验证实验部分
2.形参是自定义函数括号里的变量,实参是主函数中传递给形参的变量。函数参数是用来传递函数计算所需要的值,函数返回值是为了得到运算结果。
3.值传递中形参只是实参的副本,其变化不会导致实参的变化;引用传递中形参存储的是实参的地址,因此被调函数对形参的操作相当于间接访问,因此其变化可以导致实参值的变化。
编程实验题
————————————————————————————————————————————————2---28(1)————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { char x; cout << "Menu :A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl; do { cin >> x; if (x == 'A') { cout << "数据已经增加"<<endl; continue; } else if (x == 'D') { cout << "数据已经删除"<<endl; continue; } else if (x == 'S') { cout << "数据已经排序"<<endl; continue; } else if (x == 'Q') break; } while (1); return 0; }
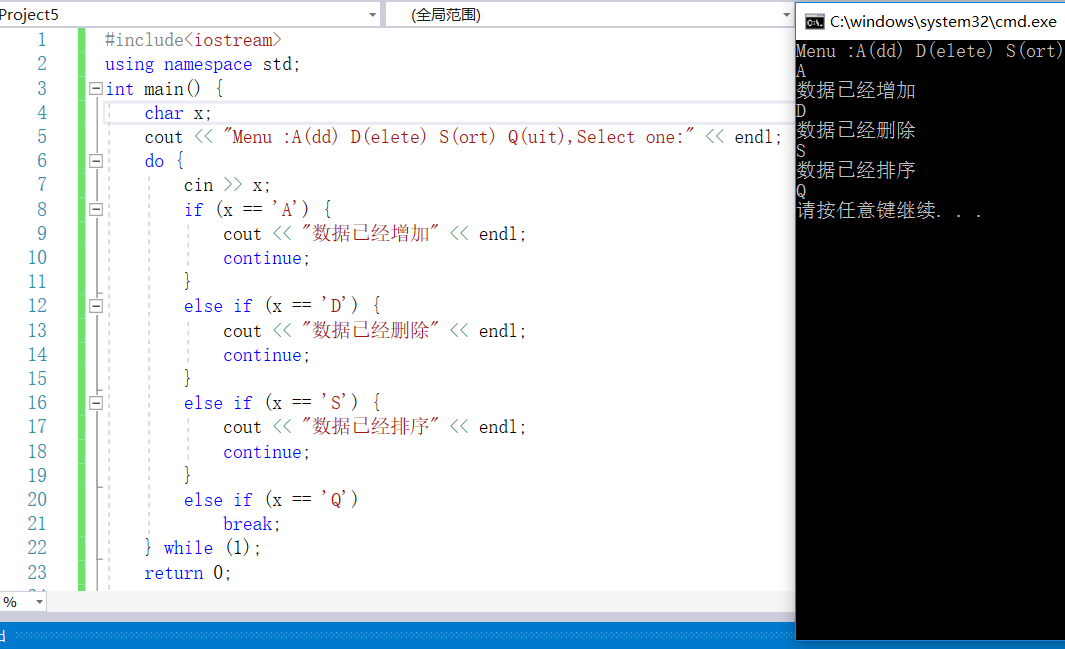
