今天来看看Map家族的另一名大将——TreeMap。前面已经介绍过Map家族的两名大将,分别是HashMap,LinkedHashMap。HashMap可以高效查找和存储元素,LinkedHashMap可以在高效查找的基础上对元素进行有序遍历,那么TreeMap又有什么特点呢?别急别急,看完这篇你就知道了。
本篇主要从以下几个方面对TreeMap进行介绍:
1、TreeMap的特性以及使用栗子
2、TreeMap继承结构简介
3、TreeMap源码分析
本篇预计食用10分钟,请各位食客合理分配时间。
一、TreeMap的特性以及使用栗子
1. 键值不允许重复
2. 默认会对键进行排序,所以键必须实现Comparable接口或者使用外部比较器
3. 查找、移除、添加操作的时间复杂度为log(n)
4. 底层使用的数据结构是红黑树
没错,又是让你欲仙欲死的红黑树,不过不要慌,跟之前介绍HashMap时的红黑树是一毛一样的,所以这一篇里,不打算再做介绍啦,如果对红黑树的内容有些遗忘了,可以动动小手,往前面翻一翻。
先来看一个TreeMap的使用小栗子。
public class TreeMapTest { public static void main(String[] args){ TreeMap<String, Integer> grades = new TreeMap<>(); grades.put("Frank", 100); grades.put("Alice", 95); grades.put("Mary", 90); grades.put("Bob", 85); grades.put("Jack", 90); System.out.println(grades); System.out.println(grades.subMap("Bob", "Jack")); System.out.println(grades.subMap("Bob", true, "Jack", true)); System.out.println(grades.ceilingEntry("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.ceilingKey("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.higherEntry("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.higherKey("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.headMap("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.headMap("Bob", true)); System.out.println(grades.tailMap("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.tailMap("Bob", true)); System.out.println(grades.containsKey("Bob")); System.out.println(grades.containsValue(90)); System.out.println(grades.descendingMap()); System.out.println(grades.descendingKeySet()); } }
输出如下:
{Alice=95, Bob=85, Frank=100, Jack=90, Mary=90}
{Bob=85, Frank=100}
{Bob=85, Frank=100, Jack=90}
Bob=85
Bob
Frank=100
Frank
{Alice=95}
{Alice=95, Bob=85}
{Bob=85, Frank=100, Jack=90, Mary=90}
{Bob=85, Frank=100, Jack=90, Mary=90}
true
true
{Mary=90, Jack=90, Frank=100, Bob=85, Alice=95}
[Mary, Jack, Frank, Bob, Alice]
可以看到,放入TreeMap中的元素默认按键值升序排列,这里的键值类型为String,使用String的CompareTo方法进行比较和排序。subMap返回当前Map的子Map,headMap和tailMap也是如此,
二、TreeMap继承结构简介
TreeMap继承自AbstractMap,实现了NavigableMap接口,继承关系图如下:
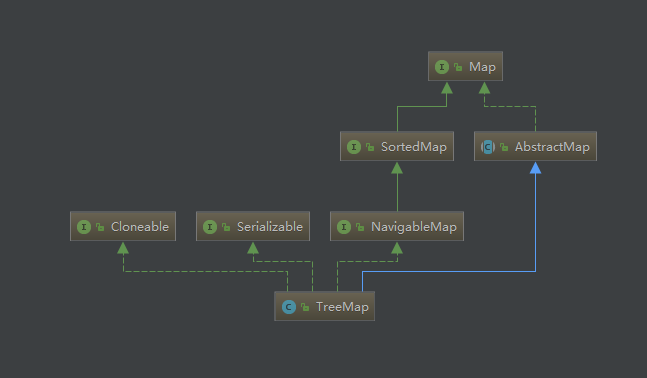
对于AbstractMap相信大家已经不陌生了,HashMap也是继承自AbstractMap,里面有对Map接口的一些默认实现。这里我们可以看到两个新的接口——SortedMap和NavigableMap。SortedMap接口继承自Map接口,从名字就能看出。SortedMap相比Map接口,憎加了排序的功能,内部的方法也不多,简单了解一下就好了
NavigableMap接口继承自SortedMap接口,主要提供一下导航方法:
说了这么多没啥营养的,接下来还是讲讲真正的干货吧。
三、TreeMap源码分析
JDK 1.8中的TreeMap源码有两千多行,还是比较多的。所以本文并不打算逐句分析所有的源码,而是挑选几个常用的内部类和方法进行分析。这些方法实现的功能分别是查找、遍历、插入、删除等,其他的方法小伙伴们有兴趣可以自己分析。TreeMap实现的核心部分是关于红黑树的实现,其绝大部分的方法基本都是对底层红黑树增、删、查操作的一个封装。就像前面所说,只要弄懂了红黑树原理,TreeMap 就没什么秘密了。关于红黑树的原理,可以参考前面关于HashMap红黑树的文章,本篇文章不会对此展开讨论。
TreeMap的主要数据结构是红黑树,而这红黑树结构的承载者便是内部类Entry,先来看看这个Entry类:
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { K key; V value; Entry<K,V> left; Entry<K,V> right; Entry<K,V> parent; boolean color = BLACK; /** * 构造函数*/ Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; } public K getKey() { return key; } public V getValue() { return value; } public V setValue(V value) { V oldValue = this.value; this.value = value; return oldValue; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue()); } public int hashCode() { int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()); int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); return keyHash ^ valueHash; } public String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } }
其实内部的结构也很简单,主要有key,value和三个分别指向左孩子,右孩子,父节点的引用,以及用来标识颜色的color成员变量。再来看看TreeMap中的几个重要的成员变量:
/** * 外部比较器 */ private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; private transient Entry<K,V> root; /** * 键值对数量 */ private transient int size = 0; private transient int modCount = 0; private static final boolean RED = false; private static final boolean BLACK = true; /** * 键值对集合 */ private transient EntrySet entrySet; /** * 键的集合 */ private transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySet; /** * 倒序Map */ private transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap;
