livesVisual = lives; timeLeftGameOverDelay = 0; initLevel(); } private void handleInputGame (float deltaTime) { if (cameraHelper.hasTarget(level.bunnyHead)) { // Player Movement if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.LEFT)) { ... } else { // Use accelerometer for movement if available if (accelerometerAvailable) { // normalize accelerometer values from [-10, 10] to [-1, 1] // which translate to rotations of [-90, 90] degrees float amount = Gdx.input.getAccelerometerY() / 10.0f; amount *= 90.0f; // is angle of rotation inside dead zone? if (Math.abs(amount) < Constants.ACCEL_ANGLE_DEAD_ZONE) { amount = 0; } else { // use the defined max angle of rotation instead of // the full 90 degrees for maximum velocity amount /= Constants.ACCEL_MAX_ANGLE_MAX_MOVEMENT; } level.bunnyHead.velocity.x = level.bunnyHead.terminalVelocity.x * amount; } // Execute auto-forward movement on non-desktop platform else if (Gdx.app.getType() != ApplicationType.Desktop) { level.bunnyHead.velocity.x = level.bunnyHead.terminalVelocity.x; } } } }
效果自己试试吧,本章到此完。
下一章将介绍Libgdx的动作和动画