————————————————————————————————————————2-28(2)———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { char x; cout << "Menu :A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:" << endl; do { cin >> x; switch (x) { case 'A': cout << "数据已经增加" << endl; continue; case'D': cout << "数据已经删除" << endl; continue; case'S': cout << "数据已经排序" << endl; continue; case'Q': exit(0);//结束main函数 } } while (1); }
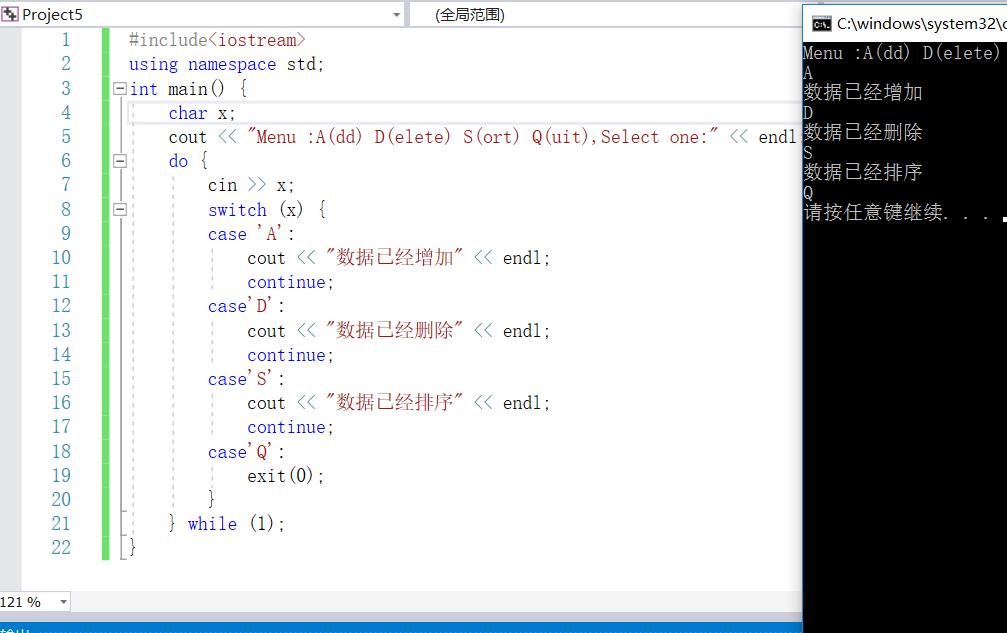
——————————————————————————2---29——————————————————————————————————————————————
算法简介:利用while/do..while/for对从1到100的每一个数进行循环。对于其中的每一个数n,再利用while/do..while/for对每个大于一小于n的数取模,定义整型变量t=0,每当模为零时,t++;若当第二个while/do..while/for循环结束时t=0,则n为质数。
———————————————2---29(1)——————————————————————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int n=1; while(n<=100){ int t=0,i=1; while (i<n) { if (n%i == 0) t++; i++; } if (t == 1) cout << n << endl; n++; } return 0; }
