KNN的函数写法
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter
def KNN_classify(k,X_train,y_train,x):
assert 1<=k<X_train.shape[0],"k must be valid"
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0],
"the size of X_train must equal to the size of y_train"
assert X_train.shape[1] == x.shape[0],
"the feature number of x must be equal to X_train"
distances=[sqrt(np.sum((x_train-x)**2)) for x_train in X_train]
nearest=np.argsort(distances)
topK_y=[y_train[i] for i in nearest[:k]]
votes=Counter(topK_y)
return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] #返回类型
使用scikit-learn中的KNN
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
import numpy as np
KNN_classifier=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=6) #传入k的值
#这里我随便搞的训练数据
x_train=np.arange(0,100).reshape(-1,2) #x是矩阵
y_train=np.random.randint(0,2,50) #y是数组
KNN_classifier.fit(x_train,y_train) #传入训练数据集
x=np.array([1,3]) #测试数据
x=x.reshape(1,-1) #测试数据只能传矩阵为参数
y=KNN_classifier.predict(x)[0] #因为我只测试了一组数据,所以取[0]即可
KNN的类写法
KNN.py
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter
from K近邻算法包.metrics import accuracy_score
class KNNClassifier:
def __init__(self, k):
"""初始化kNN分类器"""
assert k >= 1, "k must be valid"
self.k = k
self._X_train = None #私有变量
self._y_train = None
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0],
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0],
"the size of X_train must be at least k."
self._X_train = X_train
self._y_train = y_train
return self
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None,
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1],
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict]
return np.array(y_predict)
def _predict(self, x):
"""给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值"""
assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1],
"the feature number of x must be equal to X_train"
distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2))
for x_train in self._X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances)
topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y)
return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
def __repr__(self): #自我描述,在创建对象时打印
return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
测试算法正确率
model_selection.py:
import numpy as np
def train_test_split(X, y, test_ratio=0.2, seed=None):
"""将数据 X 和 y 按照test_ratio分割成X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test"""
assert X.shape[0] == y.shape[0],
"the size of X must be equal to the size of y"
assert 0.0 <= test_ratio <= 1.0,
"test_ration must be valid"
if seed: #固定随机种子,好调试
np.random.seed(seed)
shuffled_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X)) #len(矩阵)是行数
test_size = int(len(X) * test_ratio)
test_indexes = shuffled_indexes[:test_size]
train_indexes = shuffled_indexes[test_size:]
X_train = X[train_indexes]
y_train = y[train_indexes]
X_test = X[test_indexes]
y_test = y[test_indexes]
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
可以在jupyter notebook中调用一下试试:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
%run F:/python3玩转机器学习/K近邻算法/model_selection.py
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_ratio=0.2)
%run F:/python3玩转机器学习/K近邻算法/KNN.py
my_knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_predict=my_knn_clf.predict(X_test)
sum(y_predict==y_test)/len(y_test)
scikit-learn中的model_selection:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=666)
分类准确度
自己编写一个包
编写metrics.py:
import numpy as np
def accuracy_score(y_true, y_predict):
'''计算y_true和y_predict之间的准确率'''
assert y_true.shape[0] == y_predict.shape[0],
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return sum(y_true == y_predict) / len(y_true)
在KNN.py中调用:
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter
from K近邻算法包.metrics import accuracy_score
class KNNClassifier:
def __init__(self, k):
"""初始化kNN分类器"""
assert k >= 1, "k must be valid"
self.k = k
self._X_train = None #私有变量
self._y_train = None
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0],
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0],
"the size of X_train must be at least k."
