最近做移动端H5页面的自动化测试时候,需要模拟一些上拉,下滑的操作,最初考虑使用使用selenium ActionChains来模拟操作,但是ActionChains 只是针对PC端程序鼠标模拟的一系列操作对H5页面操作时无效的,后来阅读了下selenium的文档发现TouchAction可以对移动端页面自动化操作;
首先使用TouchAction的时候首先需要在头上引入该模块
from selenium.webdriver.common.touch_actions import TouchActions
通过scroll_from_element、flick_element 方法来实现下拉操作
因为我们模拟的是移动端的H5自动化测试,首先需要我们将浏览器设置成为手机浏览器;
1.以元素为起点以一定速度向下滑动,实现下拉操作
- flick_element(on_element, xoffset, yoffset, speed);
- on_element #操作元素定位
- xoffset #x轴偏移量
- yoffset #y轴偏移量
- speed #速度
注意:
向上滑动为负数,向下滑动为正数
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2017/12/28 10:26 # @Author : Hunk # @File : ex86.py.py # @Software: PyCharm import time from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.touch_actions import TouchActions """设置手机的大小""" mobileEmulation = {'deviceName': 'Apple iPhone 5'} options = webdriver.ChromeOptions() options.add_experimental_option('mobileEmulation', mobileEmulation) driver = webdriver.Chrome(chrome_options=options) driver.get('http://m.test.90dichan.com') driver.maximize_window() """定位操作元素""" button = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="pullrefresh"]/div[2]/ul/li[2]/a/div[2]/span') time.sleep(3) Action = TouchActions(driver) """从button元素像下滑动200元素,以50的速度向下滑动""" Action.flick_element(button, 0, 200, 50).perform() time.sleep(3) driver.close()
2.以元素为起点向下滑动,实现下拉操作
- scroll_from_element(on_element xoffset yoffset)
- on_element:开始元素滚动。
- xoffset:X偏移量。
- yoffset:Y偏移量。
注意:
向下滑动为负数,向上滑动为正数