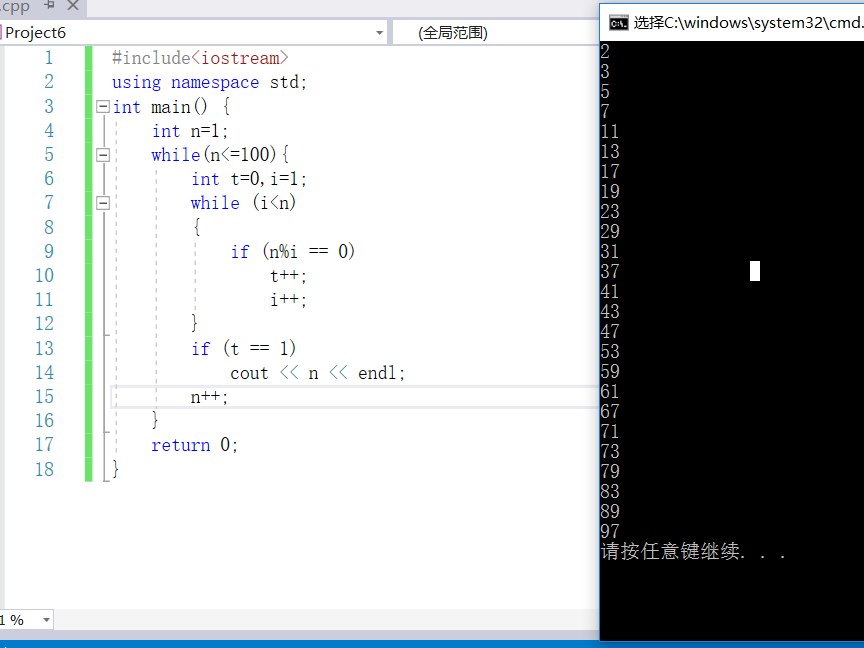
———————————————2---29(2)——————————————————————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int n=2; do { int t=0,i=1; do{ if (n%i == 0) t++; i++; }while (i < n); if (t == 1) cout << n << endl; n++; } while (n <= 100); return 0; }
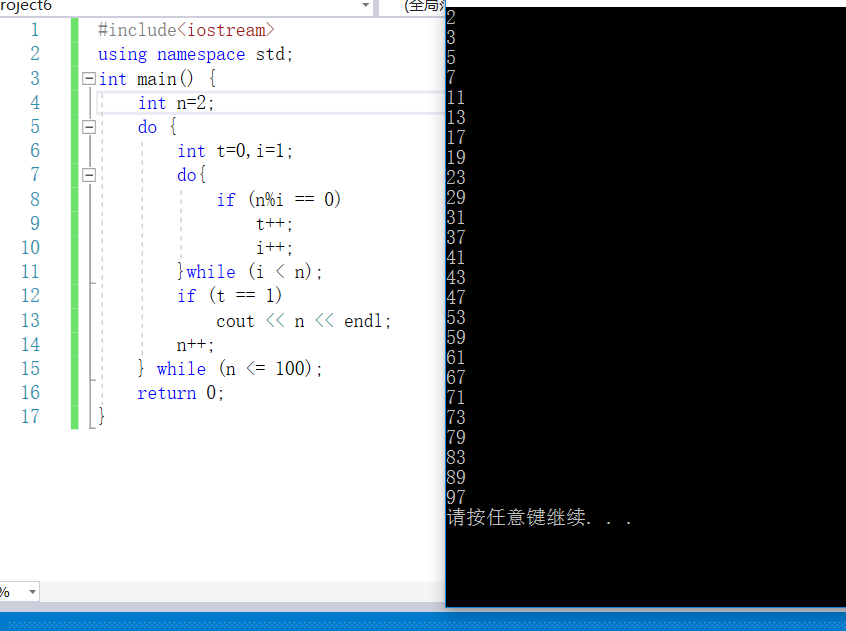
——————————————————————————2---29(3)—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 100; n++) { int t = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) if (n%i == 0) t++; if (t==1) cout <<n<<endl; } return 0; }
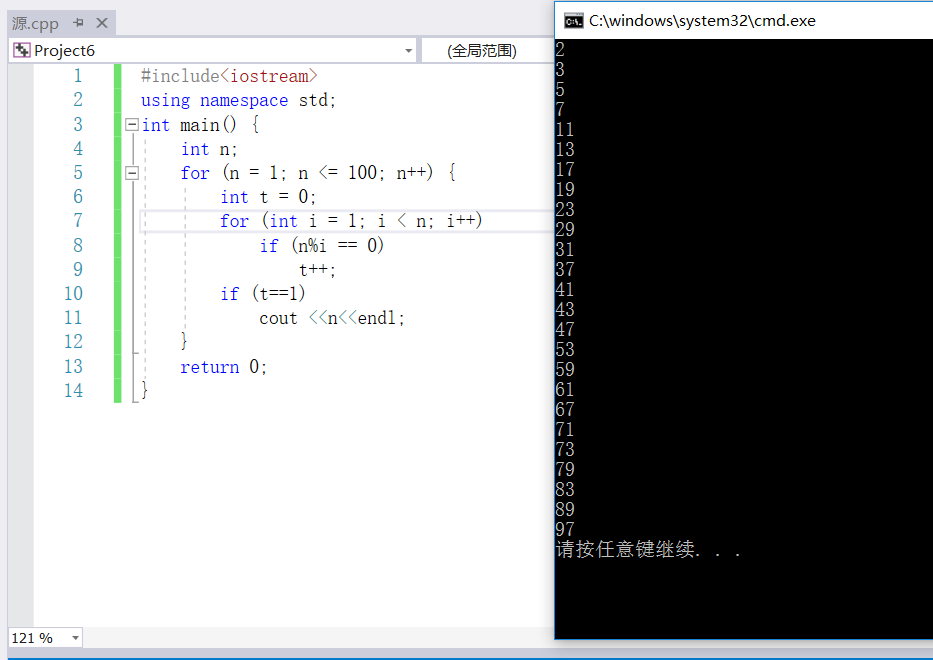
