#springmvc的概念
一个mvc框架,用来简化基于mvc架构的web应用开发。
#基本原理-五大组件
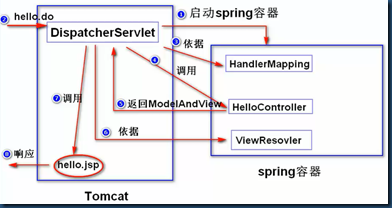
1.DispatcherServlet:作为前端控制器,整个流程控制的中心,控制其它组件执行,统一调度,降低组件之间的耦合性,提高每个组件的扩展性。接受请求,依据HandlerMapping的配置调用相应的模型来处理。
2.HandlerMapping:包含了请求路径与模型的对应关系。通过扩展处理器映射器实现不同的映射方式,例如:配置文件方式,实现接口方式,注解方式等。
3.Controller:负责处理业务逻辑。
4.ModelAndView:封装了处理结果。注:处理结果除了数据之外,还可能有视图名。
5.ViewResolver:DispatcherServlet依据ViewResolver的解析,调用真正的视图对象来生成相应的页面。
-- HandlAdapter:通过扩展处理器适配器,支持更多类型的处理器。
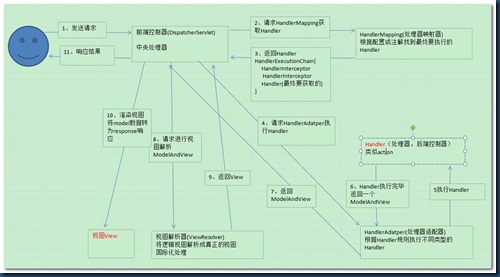
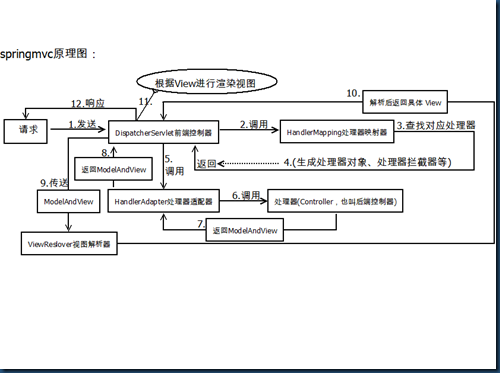
1、 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
2、 DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
3、 处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
4、 DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
5、 HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
6、 Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
7、 HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
8、 DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
9、 ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
10、DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
11、 DispatcherServlet响应用户
#编程步骤
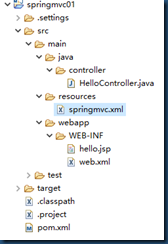
1.导包。
2.添加spring配置文件。
3.配置DispatcherServlet。
4.写Controller(处理器)。
5.写jsp。
6.在spring配置文件中,添加以下配置:
a.HandlerMapping
b.Controller
c.ViewResolver
#例子
##例一:
1.springmvc配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd"> </beans>2.配置DispatcherServlet。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" version="2.5"> <display-name>springmvc01</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- DispatcherServlet在初始化方法里面, 会读取初始化参数的值来获取spring配置文件的位置, 然后启动spring容器。 --> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.form</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>3.写Controller(处理器)。
package controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller; public class HelloController implements Controller { public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { System.out.println("handleRequest()"); /* ModelAndView有两个构造器: * (1)ModelAndView(String viewName),viewName是视图名 * (2)ModelAndView(String viewName,Map data),Map用于封装处理结果数据。 */ return new ModelAndView("hello"); } }4.写jsp。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>springmvc</title> </head> <body> <h1>springmvc</h1> </body> </html>6.在spring配置文件中,添加以下配置:
a.HandlerMapping b.Controller c.ViewResolver
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans …> <!-- 配置handleMapping --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <props> <prop key="/hello.form">helloController</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置处理器 --> <bean id="helloController" class="controller.HelloController"></bean> <!-- 配置视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> </beans>
##例二:使用注解来开发基于springmvc的web应用
###编程步骤
1.导包。
2.添加spring的配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd"> </beans>3.配置DispatcherServlet。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" version="2.5"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- DispatcherServlet在初始化方法里面, 会读取初始化参数的值来获取spring配置文件的位置, 然后启动spring容器。 --> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.form</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>4.写Controller。
package controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; /** * 如何写一个处理器: * 1.不用实现Controller接口 * 2.可以在处理器中添加多个方法,每个方法处理一种类型的请求。 * 3.方法名不做要求,返回类型可以是ModelAndView,也可以是String。 * 4.使用@Controller,将处理器纳入容器进行管理。(即,spring配置文件不用配置该处理器了)。 * 5.使用@RequestMapping,告诉前端控制器,请求路径与处理器的方法的对应关系。(spring配置文件不用配置HandlerMapping了) */ @Controller public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello.form") public String hello() { System.out.println("hello()"); return "hello"; } }5.写jsp。
<h1>Hello springMVC02!</h1>6.在spring配置文件中,添加如下配置:a.组件扫描。 b.mvc注解扫描。 c.视图解析器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans …> <!-- 配置组件扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="controller"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置mvc注解扫描 --> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> <!-- 配置视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> </beans>
## 读取请求参数值(3种方法)
1.通过request 对象