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2017/12/28 10:26 # @Author : Hunk # @File : ex86.py.py # @Software: PyCharm import time from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.touch_actions import TouchActions """设置手机的大小""" mobileEmulation = {'deviceName': 'Apple iPhone 5'} options = webdriver.ChromeOptions() options.add_experimental_option('mobileEmulation', mobileEmulation) driver = webdriver.Chrome(chrome_options=options) driver.get('http://m.test.90dichan.com') driver.maximize_window() """定位操作元素""" button = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="pullrefresh"]/div[2]/ul/li[2]/a/div[2]/span') time.sleep(3) Action = TouchActions(driver) """从button元素像下滑动200元素""" Action.scroll_from_element(button, 0, -200).perform() time.sleep(3) driver.close()
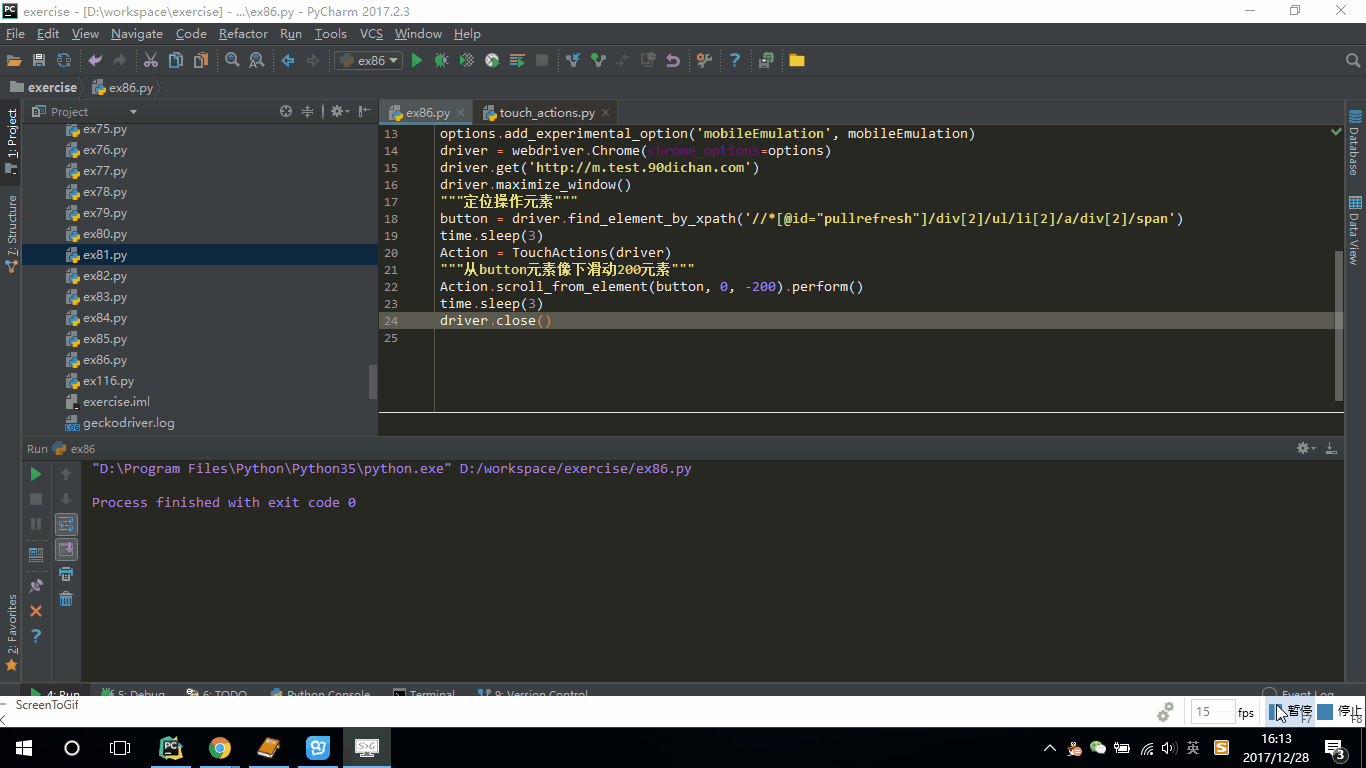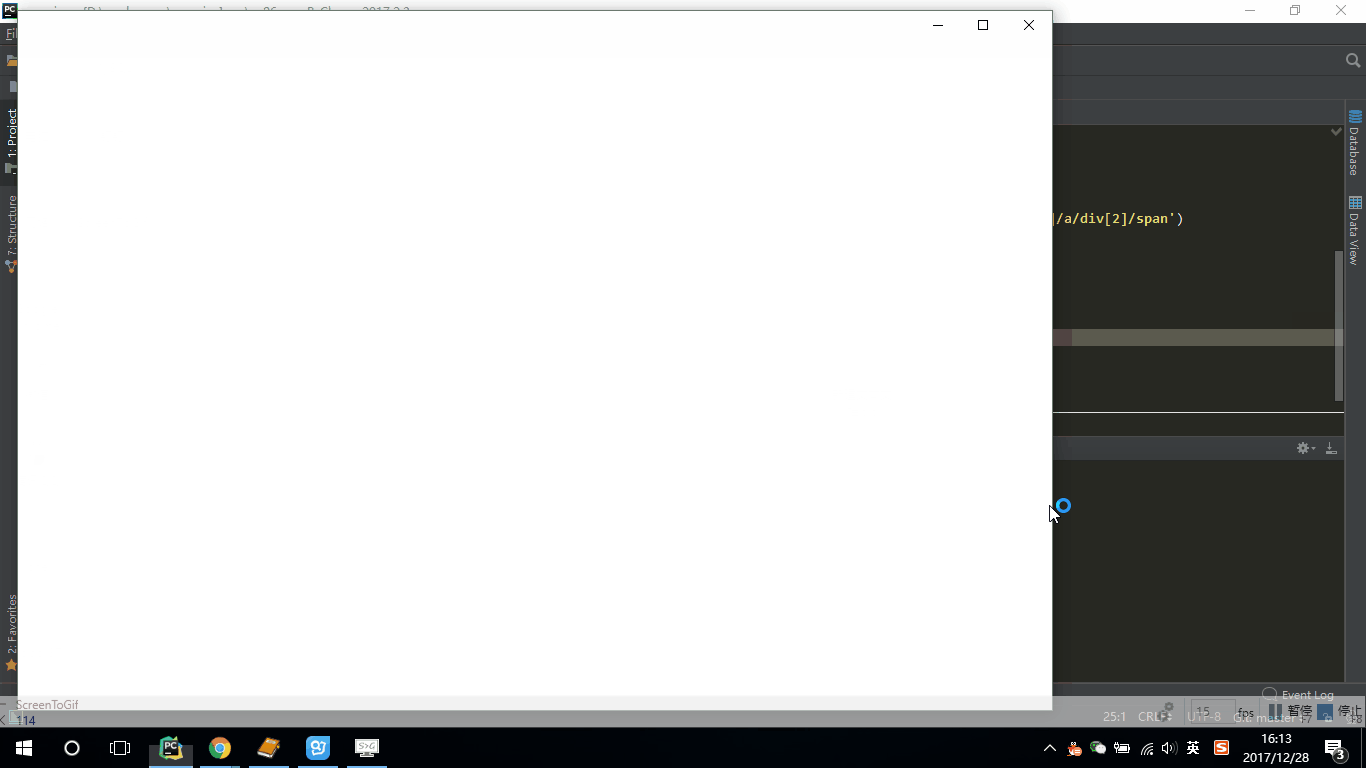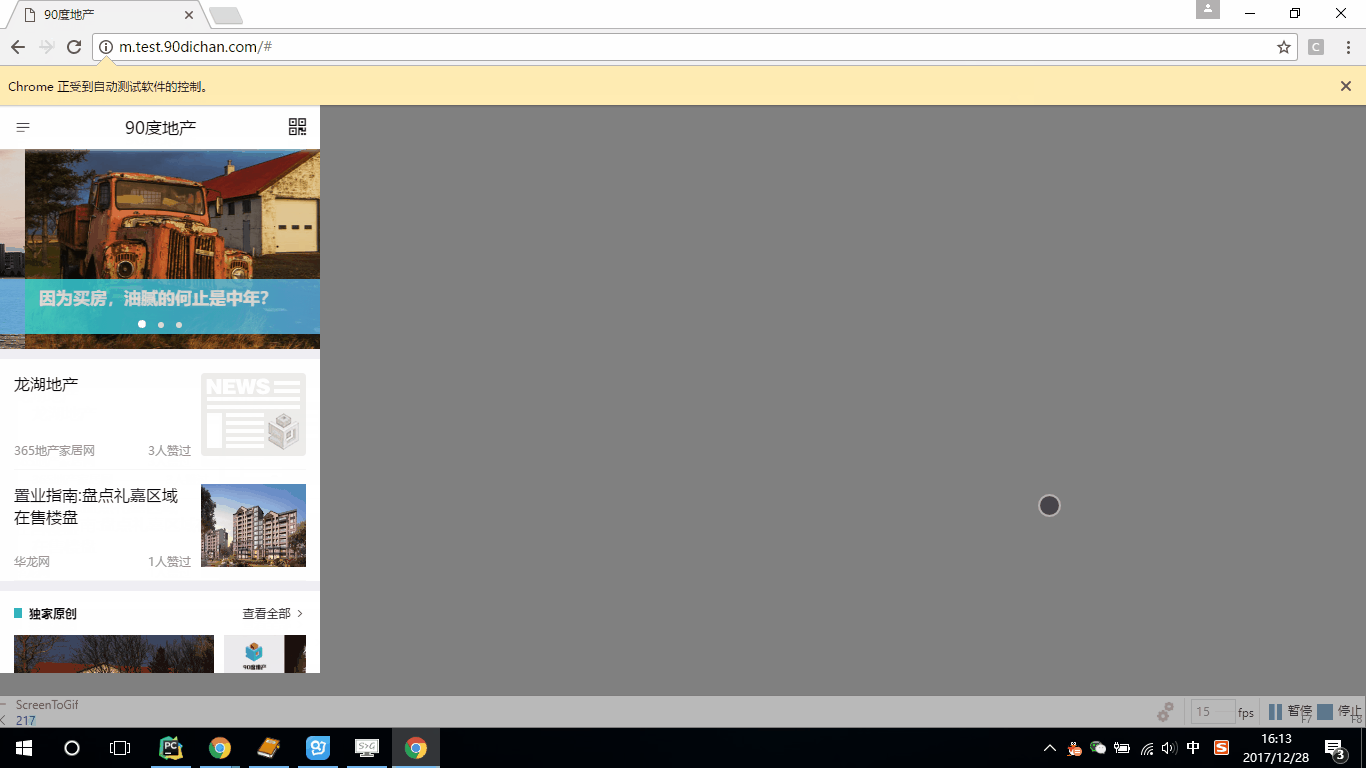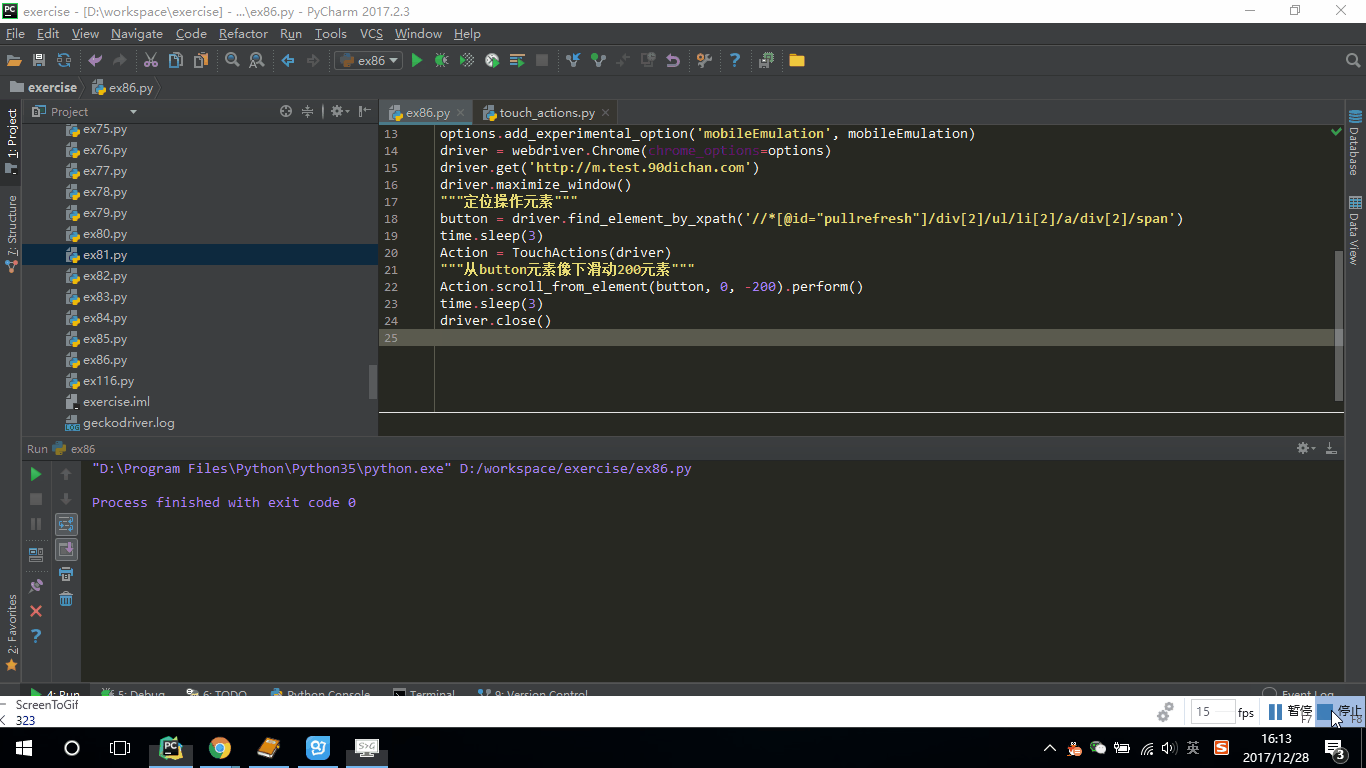
下面我们看下下拉的效果
下面看一下TouchAction提供的其他那些方法:
- double_tap(on_element) #双击
- flick_element(on_element, xoffset, yoffset, speed) #从元素开始以指定的速度移动
- long_press(on_element) #长按不释放
- move(xcoord, ycoord) #移动到指定的位置
- perform() #执行链中的所有动作
- release(xcoord, ycoord) #在某个位置松开操作
- scroll(xoffset, yoffset) #滚动到某个位置
- scroll_from_element(on_element, xoffset, yoffset) #从某元素开始滚动到某个位置
- tap(on_element) #单击
- tap_and_hold(xcoord, ycoord) #某点按住
其实上述的部分方法与ActionChains 中的鼠标操作很相似,由于与鼠标操作的书写方法一致的,所以在这里不详细介绍,具体书写方法大家可以参考下【python selenium-webdriver 元素操作之鼠标操作(四)】内容,下面我们主要来介绍下移动的操作。