————————————————————————————————————————————————————2---32(1)——————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x, seed, y;
cout << "请先输入一个随机数" << endl;
cin >> seed;
srand(seed);
x = rand()%100;
cout << "请输入你所猜测的值" << endl;
while (1) {
cin >> y;
if (y > x) {
cout << "输入值过大,请重新输入" << endl;
continue;
}
if (y < x) {
cout << "输入值过小,请重新输入" << endl;
continue;
}
if (y == x) {
cout << "输入正确" << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
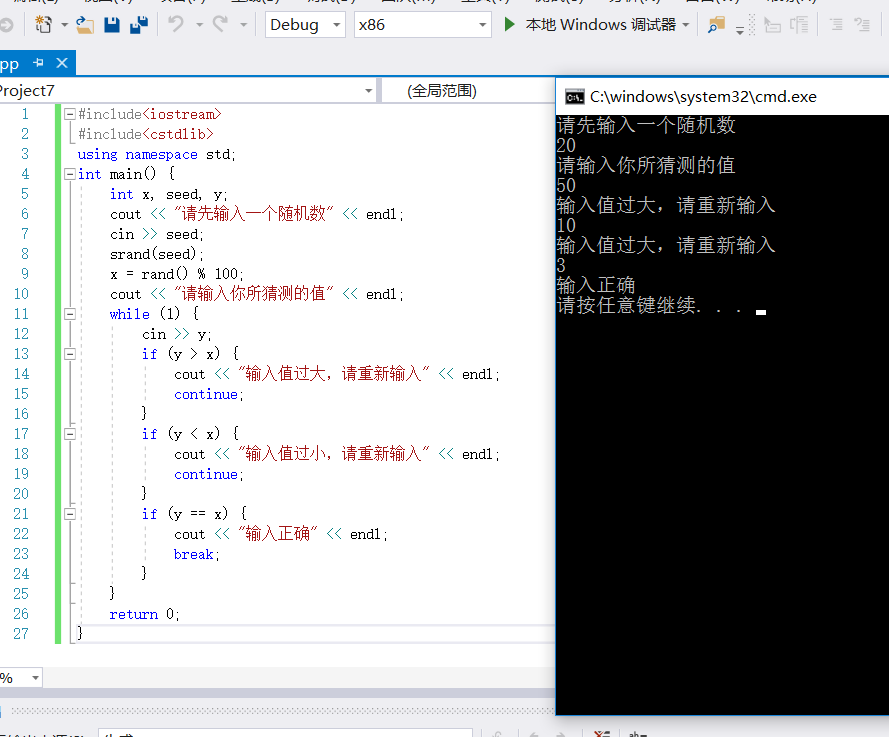
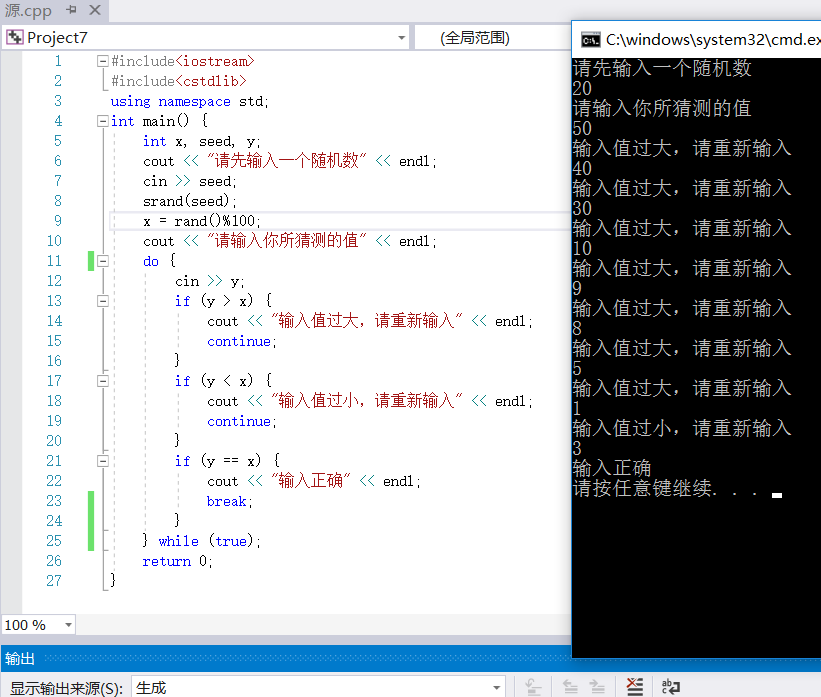
————————————————————————————————————————————————————2---32(2)——————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x, seed, y;
cout << "请先输入一个随机数" << endl;
cin >> seed;
srand(seed);
x = rand()%100;
cout << "请输入你所猜测的值" << endl;
do {
cin >> y;
if (y > x) {