self._X_train = X_train
self._y_train = y_train
return self
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None,
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1],
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict]
return np.array(y_predict)
def _predict(self, x):
"""给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值"""
assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1],
"the feature number of x must be equal to X_train"
distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2))
for x_train in self._X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances)
topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y)
return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self): #自我描述,在创建对象时打印
return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
用sklearn测试准确度
data=datasets.load_digits()
X=data.data
y=data.target
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2)
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
KNN_clf=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
KNN_clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_predict=KNN_clf.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_score(y_test,y_predict) ,也可以这样:KNN_clf.score(X_test,y_test)
超参数
超参数:在算法运行前需要决定的参数
模型参数:算法过程中运行的参数
KNN没有模型参数,KNN中的k是典型的超参数
根据上面的手写数字的数据集,暴力查找最好的k:
best_score=0.0
best_k=-1
for k in range(1,11):
knn_clf=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
score=knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test)
if score>best_score:
best_k=k
best_score=score
print("best_k=",best_k)
print("best_score=",best_score)
有时候,距离的权重可能有影响,比如: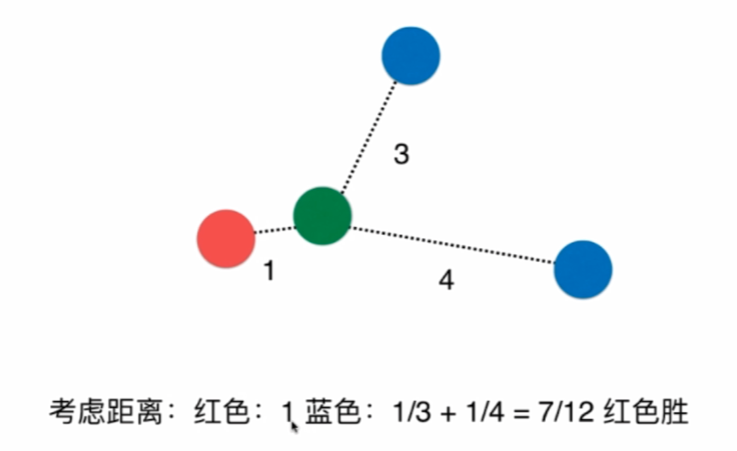
最近的是红色,那么我们按权重来比就是对距离取倒数求和。
明科夫斯基距离: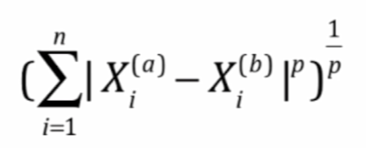
获得了一个超参数p
查找最好的p和k(网格搜索):
%%time
best_p=-1
best_score=0.0
best_k=-1
for k in range(1,11):
for p in range(1,6):
knn_clf=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k,weights="distance")
knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
score=knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test)
if score > best_score :
best_k=k
best_p=p
best_score=score
print("best_p=",best_p)
print("best_k=",best_k)
print("best_score=",best_score)
使用scikit-learn中的网格搜索:
定义网格参数:
param_grid =[
{
'weights':['uniform'],
'n_neighbors':[i for i in range(1,11)],
},
{
'weights':['distance'],
'n_neighbors':[i for i in range(1,11)],
'p':[i for i in range(1,6)]
}
]
初始化一个分类器对象:
knn_clf=KNeighborsClassifier()
导入网格搜索:
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
实例化:
grid_search = GridSearchCV(knn_clf,param_grid)
拟合:
%%time
grid_search.fit(X_train,y_train)
最优分类器:
grid_search.best_estimator_
grid_search.best_score_
grid_search.best_params_
将knn_clf赋为最优参数的分类器:
knn_clf=grid_search.best_estimator_
knn_clf.score(X_test,y_test)
加速、显示具体信息:
grid_search=GridSearchCV(knn_clf,param_grid,n_jobs=-1,verbose=2)#-1是将所有核并行 verbose是输出信息的详细情况
%%time
grid_search.fit(X_train,y_train)
数据归一化
将所有数据映射到同一尺度
最值归一化(normalization)
把所有数据映射到0~1之间
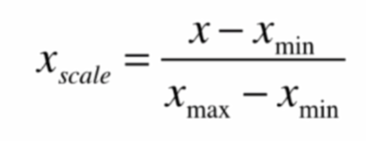
适用于分布有明显边界的情况,受outlier影响
对向量:
x1=np.random.randint(0,100,size=100)
(x1-np.min(x1))/(np.max(x1)-np.min(x1))
对矩阵:
X=np.random.randint(0,100,(50,2))
X=np.array(X,dtype=float)
对每一列特征值归一化:
X[:,0]=(X[:,0]-np.min(X[:,0]))/(np.max(X[:,0])-np.min(X[:,0]))
X[:,1]=(X[:,1]-np.min(X[:,1]))/(np.max(X[:,1])-np.min(X[:,1]))
绘制散点图:
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1])
plt.show()
均值方差归一化(standardization)
把所有数据归一到均值为0,方差为1的分布
适用于数据没有明显的边界,不受极端值影响
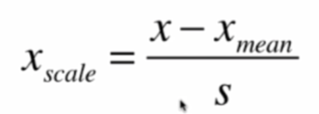
S是标准差。
实例:
x2=np.random.randint(0,100,(50,2))
x2=np.array(x2,dtype=float)
x2[:,0]=(x2[:,0]-np.mean(x2[:,0]))/np.std(x2[:,0])
x2[:,1]=(x2[:,1]-np.mean(x2[:,1]))/np.std(x2[:,1])
plt.scatter(x2[:,0],x2[:,1])
plt.show()
对测试数据集如何归一化?