comparator用于对map中的键进行排序,root指向红黑树的根节点,size表示键值对的数量,modCount相信已经不陌生了,表示内部结构被修改的次数,RED和BLACK是两个内部常量,即红黑两种颜色,false表示红,true表示黑。entrySet是键值对的集合,navigableKeySet是键的集合,最后一个descendingMap是当前map的一个倒序map。
在TreeMap中有很多内部类,可以先看图了解一下:
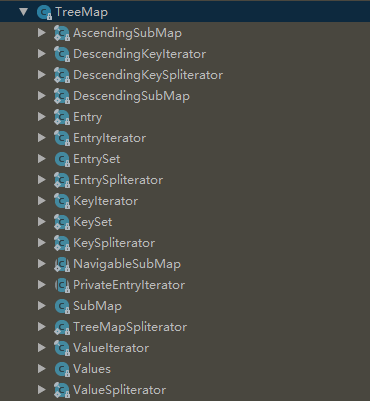
前前后后一共18个内部类,不过不要慌,其实里面跟迭代器相关的类就占了一半多(10个),跟子Map相关的类占4个,剩下4个就是跟内部集合相关的了。接下来还是一起来看看那些最常用的方法吧:
// 插入元素 public V put(K key, V value) { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null) { // 检查类型以及key是否为null // 如果外部比较器为null,且key也为null则会抛出空指针异常 // 如果TreeMap未设置外部比较器,且传入的对象未实现Comparable接口 // 则会抛出ClassCastException异常 compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check // 如果根节点不存在,则用传入的键值对信息生成一个根节点 root = new TreeMap.Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; TreeMap.Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { do { // 如果外部比较器不为空,则依次与各节点进行比较 parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) // 小于则与左孩子比较 t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) // 大于则与右孩子比较 t = t.right; else // 找到相等的key则替换其value return t.setValue(value); // 一直循环,直到待比较的节点为null } while (t != null); } else { // 如果外部比较器为null // 如果key为null则抛出空指针 if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // 如果key未实现comparable接口则会抛出异常 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { // 跟上面逻辑类似,只是用key的compareTo方法进行比较,而不是用外部比较器的compare方法 parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } // 生成键值对 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = new TreeMap.Entry<>(key, value, parent); // 连接到当前map的左孩子位置或者右孩子位置 if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; // 插入后的调整 fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null; }
其实这里的逻辑跟HashMap中TreeNode的插入逻辑十分类似,也是先找到要插入的位置,然后再进行结构调整。这里的结构调整即红黑树的结构调整,在前面HashMap中已经详细介绍过了,这里就不重复介绍了,调整过程是完全一样的。
/** * 插入后的调整 */ private void fixAfterInsertion(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> x) { // 将插入的节点初始化为红色节点 x.color = RED; // 如果x不为null且x不是根节点,且x的父节点是红色,此时祖父节点一定为黑色 while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { // 如果x的父节点为祖父节点的左孩子 if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { // y指向x的叔叔节点 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); // 如果叔叔节点也是红色,则进行变色处理 if (colorOf(y) == RED) { // 父节点变成黑色 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 叔叔节点变成黑色 setColor(y, BLACK); // 祖父节点变成黑色 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 将x指向祖父节点,继续往上调整 x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { // 如果叔叔节点是黑色节点 // 如果x是父节点的右孩子 if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { // 将x指向其父节点 x = parentOf(x); // 左旋 rotateLeft(x); } // 将x的父节点置为黑色 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 将x的祖父节点置为红色 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 将祖父节点右旋 rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } else { // 这里类似操作 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateRight(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } } root.color = BLACK; }
说完了插入,再来看看删除操作。
// 删除节点 public V remove(Object key) { // 先找到该key对应的键值对 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key); if (p == null) // 如果未找到则返回null return null; V oldValue = p.value; // 找到后删除该键值对 deleteEntry(p); return oldValue; }