cout << "输入值过大,请重新输入" << endl;
continue;
}
if (y < x) {
cout << "输入值过小,请重新输入" << endl;
continue;
}
if (y == x) {
cout << "输入正确" << endl;
break;
}
} while (true);
return 0;
}
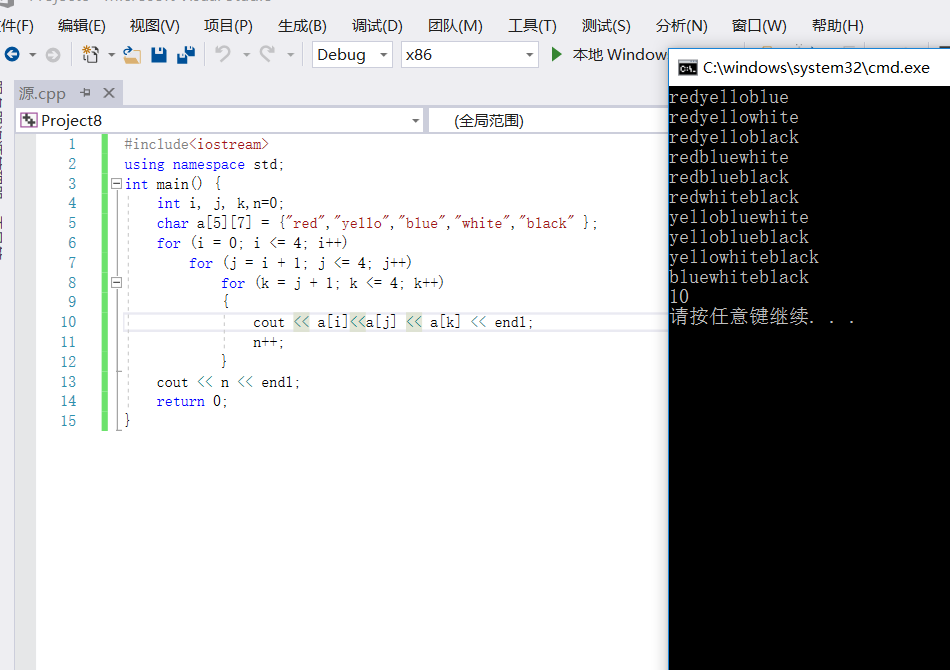
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————2---34————————————————————————————————
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i, j, k,n=0; char a[5][7] = {"red","yello","blue","white","black" }; for (i = 0; i <= 4; i++) for (j = i + 1; j <= 4; j++) for (k = j + 1; k <= 4; k++) { cout << a[i]<<a[j] << a[k] << endl; n++; } cout << n << endl; return 0; }
实验总结体会
首先认识到随机取值函数(int)rand()和(void)srand(),之后了解到引用传递和值传递的区别。引用传递与指针十分相似却又不完全一样,使用指针和引用传递在某种程度上可以起到很好的效果。对于字符数组的定义去应用需要加深了解,应用不是很熟练。