不能简单的只对测试数据集归一化,应该用(x_test-x_mean_train)/std_train
使用scikit-learn归一化
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,test_size=0.2,random_state=666)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardScaler=StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X_train)
standardScaler.mean_ #均值
standardScaler.scale_ #标准差,std已经不能再用
X_train=standardScaler.transform(X_train) #返回归一化的矩阵
X_test_standard=standardScaler.transform(X_test) #测试数据集要用训练数据集来归一化
测试归一化后的准确率:
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
knn_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) #用归一化的训练数据X训练
knn_clf.score(X_test_standard,y_test) #用归一化的测试数据X测试
返回1.0,因为鸢尾花的数据比较少,准确高也是自然地。
sklearn.preprocessing中还有MinMaxScaler(最值归一化),用法类似。
自己写StandardScaler类
preprocessing.py:
import numpy as np
class StandardScaler:
def __init__(self):
self.mean_ = None
self.scale_ = None
def fit(self, X):
"""根据训练数据集X获得数据的均值和方差"""
assert X.ndim == 2, "The dimension of X must be 2"
self.mean_ = np.array([np.mean(X[:,i]) for i in range(X.shape[1])])
self.scale_ = np.array([np.std(X[:,i]) for i in range(X.shape[1])])
return self
def transform(self, X):
"""将X根据这个StandardScaler进行均值方差归一化处理"""
assert X.ndim == 2, "The dimension of X must be 2"
assert self.mean_ is not None and self.scale_ is not None,
"must fit before transform!"
assert X.shape[1] == len(self.mean_),
"the feature number of X must be equal to mean_ and std_"
resX = np.empty(shape=X.shape, dtype=float)
for col in range(X.shape[1]):
resX[:,col] = (X[:,col] - self.mean_[col]) / self.scale_[col]
return resX
关于K近邻算法
最大的缺点:效率低下
如果训练集有m个样本,n个特征,那么每预测一个数据,要O(m*n)
可以使用KD-Tree、Ball-Tree优化,但依然低效
缺点2:高度数据相关
缺点3:预测结果不具有可解释性
维数灾难:随着维度的增加,“看似相近的两个点之间的距离会越来越大”
解决方法:降维,如PCA
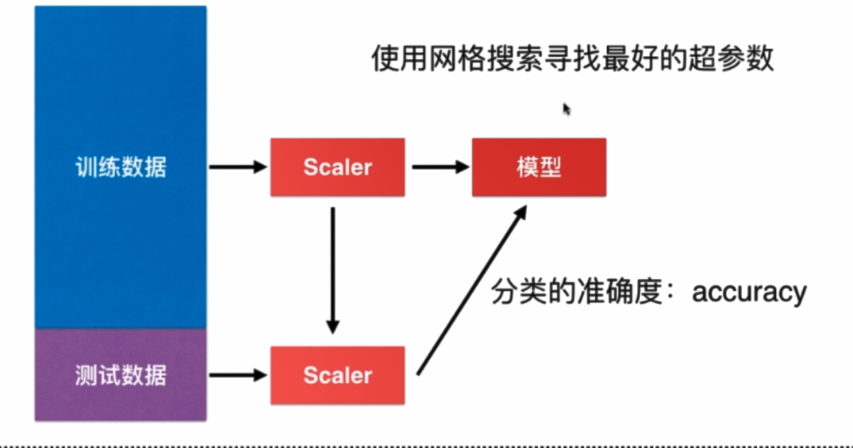
机器学习流程: