参考:http://www.dewen.net.cn/q/9077
http://coolxing.iteye.com/blog/1236909
lock,tryLock,lockInterruptibly
分别对应无限制锁,定时锁(通过while可以作为轮询锁),可中断锁。
Lock接口的 线程请求锁的 几个方法:
lock(), 拿不到lock就不罢休,不然线程就一直block。 比较无赖的做法。
tryLock(),马上返回,拿到lock就返回true,不然返回false。 比较潇洒的做法。
带时间限制的tryLock(),拿不到lock,就等一段时间,超时返回false。比较聪明的做法。
下面的lockInterruptibly()就稍微难理解一些。
先说说线程的打扰机制,每个线程都有一个 打扰 标志。这里分两种情况,
1. 线程在sleep或wait,join, 此时如果别的进程调用此进程的 interrupt()方法,此线程会被唤醒并被要求处理InterruptedException;(thread在做IO操作时也可能有类似行为,见java thread api)
2. 此线程在运行中, 则不会收到提醒。但是 此线程的 “打扰标志”会被设置, 可以通过isInterrupted()查看并作出处理。
lockInterruptibly()和上面的第一种情况是一样的, 线程在请求lock并被阻塞时,如果被interrupt,则“此线程会被唤醒并被要求处理InterruptedException”。
E.G. lock() & lockInterruptibly()
--lock()
1 package lockInterruptibly; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 5 6 public class MyService { 7 8 public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 9 private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 10 11 public void waitMethod() { 12 try { 13 lock.lock(); 14 // lock.lockInterruptibly(); 15 System.out.println("lock begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { 17 String newString = new String(); 18 Math.random(); 19 // System.out.println(i + " "); 20 } 21 System.out.println("lock end " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 22 } finally { 23 if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { 24 lock.unlock(); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 }
1 package lockInterruptibly; 2 3 public class Run { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 try { 7 final MyService service = new MyService(); 8 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 service.waitMethod(); 14 } 15 }; 16 Thread a = new Thread(runnable); 17 a.setName("A"); 18 a.start(); 19 Thread b = new Thread(runnable); 20 b.setName("B"); 21 b.start(); 22 Thread.sleep(500); 23 b.interrupt(); 24 System.out.println("main end"); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 } 30 31 }

正如lock()拿不到锁誓不罢休,线程b并未响应interrupt,一直在等待着锁。
--lockInterruptibly()
1 package lockInterruptibly; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 5 6 public class MyService { 7 8 public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 9 private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 10 11 public void waitMethod() { 12 try { 13 // lock.lock(); 14 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 15 System.out.println("lock begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { 17 String newString = new String(); 18 Math.random(); 19 // System.out.println(i + " "); 20 } 21 System.out.println("lock end " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } finally { 26 if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { 27 lock.unlock(); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 }
1 package lockInterruptibly; 2 3 public class Run { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 try { 7 final MyService service = new MyService(); 8 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 service.waitMethod(); 14 } 15 }; 16 Thread a = new Thread(runnable); 17 a.setName("A"); 18 a.start(); 19 Thread b = new Thread(runnable); 20 b.setName("B"); 21 b.start(); 22 Thread.sleep(500); 23 b.interrupt(); 24 System.out.println("main end"); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 } 30 31 }
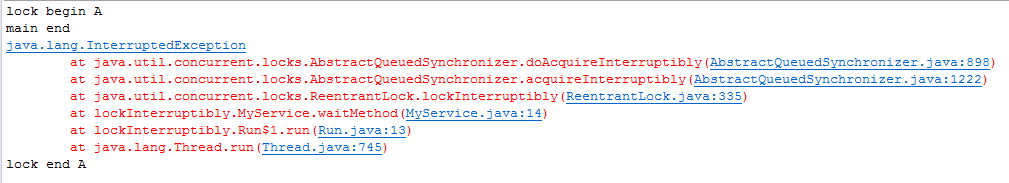
线程b并没有拿到锁,此时调用interrupt方法,则线程b被唤醒并被要求处理InterruptedException,即抛出了InterruptedException
当然,线程b也并不会执行了
但是当线程b拿到锁执行时才调用interrupt,这时候线程b并不会中断
tryLock() & tryLock(long, TimeUnit)
|--void lock(): 执行此方法时, 如果锁处于空闲状态, 当前线程将获取到锁. 相反, 如果锁已经被其他线程持有, 将禁用当前线程, 直到当前线程获取到锁.
|--boolean tryLock(): 如果锁可用, 则获取锁, 并立即返回true, 否则返回false. 该方法和lock()的区别在于, tryLock()只是"试图"获取锁, 如果锁不可用, 不会导致当前线程被禁用, 当前线程仍然继续往下执行代码. 而lock()方法则是一定要获取到锁, 如果锁不可用, 就一直等待, 在未获得锁之前,当前线程并不继续向下执行. 通常采用如下的代码形式调用tryLock()方法:
|--boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):如果锁定在给定等待时间内没有被另一个线程保持,且当前线程未被中断,则获取该锁定。
通常采用如下的代码形式调用tryLock()方法:
1 Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 2 if (lock.tryLock()) { 3 try { 4 // manipulate protected state 5 } finally { 6 lock.unlock(); 7 } 8 } else { 9 // perform alternative actions 10 }
此用法可确保如果获取了锁, 则会释放锁; 如果未获取锁, 则不会试图将其释放.
--tryLock()
1 package tryLock.copy.copy; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 5 6 /** 7 * boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 如果锁定在给定等待时间内没有被另一个线程保 8 * 持,且当前线程未被中断,则获取该锁定 9 * 10 * @author MicroCat 11 * 12 */ 13 public class MyService { 14 15 public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 16 17 public void waitMethod() { 18 if (lock.tryLock()) { 19 try { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 获得锁"); 21 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { 22 if (i % 100 == 0) { 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i); 24 } 25 } 26 } finally { 27 lock.unlock(); 28 } 29 } else { 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 没有获得锁"); 31 } 32 } 33 34 }
1 package tryLock.copy.copy; 2 3 public class Run { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 6 final MyService service = new MyService(); 7 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { 8 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 service.waitMethod(); 12 } 13 }; 14 Thread a = new Thread(runnable); 15 a.setName("A"); 16 a.start(); 17 Thread b = new Thread(runnable); 18 b.setName("B"); 19 b.start(); 20 } 21 22 }

线程b没有获得锁,a线程执行完也没有继续执行
--tryLock(long, TimeUnit)
1 package tryLock.copy.copy.copy; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 5 6 /** 7 * boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 如果锁定在给定等待时间内没有被另一个线程保 8 * 持,且当前线程未被中断,则获取该锁定 9 * 10 * @author MicroCat 11 * 12 */ 13 public class MyService { 14 15 public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 16 17 public void waitMethod() { 18 try { 19 if (lock.tryLock(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { 20 try { 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 获得锁"); 22 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { 23 if (i % 100 == 0) { 24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i); 25 } 26 } 27 } finally { 28 lock.unlock(); 29 } 30 } else { 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 没有获得锁"); 32 } 33 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 34 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 }
1 package tryLock.copy.copy.copy; 2 3 public class Run { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 6 final MyService service = new MyService(); 7 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { 8 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 service.waitMethod(); 12 } 13 }; 14 Thread a = new Thread(runnable); 15 a.setName("A"); 16 a.start(); 17 Thread b = new Thread(runnable); 18 b.setName("B"); 19 b.start(); 20 } 21 22 }
在给定时间内各线程都有拿到锁,所以线程a,b都有执行