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { // 为了性能,卸载了比较器的版本 if (comparator != null) return getEntryUsingComparator(key); if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; TreeMap.Entry<K,V> p = root; // 使用compareTo方法进行查找 while (p != null) { int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key); if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; else return p; } return null; } // 使用比较器的getEntry版本。 从getEntry分离以获得性能。 // (对于大多数方法而言,这不值得做,这些方法较少依赖于比较器性能,但在这里是值得的。) final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K k = (K) key; Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; // 使用比较器进行二分查找 if (cpr != null) { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key); if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; else return p; } } return null; } /** * 删除节点,并调整红黑树以保持它的平衡 */ private void deleteEntry(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> p) { modCount++; size--; // 如果p的左右孩子均不为空,则找到p的后继节点,并且将p指向该后继节点 if (p.left != null && p.right != null) { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> s = successor(p); p.key = s.key; p.value = s.value; p = s; } // p has 2 children // 修复替补节点 // 用替补节点替换待删除的节点后,需要对其原来所在位置结构进行修复 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right); if (replacement != null) { replacement.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = replacement; else if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = replacement; else p.parent.right = replacement; p.left = p.right = p.parent = null; // 如果p的颜色是黑色,则进行删除后的修复 if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(replacement); } else if (p.parent == null) { root = null; } else { if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(p); if (p.parent != null) { if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = null; else if (p == p.parent.right) p.parent.right = null; p.parent = null; } } } /** * 返回指定节点的后继节点 */ static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> t) { if (t == null) return null; else if (t.right != null) { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> p = t.right; // 如果右子树不为空,则找到右子树的最左节点作为后继节点 while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; } else { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> p = t.parent; TreeMap.Entry<K,V> ch = t; // 如果右子树为空且当前节点为其父节点的左孩子,则直接返回 // 如果为其父节点的右孩子,则一直往上找,直到找到根节点或者当前节点为其父节点的左孩子时,用其做为后继节点 while (p != null && ch == p.right) { ch = p; p = p.parent; } return p; } } /** * 进行删除后的结构修复 * @param x */ private void fixAfterDeletion(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> x) { while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) { // 如果x是父节点的左孩子 if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { // sib指向x的兄弟节点 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); // 如果sib是红色,则进行变色处理 if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { // 兄弟节点改为黑色 setColor(sib, BLACK); // 父节点改为红色 setColor(parentOf(x), RED); // 父节点左旋 rotateLeft(parentOf(x)); // sib指向x的父节点的右孩子 sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); } // 如果sib的左孩子和右孩子都是黑色,则进行变色处理 if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { // 将sib置为红色 setColor(sib, RED); // x指向其父节点 x = parentOf(x); } else { // 如果sib的右孩子是黑色而左孩子是红色,则变色右旋 if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateRight(sib); sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); } // 变色左旋 setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK); rotateLeft(parentOf(x)); x = root; } } else { // symmetric // 跟上面操作类似 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { setColor(sib, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(x), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(x)); sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); } if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(sib, RED); x = parentOf(x); } else { if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateLeft(sib); sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); } setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK); rotateRight(parentOf(x)); x = root; } } } setColor(x, BLACK); }
嗯,对比一下HashMap的删除操作,核心步骤是完全一样的,所以可以对照前面的HashMap红黑树详解进行食用。
到此,这一篇就很水的讲完啦= =
最近这段时间烦心事比较多,对发展方向也考虑了很多,想做的事情很多,反而让我止步不前,不过很多事情是急不来的,还是好好写写博客,多做总结分享吧。
机会只留给有准备的人。