编写计算机程序时,总会碰到一些异常事件。
如果在每个可能发生这些事件的地方都使用条件语句,不仅效率低下、缺乏灵活性,还可能导致程序的可读性比较差。
好在Python提供了功能强大的异常处理机制。
一、异常是什么
Python使用异常对象来表示异常状态,并在遇到错误时引发异常。异常对象未被处理或捕获时,程序将终止并显示一条错误信息。
>>> 1/0 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
二、捕获异常
异常比较有趣的地方是可对其进行处理,通常称之为捕获异常。
1、使用try/except语句捕获异常
try: 1/0 except ZeroDivisionError: print('ZeroDivisionError happened.') 结果: ZeroDivisionError happened.
try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except ZeroDivisionError: print("The second number can't be zero!")
示例:
Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: 0
The second number can't be zero
如果在这里并没有捕获异常,异常将向程序的最顶层传播。
2、多个except子句
针对不同的异常类型,可以使用多个except子句进行捕获。
try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except ZeroDivisionError: print("The second number can't be zero!") except ValueError: print("That wasn't a number, was it?") 结果: Enter the first number: 1 Enter the second number: 0 The second number can't be zero! Enter the first number: 1 Enter the second number: a That wasn't a number, was it?
也可在一个元组中指定这些异常:
try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except (ZeroDivisionError, ValueError): print("Yous numbers wrong!")
3、捕获对象
可以在except字句中访问异常对象本身,同时向用户显示具体错误信息。
try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except (ZeroDivisionError, ValueError) as e: print(e)
4、捕获所有异常
如果要使用一段代码捕获所有的异常,只需在except字句中不指定任何异常类即可。
try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except: print('Something wrong happened......')
像这样捕获所有的异常很危险,因为很有可能会隐藏你没有考虑过的错误。
更好的选择是使用except Exception as e并对异常对象进行检查。这样做将忽略不是从Exception派生而来的为数不多的异常,如SystemExit和KeyboardInterrupt,因为他们是从BaseException(Exception的父类)派生而来的。
5、else子句
try/except语句可以添加一个else子句,用来在没有出现异常时执行一个代码块。
try: print('A simple task') except: print('What? Something went wrong?') else: print('Ah ... It went as planned.')
结果:
A simple task
Ah ... It went as planned
使用else子句,可实现特定条件下的循环操作:
while True: try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except Exception as e: print('Invalid input: ', e)
print('Please try again......') else: break 结果: Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: 0
Invalid input: division by zero
Please try again......
Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: a
Invalid input: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'a'
Please try again......
Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: 2
0.5
6、finally子句
finally子句可用于执行清理工作,无论是否发生异常。
while True: try: x = int(input('Enter the first number: ')) y = int(input('Enter the second number: ')) print(x / y) except Exception as e: print('Invalid input: ', e) print('Please try again......') else: break finally: print('Cleaning up ...')
结果:
Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: 0
Invalid input: division by zero
Please try again......
Cleaning up ...
Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: a
Invalid input: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'a'
Please try again......
Cleaning up ...
Enter the first number: 1
Enter the second number: 2
0.5
Cleaning up ..
7、raise
捕获异常后,如果要继续向上传播,可调用内置函数raise且不提供任何参数。
try: 1/0 except ZeroDivisionError: raise ValueError 结果: ZeroDivisionError: division by zero During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred: Traceback (most recent call last): File "/Volumes/DATA/python/python_test/test.py", line 371, in <module> raise ValueError ValueError
可使用raise A from B 语句来提供自己的异常上下文,也可使用None来禁用上下文。
try: 1/0 except ZeroDivisionError as e: raise ValueError from e 结果: ZeroDivisionError: division by zero The above exception was the direct cause of the following exception: Traceback (most recent call last): File "/Volumes/DATA/python/python_test/test.py", line 424, in <module> raise ValueError from e ValueError
try: 1/0 except ZeroDivisionError: raise ValueError from None 结果: raise ValueError from None ValueError
三、警告信息
如果你只是想发出警告而不是异常信息,可使用模块warnings中的函数warn。
>>> from warnings import warn >>> warn('Something will be wrong.') __main__:1: UserWarning: Something will be wrong.
警告只会显示一次。
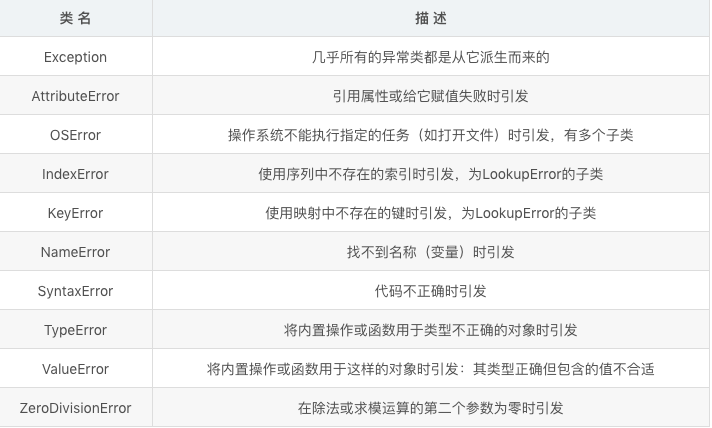
四、附:一些内置的异常类