2.使用@RequestParam注解
3.使用javabean封装请求参数值
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="login3.form" method="post"> 账号:<input name="adminCode" /><br> 密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"/><br> <input type="submit" value="登陆" /> </form> </body> </html>package controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; /** * 如何写一个处理器: * 1.不用实现Controller接口 * 2.可以在处理器中添加多个方法,每个方法处理一种类型的请求。 * 3.方法名不做要求,返回类型可以是ModelAndView,也可以是String。 * 4.使用@Controller,将处理器纳入容器进行管理。(即,spring配置文件不用配置该处理器了)。 * 5.使用@RequestMapping,告诉前端控制器,请求路径与处理器的方法的对应关系。(spring配置文件不用配置HandlerMapping了) */ @Controller public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello.form") public String hello() { System.out.println("hello()"); return "hello"; } @RequestMapping("/toLogin.form") public String toLogin() { System.out.println("toLogin()"); return "login"; } @RequestMapping("/login.form") //方法1:通过请求对象获取请求参数值 public String login(HttpServletRequest request) { System.out.println("login()"); String adminCode = request.getParameter("adminCode"); String pwd = request.getParameter("pwd"); System.out.println(adminCode+":"+pwd); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/login2.form") //方法2:使用@RequestParam注解 public String login2(String adminCode,@RequestParam("pwd") String password) { System.out.println("login2()"); System.out.println(adminCode+":"+password); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/login3.form") //方法3:将请求参数封装成javabean。 public String login3(AdminParam ap) { System.out.println("login3()"); System.out.println(ap.getAdminCode()+":"+ap.getPwd()); return "index"; } }package controller; public class AdminParam { private String adminCode; private String pwd; public String getAdminCode() { return adminCode; } public void setAdminCode(String adminCode) { this.adminCode = adminCode; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } }
## 向页面传值(4种方法)
1.使用request(将数据绑定到request,然后转发到某个jsp)。
注:springmvc默认使用转发。
2.使用ModelAndView(将数据先封装到ModelAndView对象里面,然后将该对象作为方法的返回值。)
3.使用ModelMap(将该对象作为方法的参数,然后将数据绑定到该对象。)
4.使用session。
@RequestMapping("/login4.form") //方法1:使用request向页面传参 public String login4(AdminParam ap,HttpServletRequest request) { System.out.println("login4()"); System.out.println(ap.getAdminCode()+":"+ap.getPwd()); //将数据绑定到request request.setAttribute("adminCode", ap.getAdminCode()); //springmvc默认使用转发 不需要使用request.getRequestDispatcher("WEB-INF/index.jsp").forword(request,respsnse); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/login5.form") //方法2:使用ModelAndView 向页面传参 public ModelAndView login5(AdminParam ap) { System.out.println("login5()"); String adminCode = ap.getAdminCode(); System.out.println(adminCode); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("adminCode", adminCode); //构造ModelAndView对象 ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("index",map); return mav; } @RequestMapping("/login6.form") //方法3:使用ModelMap。 public String login6(AdminParam ap,ModelMap mm) { System.out.println("login6()"); String adminCode = ap.getAdminCode(); System.out.println(adminCode); mm.addAttribute("adminCode",adminCode); //相当于request.setAttribute... return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/login7.form") //方法4:使用session public String login7(AdminParam ap,HttpSession session) { System.out.println("login7()"); String adminCode = ap.getAdminCode(); System.out.println(adminCode); session.setAttribute("adminCode", adminCode); return "index"; }
## 重定向
1.如果方法的返回值是String
return "redirect:toIndex.form";
2.如果方法的返回值是ModelAndView
RedirectView rv = new RedirectView("toIndex.form");
return new ModelAndView(rv);
@RequestMapping("/login8.form") //重定向 public String login8(AdminParam ap,HttpSession session) { System.out.println("login8()"); String adminCode = ap.getAdminCode(); System.out.println(adminCode); session.setAttribute("adminCode", adminCode); return "redirect:toIndex.form"; } @RequestMapping("/login9.form") public ModelAndView login9() { System.out.println("login9()"); RedirectView rv = new RedirectView("toIndex.form"); return new ModelAndView(rv); } @RequestMapping("/toIndex.form") public String toIndex() { System.out.println("toIndex()"); return "index"; }