引言:
关于java IO流的操作是非常常见的,基本上每个项目都会用到,每次遇到都是去网上找一找就行了,屡试不爽。上次突然一个同事问了我java文件的读取,我一下子就懵了第一反应就是去网上找,虽然也能找到,但自己总感觉不是很踏实,所以今天就抽空看了看java IO流的一些操作,感觉还是很有收获的,顺便总结些资料,方便以后进一步的学习...
IO流的分类:
1、根据流的数据对象来分:
高端流:所有的内存中的流都是高端流,比如:InputStreamReader
低端流:所有的外界设备中的流都是低端流,比如InputStream,OutputStream
如何区分:所有的流对象的后缀中包含Reader或者Writer的都是高端流,反之,则基本上为低端流,不过也有例外,比如PrintStream就是高端流
2、根据数据的流向来分:
输出流:是用来写数据的,是由程序(内存)--->外界设备
输入流:是用来读数据的,是由外界设备--->程序(内存)
如何区分:一般来说输入流带有Input,输出流带有Output
3、根据流数据的格式来分:
字节流:处理声音或者图片等二进制的数据的流,比如InputStream
字符流:处理文本数据(如txt文件)的流,比如InputStreamReader
如何区分:可用高低端流来区分,所有的低端流都是字节流,所有的高端流都是字符流
4、根据流数据的包装过程来分:
原始流:在实例化流的对象的过程中,不需要传入另外一个流作为自己构造方法的参数的流,称之为原始流。
包装流:在实例化流的对象的过程中,需要传入另外一个流作为自己构造方法发参数的流,称之为包装流。
如何区分:所以的低端流都是原始流,所以的高端流都是包装流
IO流对象的继承关系(如下图):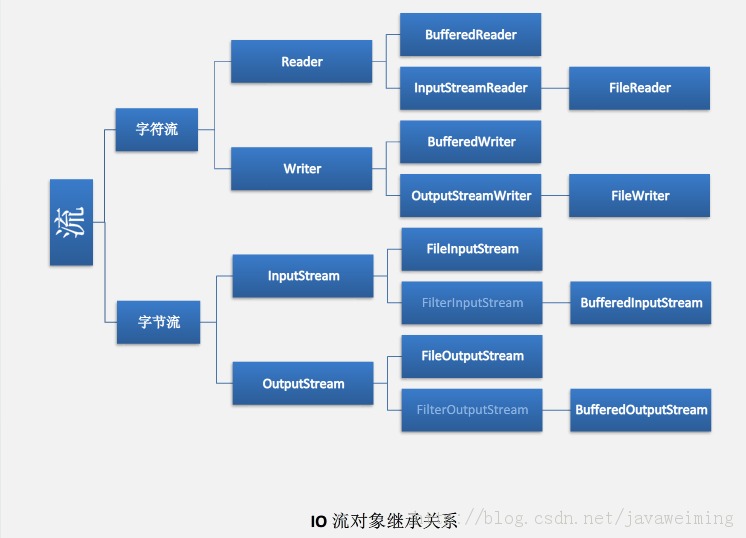
下面来看一些具体的代码例子:
按字节来读取文件
public class ReadFromFile {
/**
* 以字节为单位读取文件,常用于读二进制文件,如图片、声音、影像等文件。
*/
public static void readFileByBytes(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
InputStream in = null;
try {
System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读一个字节:");
// 一次读一个字节
in = new FileInputStream(file);
int tempbyte;
while ((tempbyte = in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print(tempbyte);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:");
// 一次读多个字节
byte[] tempbytes = new byte[100];
int byteread = 0;
in = new FileInputStream(fileName);
ReadFromFile.showAvailableBytes(in);
// 读入多个字节到字节数组中,byteread为一次读入的字节数
while ((byteread = in.read(tempbytes)) != -1) {
System.out.print(tempbytes, 0, byteread);
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
按字符来读取文件
/**
* 以字符为单位读取文件,常用于读文本,数字等类型的文件
*/
public static void readFileByChars(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
Reader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读一个字符:");
// 一次读一个字符
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
int tempchar;
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) {
// 对于windows下,
这两个字符在一起时,表示一个换行。
// 但如果这两个字符分开显示时,会换两次行。
// 因此,屏蔽掉
,或者屏蔽
。否则,将会多出很多空行。
if (((char) tempchar) != '
') {
System.out.print((char) tempchar);
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字符:");
// 一次读多个字符
char[] tempchars = new char[30];
int charread = 0;
//由于要以字符来读取,所以需要套上字符流
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName));
// 读入多个字符到字符数组中,charread为一次读取字符数
while ((charread = reader.read(tempchars)) != -1) {
// 同样屏蔽掉
不显示
if ((charread == tempchars.length)
&& (tempchars[tempchars.length - 1] != '
')) {
System.out.print(tempchars);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < charread; i++) {
if (tempchars[i] == '
') {
continue;
} else {
System.out.print(tempchars[i]);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
按行来读取文件
/**
* 以行为单位读取文件,常用于读面向行的格式化文件
*/
public static void readFileByLines(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以行为单位读取文件内容,一次读一整行:");
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
int line = 1;
// 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 显示行号
System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + tempString);
line++;
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
将一个文件的内容写入另一个文件(按行来写)
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("c:\test.txt");
BufferedReader read=null;
BufferedWriter writer=null;
try {
writer=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c:\zwm.txt"));
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
try {
read=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
while((tempString=read.readLine())!=null){
writer.append(tempString);
writer.newLine();//换行
writer.flush();//需要及时清掉流的缓冲区,万一文件过大就有可能无法写入了
}
read.close();
writer.close();
System.out.println("文件写入完成...");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JAVA IO流 读写文件
JAVA IO流中对象,字符串的读写
package object;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 名称:IO流中数据的读写
* 作者: 206工作室
* 时间:2009-12-27
* 版本:1.0
*/
public class ObjectOutTest {
/* 将对象写入文件方法 */
public void write(Object o, String path) {
try {
/* 创建存取文件 */
FileOutputStream fileStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
/* 将存取文件写入对象 */
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(fileStream);
/* 写入对象 */
os.writeObject(o);
System.out.println("写入数据成功");
/* 关闭ObjectOutputStream */
os.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/* 将对象从文件中读出来 */
public void read(String path) {
try {
/* 连接到要读取的文件 */
FileInputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream(path);
/* 怎样读取连接到的文件 */
ObjectInputStream os = new ObjectInputStream(fileStream);
/* 读取对象 */
Dog dog = (Dog) os.readObject();
System.out.println("输出结果:" + dog.getName() + " is a "
+ dog.getSex() + ",高:" + dog.getHeight() + ",长:"
+ dog.getLength());
/* 关闭对象 */
os.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/* 往文件写入字符串 */
public void wirteString(String path, String context) {
try {
/* 创建写入对象 */
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(path);
/* 创建缓冲区 */
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
/* 写入字符串 */
writer.write(context);
/* 关掉对象 */
writer.close();
System.out.println("写入字符串成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/* 读取文件中的字符串 */
public void readString(String path) {
try {
/* 创建读取对象 */
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(path);
/* 创建缓存区 */
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
/* 读取文件 */
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("读取成功:" + line);
}
/* 关闭对象 */
reader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/* 出函数入口 */
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Dog为外部类必须序列化才能实现它的对象的读取
Dog d = new Dog();
d.setHeight(12);
d.setLength(23);
d.setName("bobi");
d.setSex('b');
ObjectOutTest qqt = new ObjectOutTest();
qqt.wirteString("F:/IO/cc.sex", "chengchao 123456789");
qqt.readString("F:/IO/cc.sex");
}
}